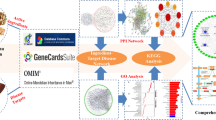
Abstract
Objective
Using network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of the ‘invigorating qi and promoting blood circulation’ drug pair Ginseng-Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) on treatment of ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Methods
The chemical constituents of ginseng and Danshen drug pair were identified by searching the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP), and the potential targets of the pair were identified. The pharmacodynamics of the pair was analyzed using network pharmacology. The targets of IHD were identified by database screening. Using protein-protein interaction network, the interaction targets of Ginseng-Danshen on IHD were constructed. A “constituent-target-disease” interaction network was constructed using Cytoscape software, Gene Ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis and biological pathway enrichment analysis were carried out, and the mechanism of improving myocardial ischemia by the Ginseng-Danshen drug pair was investigated.
Results
Seventeen active constituents and 53 targets were identified from ginseng, 53 active constituents and 61 targets were identified from Danshen, and 32 protein targets were shared by ginseng and Danshen. Twenty GO terms were analyzed, including cytokine receptor binding, cytokine activity, heme binding, and antioxidant activity. Sixty Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signaling pathways were analyzed, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-serine-threonine kinase (PI3K-AKT) signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, interleukin 17 signaling pathway, tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway, and the advanced glycation end product (AGE)-the receptor for AGE (RAGE) signaling pathway in diabetic complications.
Conclusion
The specific mechanism of Ginseng-Danshen drug pair in treating IHD may be associated with improving the changes of metabolites inbody, inhibiting the production of peroxides, removing the endogenous oxygen free radicals, regulating the expression of inflammatory factors, reducing myocardial cell apoptosis and promoting vascular regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen R V, Hjortbak MV, Hans EB. Ischemic heart disease: an update. Semin Nucl Med 2020;50:195–207.
Wu ZG. Therapeutic angiogenesis: the combination point of Chinese and Western medicine in prevention and treatment of ischemic heart disease. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:323–324.
Wang DT, Wang L, Yin HJ. Analysis of medication rules of corrective treatment for coronary heart disease of qi-deficiency and blood-stasis syndrome. J Med Res (Chin) 2016;45:66–69.
Li W, Lu PF, Gao D, Song J, Chen KJ. Effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Capsule on angiogenesis in hindlimb ischemic rats. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:39–45.
Li FH, Guo SW, Wang CG, Huang XL, Wang H, Tan XB, et al. Yiqihuoxue decoction protects against post-myocardial infarction injury via activation of cardiomyocytes PGC-1α expression. BMC Complement Altern Med 2018; 18:253.
Tan YF, Yu J, Pan WJ, Qi JY, Zhang MZ. Protective mechanisms of Suxiao Jiuxin Pills on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:583–590.
Zhang YM, Zhang ZY, Wang RX. Protective mechanisms of quercetin against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Front Physiol 2020;11:956.
Jin YY, Gao H, Zhang XY, Ai H, Zhu XL, Wang J. Shenfu Injection inhibits inflammation in patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiac shock. Chin J Integr Med 2017; 23:170–175.
Shi B, Huang Y, Ni J, Chen J, Wei J, Gao H, et al. Qi Dan Li Xin Pill improves chronic heart failure by regulating mTOR/p70S6k-mediated autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis. Sci Rep 2020;10:6105.
Ji ZC, Hu HY, Yang FW, Zhang LS, Jin XY, Wang HC, et al. Network meta-analysis of Yiqi Huoxue Chinese patent medicine for coronary heart disease with angina pectoris. Chin J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2019;9:1927–1937.
Zheng K, Wu J, Zhang FF. Study on medication rules of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of coronary heart disease based on data mining. Chin Med Herald 2018;36:113–116.
Ru JL, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W, Li BH, Huang C, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 2014;6:13.
Yang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Chen J. Association of interleukin-6 methylation in leukocyte DNA with serum level and the risk of ischemic heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2016;76:291–295.
Makki N, Thiel KW, Miller FJ Jr. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci 2013;14:20597–20613.
Ganguly R, Hasanally D, Stamenkovic A, Maddaford TG, Chaudhary R, Pierce GN, et al. Alpha linolenic acid decreases apoptosis and oxidized phospholipids in cardiomyocytes during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Cell Biochem 2018;437:163–175.
Wang YG, Yu YW, Zheng G. Research and strategies on angiogenesis of combined application of ginseng and red sage root in prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease. J Shaanxi Coll Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2012;35:67–70.
Guo CA, Guo S. Insulin receptor substrate signaling controls cardiac energy metabolism and heart failure. J Endocrinol 2017;233:131–143.
Ribeiro PVM, Tavares JF, Costa MAC, Mattar JB, Alfenas RCG. Effect of reducing dietary advanced glycation end products on obesity-associated complications: a systematic review. Nutr Rev 2019;77:725–734.
Bao JM, He MY, Liu YW, Lu YJ, Jiang Y. AGE/RAGE/Akt pathway contributes to prostate cancer cell proliferation by promoting Rb phosphorylation and degradation. Am J Cancer Res 2015;5:1741.
Wu Z, Ding L, Bao J, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Wang J, et al. Co-infection of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Escherichia coli triggers inflammatory injury involving the IL-17 signaling pathway. Front Microbiol 2019;15:2615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the review of the manuscript. Xin GJ, Fu JH, Li L, and Liu JX conceived and designed the study; Xin GJ, Zhao YW, Li LM and Jia FF performed the study; Guo H and Meng HX analyzed the date; Xin GJ and Han X wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81774145), Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81503292); and National Key Basic Research and Development Program (No. 2015cb554406)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Gj., Zhao, Yw., Li, Lm. et al. Mechanism of ‘Invigorating Qi and Promoting Blood Circulation’ Drug Pair Ginseng-Danshen on Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Based on Network Pharmacology. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 440–445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-2859-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-2859-y