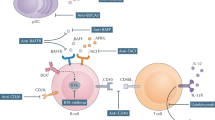
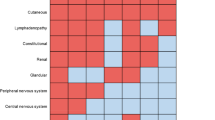
Abstract
Primary Sjögren’s syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disease that can lead to systemic manifestations. At present, immunomodulatory agents have not shown good efficacy, many patients in China seek Chinese medicine treatment. Chinese medicine can comprehensively improve the symptoms of patients through Chinese pattern diagnosis and individualized treatment. Fundamental researches are providing scientific bases for the therapeutic effect of Chinese medicine. Professional Chinese medicine treatment can be integrated into the conventional management of primary Sjögren’s syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fox RI. Sjögren syndrome. Lancet 2005;366:321–331.
Retamozo S, Brito-Zeron P, Zeher M, Kathy LS, Seror R, Mandl T, et al. Epidemiologic subsets drive a differentiated clinical and immunological presentation of primary Sjögren syndrome: analysis of 9302 patients from the big data international Sjögren Cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69: Suppl 10;876.
Zintzaras E, Voulgarelis M, Moutsopoulos HM. The risk of lymphoma development in autoimmune diseases: a metaanalysis. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:2337–2344.
Nocturne G, Mariette X. Sjögren syndrome-associated lymphomas: an update on pathogenesis and management. Br J Haematol 2015;168:317–327.
Ramos-Casals M, Tzioufas AG, Stone JH, Siso A, Bosch X. Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome: a systematic review. JAMA 2010;304:452–460.
Gottenberg JE, Cinquetti G, Larroche C, Combe B, Hachulla E, Meyer O, et al. Efficacy of rituximab in systemic manifestations of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: results in 78 patients of the AutoImmune and Rituximab registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:1026–1031.
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Mariette X, Jousse-Joulin S, Berthelot JM, Perdriger A, Puechal X, et al. Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome with rituximab: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2014;160:233–242.
Bowman SJ, Everett CC, O’Dwyer JL, Emery P, Pitzalis C, Ng WF, et al. Randomized controlled trial of rituximab and cost-effectiveness analysis in treating fatigue and oral dryness in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:1440–1450.
Yu MC, Lin SK, Lai JN, Wei JC, Cheng YC. The traditional Chinese medicine prescription patterns of Sjögren’s patients in Taiwan: a population-based study. J Ethnopharmacol 2014;155:435–442.
Zhang SY. The TCM etiology, pathogenesy and differential treatment for Sjogren’s syndrome. J Tradit Chin Med 2011;31:73–78.
Luo H, Li X, Liu J, Andrew F, George L. Chinese herbal medicine in treating primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review of randomized trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012;2012:640658.
Li B, Hou J, Yang Y, Piao X, Chen Y, Xue L, et al. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine Compound Jie Du Tong Luo Sheng Jin Granules treatment in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017;2017:1315432.
Wu GL, Li TY, Fan Y, Yu GY. Therapeutic effect of Chinese herbal medicine for strengthening qi, nourishing yin, and removing stasis on serum osteopontin and quality of life of patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:710–714.
Zhang JH, Zhang JY, Xie JJ. Clinical observations on combined use of acupuncture and medicine for primary Sjögren syndrome. Shanghai J Acupunt Moxibust (Chin) 2018;37:1399–1404.
Cheng B. Clinical observation on treatment of Sjögren syndrome by combination of Chinese herbal medicine and acupoint application. Guide Chin Med (Chin) 2018;16:35–37.
Wang D, Zhao H, Lu QJ, Xue L. Analysis of the expression of AQP5 in rats with Sjögren syndrome intervened by detoxicating medicine, meridians-relieving medicine and engender fluid medicine. Chin Med Herb (Chin) 2012;9:24–26.
Zhang QD, Wei M X, Lin Q. Intervention of Danqi Granule on expression of aquaporin-5 in submandibular glands of rat model with Sjögren’s syndrome. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul (Chin) 2010;16:105–109.
Jiang ZR, Liu YY, Wang CB. Effect of Jiedu Huayu Shengjin Decoction on AQP5 expression in submandibular gland of Sjögren syndrome model mice. Acta Chin Med (Chin) 2017;32:2144–2148.
Lin X, Liu JY, Chung W, Sze SC, Li H, Lao L, et al. Polysaccharides of Dendrobium officinale induce aquaporin 5 translocation by activating M3 muscarinic receptors. Planta Med 2015;81:130–137.
Wu GL, Pu XH, Yu GY, Li TY. Effects of total glucosides of peony on AQP-5 and its mRNA expression in submandibular glands of NOD mice with Sjogren’s syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2015;19:173–178.
Wu X, Ren C, Zhou H, Zhang L, Juan C, Yang Y. Therapeutic effect of Zeng Ye Decoction on primary Sjögren’s syndrome via upregulation of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 expression levels. Mol Med Rep 2014;10:429–434.
Qian X, Shi X, Wang H. Effect of paeoniflorin on the calcium ion concentration in salivary gland cells using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Am J Transl Res 2016;8:3678–3688.
Wei F, Wei MX, Murakami M. Mechanism involved in Danshen-induced fluid secretion in salivary glands. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:1444–1456.
Wang D, Zhao H. The influence of Yang Yin Sheng Jin herbs and Huo Xue Tong Luo herbs in the rats with Sjögren’s syndrome by IgA, IgG and IgM. Guide Chin Med (Chin) 2012;10:399–400.
Wang D, Xue L, Sun YL, Yang Y, Hu JD. Clinical study on the regulatory effect of “Jiedu Tongluo Shengjin Formula” on peripheral blood expression of PD-1 and its ligands in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome due to yin deficiency. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2014;48:48–51.
Wu G, Wu N, Li T, Lu W, Yu G. Total glucosides of peony ameliorates Sjögren’s syndrome by affecting Th1/Th2 cytokine balance. Exp Ther Med 2016;11:1135–1141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573925); Scientific Research Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No. 17401935500); Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment of Difficult Diseases from Shanghai Hospital Development Center (No. 16CR2047B) Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai (200437), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Jq., Xue, L. Challenges in Treatment of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome and Opportunities for Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 483–485 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3226-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3226-0