Abstract
Objective
To observe the imbalance of anatomical and functional innervation factors of sympathetic nerves, nerve growth factor (NGF) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), in salt-sensitive hypertensive heart failure rats and to explore the effects of treatment with Guizhi Decoction (桂枝汤) on sympathetic remodeling by inhibiting cholinergic transdifferentiation.
Methods
SS-13BN and Dahl salt-sensitive (DS) rats were divided into 3 groups: SS-13BN group (control group, n=9), DS group (model group, n=9) and GS group (Guizhi Decoction, n=9). After 10 weeks of a high-salt diet, the GS group rats were given Guizhi Decoction and other two groups were given saline at an equal volume as a vehicle. After 4 weeks’ intragastric administration, rats were executed to detect the relevant indicators. Echocardiography and plasma n-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels were used to assess cardiac function. Noradrenaline (NA) levels in the plasma and myocardium were detected to evaluate the sympathetic function. NGF and LIF expression were detected in the myocardium by Western blot or quantitative real-time PCR. Double immunofluorescence or Western blot was used to detect tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), choline acetyltransferase (CHAT) and growth associated protein 43 (GAP43) in order to reflect anatomical and functional changes of sympathetic nerves.
Results
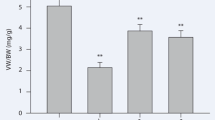
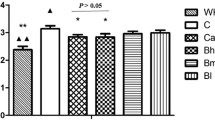
DS group had anatomical and functional deterioration of sympathetic nerves in the decompensation period of heart failure compared with SS-13BN group. Compared with the DS group, Guizhi Decoction significantly decreased the expression of LIF mRNA/protein (P<0.01), increased the expression of NGF (P<0.05 or P<0.01), enhanced the levels of TH+/GAP43+ and TH+/CHAT+ positive nerve fibers (P<0.01), and improved the protein expression of TH and GAP43 in left ventricle, but had no effect on CHAT (P>0.05). Guizhi Decoction inhibited inflammatory infiltration and collagen deposition of myocardial injury, increased the content of myocardial NA (P<0.05), reduced the plasma NA level (P<0.01), improved cardiac function (P<0.01), and improved weight and blood pressure to some extent (P<0.05), compared with DS group.
Conclusions
Guizhi Decoction could inhibit cholinergic transdifferentiation of sympathetic nerves, improve the anatomical and functional denervation of sympathetic nerves, and delay the progression of decompensated heart failure. The mechanism may be associated with the correction of the imbalance of NGF and LIF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parisi V, Rengo G, Perrone-Filardi P, Pagano G, Femminella GD, Paolillo S, et al. Increased epicardial adipose tissue volume correlates with cardiac sympathetic denervation in patients with heart failure. Circ Res 2016;118:1244–1253.
Yamaguchi N, Yamakawa K, Rajendran PS, Takamiya T, Vaseghi M. Antiarrhythmic effects of vagal nerve stimulation after cardiac sympathetic denervation in the setting of chronic myocardial infarction. Heart Rhythm 2018;15:1214–1222.
Naar J, Jaye D, Linde C, Neužil P, Doškář P, Málek F, et al. Effects of spinal cord stimulation on cardiac sympathetic nerve activity in patients with heart failure. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2017;40:504–513.
Berukstis A, Vajauskas D, Gargalskaite U, Misonis N, Burneikaite G, Zakarkaite D, et al. Impact of renal sympathetic denervation on cardiac sympathetic nerve activity evaluated by cardiac MIBG imaging. Eurointervention 2016;11:1070–1076.
Kimura K, Ieda M, Fukuda K. Development, maturation, and transdifferentiation of cardiac sympathetic nerves. Circ Res 2012;110:325–336.
Fukuda K, Kanazawa H, Aizawa Y, Ardell JL, Shivkumar K. Cardiac innervation and sudden cardiac death. Circ Res 2015;116:2005–2019.
Dhingra R, Pencina MJ, Wang TJ, Nam BH, Benjamin EJ, Levy D, et al. Electrocardiographic QRS duration and the risk of congestive heart failure: the framingham heart study. Hypertension 2006;47:861–867.
