Abstract
Objective
To assess the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on expression of cytoskeletal proteins from Sertoli cells (SCs) and spermatogenesis in rats with oligozoospermia of insufficiency of Shen (Kidney) essence syndrome (OIKES).
Methods
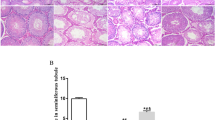
Twenty healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to four groups using a random number table: control, tripterygium glycosides (TG) treatment, sham and EA groups (n=5 in each group). A rat model of OIKES was established by oral gavage with TG. The EA group was treated with TG and received EA at Shenshu (BL 23) and Zusanli (ST 36) acupoints for 20 min, once daily for 30 days, while the sham group received EA at identical acupoints with skin penetration without stimulation. After 30 days, the final body weight and coefficients for the testis and epididymis were calculated and sperm parameters were measured. Immunohistochemical analyses were performed to detect expression of vimentin and α-tubulin in SCs and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunoreactivity in germ cells. Apoptosis in germ cells was quantified by the transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling assay.
Results
Compared with the control group, the final body weight and testis/epididymis coefficients of rats in the TG-treated group were not significantly different, but the sperm count and motility were lower (P<0.05). Expressions of vimentin and α-tubulin were also significantly weaker (P<0.01). The PCNA immunoreactivity of germ cells was decreased (P=0.059), whereas the apoptotic index of germ cells was increased significantly (P<0.01). In contrast, EA at BL 23 and ST 36 acupoints significantly improved the final body weight as well as the sperm count, concentration and motility (P<0.01 or P<0.05). EA increased expression of vimentin and α-tubulin in SCs markedly, and significantly enhanced PCNA immunoreactivity with decreased apoptosis in germ cells (P<0.01 or P<0.05).
Conclusions
EA at BL 23 and ST 36 acupoints has protective effects on spermatogenesis in rats with OIKES. This effect seems to be achieved by attenuating TG-induced disruption of cytoskeletal protein in SCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dimitriadis F, Tsiampali C, Chaliasos N, Tsounapi P, Takenaka A, Sofikitis N. The Sertoli cell as the orchestra conductor of spermatogenesis: spermatogenic cells dance to the tune of testosterone. Hormones (Athens) 2015;14:479–503.
Svingen T, Koopman P. Building the mammalian testis: origins, differentiation, and assembly of the component cell populations. Genes Dev 2013;27:2409–2426.
Hermo L, Pelletier RM, Cyr DG, Smith CE. Surfing the wave, cycle, life history, and genes/proteins expressed by testicular germ cells. Part 5: intercellular junctions and contacts between germs cells and Sertoli cells and their regulatory interactions, testicular cholesterol, and genes/proteins associated with more than one germ cell generation. Microsc Res Tech 2010;73:409–494.
Vogl AW, Vaid KS, Guttman JA. The Sertoli cell cytoskeleton. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008;636:186–211.
Johnson KJ. Testicular histopathology associated with disruption of the Sertoli cell cytoskeleton. Spermatogenesis 2014;4:e979106.
Mao PM, Li HS, Wang B, Mo XW. Progress in research on preparation of animal model of tripterygium glycoside induced infertility. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;35:254–256.
Xu YP, Liu BX, Zhang XP, Yang CW, Wang CH. A Chinese herbal formula, Wuzi Yanzong Pill, improves spermatogenesis by modulating the secretory function of Sertoli cells. Chin J Integr Med 2014;20:194–199.
Qu F, Li R, Sun W, Lin G, Zhang R, Yang J, et al. Use of electroacupuncture and transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation in reproductive medicine: a group consensus. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2017;18:186–193.
Siterman S, Eltes F, Schechter L, Maimon Y, Lederman H, Bartoov B. Success of acupuncture treatment in patients with initially low sperm output is associated with a decrease in scrotal skin temperature. Asian J Androl 2009;11:200–208.
