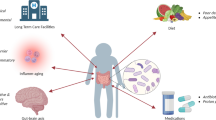
Abstract
Chinese medicine (CM) has a good clinical effect on osteoarthritis (OA), but the mechanism is not very clear. Evidence-based medicine researches have shown that intestinal flora plays a role in the pathogenesis and succession of OA. Intestinal flora affects the efficacy of CM, and CM can affect the balance of intestinal flora. This paper focuses on the relationship between intestinal flora, intestinal microenvironment, brain-gut axis, metabolic immunity and OA, and preliminarily expound the significance of intestinal flora in the pathogenesis of OA and the mechanism of CM intervention. The above discussion will be of great significance in the prevention and treatment of OA by CM from the perspective of intestinal flora.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaney Davidson EN, van Caam AP, Pm VDK. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: biology. Osteoarthr Cartil 2016;25:175–180.
Hosnijeh FS, Siebuhr AS, Uitterlinden AG, Oei EH, Hofman A, Karsdal MA, et al. Association between biomarkers of tissue inflammation and progression of osteoarthritis: evidence from the Rotterdam study cohort. Arthritis Res Ther 2016;18:81–90.
Zhang J, Chen SL, Li LB. Correlation between intestinal flora and serum inflammatory factors in patients with Crohn’s disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2017;21:4913–4917.
Vaughn AR, Notay M, Clark AK, Sivanmani RK. Skin-gut axis: the relationship between intestinal bacteria and skin health. World J Dermatol 2017;6:52–58.
Yu D, Dai J, Ouyang H, Sun L, Chen Y. Regulation of gut commensal flora attenuates osteoarthritis through interleukin 17. J Orthop Translat 2016;7:133.
Feng XB, Jiang J, Li M, Wang G, You JW, Zuo J. Role of intestinal flora imbalance in pathogenesis of pouchitis. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2016;9:786–790.
Hasenoehrl C, Taschler U, Storr M, Schicho R. The gastrointestinal tract—a central organ of cannabinoid signaling in health and disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2016;28:1765–1780.
Song M, Zhou L, Liu X, Ji L, Huang K, Hou H, et al. The relationship between digestive system diseases complicated with osteoporosis and intestinal flora. Chin J Osteoporosis (Chin) 2018;24:130–134.
Daniels J, Deshpande V, Serra S, Chetty R. Incidental single-organ vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract: an unusual form of single-organ vasculitis with coexistent pathology. Pathology 2017;49:661–665.
Abdel-Daim M, Zakhary NI, Aleya L, Bungǎu SG, Bohara RA, Siddiqi NJ. Aging, metabolic, and degenerative disorders: biomedical value of antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018;2018:1–2.
Cicuttini FM, Wluka AE. Not just loading and age: the dynamics of osteoarthritis, obesity and inflammation. Med J Aust 2016;204:47–47e1.
Jais A, Brüning JC. Hypothalamic inflammation in obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 2017;127:24–32.
Collins KH, Paul HA, Reimer RA, Seerattan RA, Hart DA, Herzog W. Relationship between the gut microbiota, l ipopolysacchar ide, inf lammat ion, and metabol ic osteoarthritis development: studies in a rat model. Osteoarthr Cartil 2015;23:1989–1998.
Hernandez CJ, Guss JD, Luna M, Goldring SR. Links between the microbiome and bone. J Bone Miner Res 2016;31:1638–1646.
Biniecka M, Canavan M, Mcgarry T, Gao WL, McCormick JL, Cregan S, et al. Dysregulated bioenergetics: a key regulator of joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:2192–2200.
Zhu W, Li J, Wu B. Gene expression profiling of the mouse gut: effect of intestinal flora on intestinal health. Mol Med Rep 2018;17:3667–3673.
Burokas A, Arboleya S, Moloney RD, Peterson VL, Murphy K, Clarke G, et al. Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biol Psychiatry 2017;82:472–487.
Fung TC, Olson CA, Hsiao EY. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat Neurosci 2017;20:145–155.
Caputi V, Giron MC. Microbiome-gut-brain axis and toll-like receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:1689–1708.
Foster JA, Rinaman L, Cryan JF. Stress and the gut-brain axis: regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol Stress 2017;7:124–136.
Kelly JR, Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Brain-gut-microbiota axis: challenges for translation in psychiatry. Ann Epidemiol 2016;26:366–372.
Santocchi E, Guiducci L, Fulceri F, Billeci L, Buzzigoli E, Apicella F, et al. Gut to brain interaction in autism spectrum disorders: a randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC Psychiatry 2016;16:183–199.
Wilson ID, Nicholson JK. Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl Res 2017;179:204–222.
Boulangé CL, Neves AL, Chilloux J, Nicholson JK, Dumas ME. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med 2016;8:42.