Lo SS, Mathias CJ, Sutton MS. QT interval and dispersion in primary autonomic failure. Heart 1996;75:498–501.
Oka H, Mochio S, Sato K, Isogai Y. Correlation of altered Q-T interval and sympathetic nervous system dysfunction in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Eur Neurol 1994;34:23–29.
Caporali A, Salanewby GB, Meloni M, Graiani G, Pani E, Cristofaro B, et al. Identification of the prosurvival activity of nerve growth factor on cardiac myocytes. Cell Death Differ 2008;15:299–311.
Meloni M, Caporali A, Graiani G, Lagrasta C, Katare R, Van LS, et al. Nerve growth factor promotes cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Circ Res 2010;106:1275–1284.
Zigmond RE, Hyatt SH, Mohney RP, Schreiber RC, Shadiack AM, Sun Y, et al. Changes in neuropeptide phenotype after axotomy of adult peripheral neurons and the role of leukemia inhibitory factor. Perspect Dev Neurobiol 1996;4:75–90.
Fukada K. Hormonal control of neurotransmitter choice in sympathetic neurone cultures. Nature 1980;287:553–555.
Li X, Jiang YH, Jiang P, Yang JL, Ma DF, Yang CH. Effect of Guizhi Decoction on heart rate variability and regulation of cardiac autonomic nervous imbalance in diabetes mellitus rats. Chin J Integr Med 2014;20:524–533.
Fromy B, Lingueglia E, Sigaudoroussel D, Saumet JL, Lazdunski M. Asic3 is a neuronal mechanosensor for pressure-induced vasodilation that protects against pressure ulcers. Nat Med 2012;18:1205–1207.
Sambhi MP, White FN. The electrocardiogram of the normal and hypertensive rat. Circ Res 1960;8:129–134.
Jiang YH, Jiang P, Yang JL, Ma DF, Lin HQ, Su WG, et al. Cardiac dysregulation and myocardial injury in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced rat model of sympathetic denervation. Plos One 2015;10:e0133971.
Ohtake M, Hattori T, Murase T, Takahashi K, Takatsu M, Ohtake M, et al. Glucocorticoids activate cardiac mineralocorticoid receptors in adrenalectomized Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Nagoya J Med Sci 2014;76:59–72.
Zhang SK, Cui NQ, Zhuo YZ, Hu JG, Liu JH, Li DH, et al. Modified Xiaochaihu decoction promotes collagen degradation and inhibits pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis rats. Chin J Integr Med 2017;28:1–4.
Mabe AM, Hoover DB. Structural and functional cardiac cholinergic deficits in adult neurturin knockout mice. Cardiovasc Res 2009;82:93–99.
Meiri KF, Pfenninger KH, Willard MB. Growth-associated protein, GAP-43, a polypeptide that is induced when neurons extend axons, is a component of growth cones and corresponds to pp46, a major polypeptide of a subcellular fraction enriched in growth cones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986;83:3537–3541.
Bartkowska K, Turlejski K, Djavadian RL. Neurotrophins and their receptors in early development of the mammalian nervous system. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2010;70:454–467.
Shelton DL, Reichardt LF. Expression of the betanerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984;81:7951–7955.
Zhou S, Chen LS, Miyauchi Y, Miyauchi M, Kar S, Kangavari S, et al. Mechanisms of cardiac nerve sprouting after myocardial infarction in dogs. Circ Res 2004;95:76–83.
Backs J, Haunstetter A, Gerber SH, Metz J, Borst MM, Strasser RH, et al. The neuronal norepinephrine transporter in experimental heart failure: evidence for a posttranscriptional downregulation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2001;33:461–472.
Himura Y, Felten SY, Kashiki M, Lewandowski TJ, Delehanty JM, Liang CS. Cardiac noradrenergic nerve terminal abnormalities in dogs with experimental congestive heart failure. Circulation 1993;88:1299–1309.
Kimura K, Ieda M, Kanazawa H, Yagi T, Tsunoda M, Ninomiya S, et al. Cardiac sympathetic rejuvenation: a link between nerve function and cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res 2007;100:1755–1764.