Dieterle S, Li C, Greb R, Bartzsch F, Hatzmann W, Huang D. A prospective randomized placebo-controlled study of the effect of acupuncture in infertile patients with severe oligoasthenozoospermia. Fertil Steril 2009;92:1340–1343.
Zhang C, Zhang CY, Li BB, Zhang HF, Yuan T, Fu YM. Multiglycosides of Tripterygium wilfordii increase sperm apoptosis in male rats. Natl J Androl (Chin) 2010;16:786–789.
Li ZR, Fang JQ, Yi SX, eds. Experimental acupuncture science. 2th ed. Beijing: Chinese Medicine Press;2007:228–233.
Zhu WF, ed. Chinese medicine diagnostic science. 5th ed. Beijing: Chinese Medicine Press; 2005:195–196.
Dkhil MA, Zrieq R, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel Moneim AE. Selenium nanoparticles attenuate oxidative stress and testicular damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Molecules 2016;21:E1517.
Ma B, Qi H, Li J, Xu H, Chi B, Zhu J, et al. Triptolide disrupts fatty acids and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) levels in male mice testes followed by testicular injury: a GC-MS based metabolomics study. Toxicology 2015;336:84–95.
Gao J, Zuo Y, So KH, Yeung WS, Ng EH, Lee KF. Electroacupuncture enhances spermatogenesis in rats after scrotal heat treatment. Spermatogenesis 2012;2:53–62.
Zhou L, Xia Y, Ma X, Tang L, Lu J, Tang Q, et al. Effects of "menstrual cycle-based acupuncture therapy" on IVF-ET in patients with decline in ovarian reserve. Chin Acupunct Moxibust (Chin) 2016;36:25–28.
Song FJ, Zheng SL, Ma DZ. Clinical observation on acupuncture for treatment of infertility of ovulatory disturbance. Chin Acupunct Moxibust (Chin) 2008;28:21–23.
Fu B, Lun X, Gong Y. Effects of the combined therapy of acupuncture with herbal drugs on male immune infertility—a clinical report of 50 cases. J Tradit Chin Med 2005;25:186–189.
Huang DM, Huang GY, Lu FE, Stefan D, Andreas N, Robert G. Acupuncture for infertility: is it an effective therapy? Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:386–395.
Zhang M, Huang G, Lu F, Paulus WE, Sterzik K. Influence of acupuncture on idiopathic male infertility in assisted reproductive technology. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 2002;22:228–230.
Fischl F, Riegler R, Bieglmayer C, Nasr F, Neumark J. Modification of semen quality by acupuncture in subfertile males. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 1984;44:510–512.
Osmanagic-Myers S, Rus S, Wolfram M, Brunner D, Goldmann WH, Bonakdar N, et al. Plectin reinforces vascular integrity by mediating crosstalk between the vimentin and the actin networks. J Cell Sci 2015;128:4138–4150.
Lie PP, Mruk DD, Lee WM, Cheng CY. Cytoskeletal dynamics and spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2010;365:1581–1592.
Dráber P, Sulimenko V, Dráberová E. Cytoskeleton in mast cell signaling. Front Immunol 2012;3:130.
Wloga D, Gaertig J. Post-translational modifications of microtubules. J Cell Sci 2010;123:3447–3455.
Langevin HM, Bouffard NA, Badger GJ, Churchill DL, Howe AK. Subcutaneous tissue fibroblast cytoskeletal remodeling induced by acupuncture: evidence for a mechanotransduction-based mechanism. J Cell Physiol 2006;207:767–774.
Tian HM, Yan J, Yi SX, Zhang YJ, Wen Y. Observation on changes of the intragastric protein phosphorylation level involving electroacupuncture-induced improvement of the injured gastric mucosa in the rat. Acupunct Res (Chin) 2009;34:147–151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81273767 and 81473690)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Tw., Qin, M., Liu, Bx. et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Spermatogenesis in Rats with Oligozoospermia of Insufficiency of Shen (Kidney) Essence Syndrome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 292–297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2915-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2915-9