Hartstra AV, Bouter KEC, Bäckhed F, Zhang J, Licinio J, Wong ML, et al. Insights into the role of the microbiome in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:159–165.
Wang XM, Wang Y, Yu SG, Zhao BX, Hu HY, Wu HG. Moxibustion inhibits interleukin-12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha and modulates intestinal flora in rat with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:6819–6828.
Rooks MG, Garrett WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2016;16:341–352.
McLean MH, Dieguez D, Miller LM, Young HA. Does the microbiota play a role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases? Gut 2015;64:332–341.
Cross SN, Potter JA, Aldo P, Kwon JY, Pitruzzello M, Tong M, et al. Viral infection sensitizes human fetal membranes to bacterial lipopolysaccharide by MERTK inhibition and inflammasome activation. J Immunol 2017;199:2885–2897.
Miao RX, Zhu X, Wan CM, Wang ZL, Wen Y, Li YY. Effect of Clostridium butyricum supplementation on the development of intestinal flora and the immune system of neonatal mice. Exp Ther Med 2018;15:1081–1086.
Raj DA, Moser J, van der Pol SM, van Os RP, Holtman IR, Brouwer N, et al. Enhanced microglial pro-inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide correlates with brain infiltration and blood-brain barrier dysregulation in a mouse model of telomere shortening. Aging Cell 2015;14:1003–1013.
Ye HY, Jin J, Jin LW, Chen Y, Zhou ZH, Li ZY. Chlorogenic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway. Inflammation 2017;40:523–529.
Nasi S, So A, Combes C, Daudon M, Busso N. Interleukin-6 and chondrocyte mineralization act in tandem to promote experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1372–1380.
Radojčić MR, Thudium CS, Henriksen K, Tan K, Karlsten R, Dudley A. Biomarker of extracellular matrix remodelling C1M and proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 are related to synovitis and pain in end-stage knee osteoarthritis patients. Pain 2017;158:1254–1263.
Geurts J, Juri D, Müller M, Schären S, Netzer C. Novel ex vivo human osteochondral explant model of knee and spine osteoarthritis enables assessment of inflammatory and drug treatment responses. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:1314–1324.
Wu B, Cui H, Peng X, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Huang J. Analysis of the Toll-Like Receptor 2-2 (TLR2-2) and TLR4 mRNA expression in the intestinal mucosal immunity of broilers fed on diets supplemented with nickel chloride. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2014;11:657–670.
Vaziri N D, Zhao Y, Pahl MV. Altered intestinal microbial flora and impaired epithelial barrier structure and function in CKD: the nature, mechanisms, consequences and potential treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2016;31:737–746.
Maricar N, Callaghan MJ, Parkes MJ, Felson DT, O’Neill TW. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of clinical assessments in knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 2016;43:2171–2178.
Ulbrich F, Lerach T, Biermann J, Kaufmann KB, Lagreze WA, Buerkle H, et al. Argon mediates protection by interleukin-8 suppression via a TLR2/TLR4/STAT3/NF-κB pathway in a model of apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells in-vitro and following ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat retina in-vivo. J Neurochem 2016;138:859–873.
Tang R, Lin YM, Liu HX, Wang ES. Neuroprotective effect of docosahexaenoic acid in rat traumatic brain injury model via regulation of TLR4/NF-Kappa B signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2018;99:64–71.
Lim R, Barker G, Lappas M. The TLR2 ligand FSL-1 and the TLR5 ligand Flagellin mediate pro-inflammatory and pro-labour response via MyD88/TRAF6/NF-κB-dependent signaling. Am J Reprod Immunol 2014;71:401–417.
Jiao G. Research progress on prevention and treatment of glucolipid metabolic disease with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2017;23:5–11.
Stenblom EL, Weström B, Linninge C, Bonn P, Farrell M, Rehfeld JF, et al. Dietary green-plant thylakoids decrease gastric emptying and gut transit, promote changes in the gut microbial flora, but does not cause steatorrhea. Nutr Metab 2016;13:67–76.
Wu GL, Yu GY, Lu WW. Research status on regulation of Chinese herbal compound on intestinal microecology. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2015;40:3534–3537.
Liu L, Meng J. Perspective on intestinal microecology using basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2016;39:724–727.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to He XY, Ou CL, Xie L and Cao SJ for their helpful discussion and critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lu M and Zhou Q designed the article structure. Lu FG and Wang HX guided the writing of content. Wu YR and Kuang GY wrote the manuscript. All authors provided edits to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81574004, 81874476) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No. 2019JJ50462) and TAN Xin-hua Famous Medical Studio (No. 004-04)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Yr., Kuang, Gy., Lu, Fg. et al. Pathological Relationship between Intestinal Flora and Osteoarthritis and Intervention Mechanism of Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 716–720 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3224-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3224-2