Kimura K, Kanazawa HM, Ieda M, Kawaguchi-Manabe H, Miyake Y, Yagi T, et al. Norepinephrine-induced nerve growth factor depletion causes cardiac sympathetic denervation in severe heart failure. Auton Neurosci 2010;156:27–35.
Kaye DM, Vaddadi G, Gruskin SL, Du XJ, Esler MD. Reduced myocardial nerve growth factor expression in human and experimental heart failure. Circ Res 2000;86:E80–84.
Qin F, Vulapalli RS, Stevens SY, Liang CS. Loss of cardiac sympathetic neurotransmitters in heart failure and NE infusion is associated with reduced NGF. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2002;282:H363–371.
Kreusser MM, Haass M, Buss SJ, Hardt SE, Gerber SH, Kinscherf R, et al. Injection of nerve growth factor into stellate ganglia improves norepinephrine reuptake into failing hearts. Hypertension 2006;47:209–215.
Lam NT, Currie PD, Lieschke GJ, Rosenthal NA, Kaye DM. Nerve growth factor stimulates cardiac regeneration via cardiomyocyte proliferation in experimental heart failure. Plos One 2012;7:e53210.
Zimmers TA, Fishel ML, Bonetto A. STAT3 in the systemic inflammation of cancer cachexia. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2016;54:28–41.
Auernhammer CJ, Melmed S. Leukemia-inhibitory factorneuroimmune modulator of endocrine function. Endocr Rev 2000;21:313–345.
Stewart CL, Kaspar P, Brunet LJ, Bhatt H, Gadi I, Köntgen F, et al. Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of leukaemia inhibitory factor. Nature 1992;359:76–79.
Hu W, Feng Z, Teresky AK, Levine AJ. p53 regulates maternal reproduction through LIF. Nature 2007;450:721–724.
Zouein FA, Kurdi M, Booz GW. LIF and the heart: just another brick in the wall? Eur Cytokine Netw 2013;24:11–19.
Kang X, Zhou HJ, Yang J, Zhong JH, Tang T, Cui HC, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction attenuates glial scar by downregulating expression of leukemia inhibitory factor in intracerebral hemorrhagic rats. Chin J Integr Med 2019;25:264–269.
Kanazawa H, Ieda M, Kimura K, Arai T, Kawaguchi-Manabe H, Matsuhashi T, et al. Heart failure causes cholinergic transdifferentiation of cardiac sympathetic nerves via gp130-signaling cytokines in rodents. J Clin Invest 2010;120:408–421.
Fernandez SF, Canty JM Jr. Adrenergic and cholinergic plasticity in heart failure. Circ Res 2015;116:1639–1642.
Zigmond RE, HyattSachs H, Baldwin C, Qu XM, Sun Y, McKeon TW, et al. Phenotypic plasticity in adult sympathetic neurons: changes in neuropeptide expression in organ culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:1507–1511.
Furshpan EJ, Landis SC, Matsumoto SG, Potter DD. Synaptic functions in rat sympathetic neurons in microcultures. I.Secretion of norepinephrine and acetylcholine. J Neurosci 1986;6:1061–1079.
Page RL, Wharton JM, Prystowsky EN. Effect of continuous vagal enhancement on concealed conduction and refractoriness within the atrioventricular node. Am J Cardiol 1996;77:260–265.
Schevchuck A, West MB. Late-onset advanced heart block due to vagal nerve stimulation. Am J Ther 2014;21:545–547.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wang YC performed experiments, data analysis and drafted the manuscript. Ma DF and Jiang P carried out data collection and analysis. Zhou GF, Li ZY, Zhang YM and Yang JL were responsible for animal care and telemetry. Li X designed the study, supervised the experiment and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81673970)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yc., Ma, Df., Jiang, P. et al. Guizhi Decoction (桂枝汤) Inhibits Cholinergic Transdifferentiation by Regulating Imbalance of NGF and LIF in Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Heart Failure Rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 188–196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-2706-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-2706-6