Abstract
Objective
To elucidate the action mechanism of Xingnaojing Injection (醒脑静注射液, XNJI) for sepsis, and to target screen the potential bioactive ingredients.
Methods
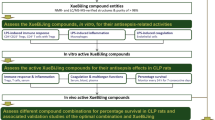
An integrated protocol that combines in silico target screen (molecular docking) and database mapping was employed to find the potential inhibitors from XNJI for the sepsis-related targets and to establish the compound–target (C-T) interaction network. The XNJI's bioactive components database was investigated and the sepsis-associated targets were comprehensively constructed; the 3D structure of adenosine receptor A2a and 5-lipoxygenase proteins were established and evaluated with homology modeling method; system network pharmacology for sepsis treatment was studied between the bioactive ingredients and the sepsis targets using computational biology methods to distinguish inhibitors from non inhibitors for the selected sepsis-related targets and C-T network construction.
Results
Multiple bioactive compounds in the XNJI were found to interact with multiple sepsis targets. The 32 bioactive ingredients were generated from XNJI in pharmacological system, and 21 potential targets were predicted to the sepsis disease; the biological activities for some potential inhibitors had been experimentally confirmed, highlighting the reliability of in silico target screen. Further integrated C-T network showed that these bioactive components together probably display synergistic action for sepsis treatment.
Conclusions
The uncovered mechanism may offer a superior insight for understanding the theory of the Chinese herbal medicine for combating sepsis. Moreover, the potential inhibitors for the sepsis-related targets may provide a good source to find new lead compounds against sepsis disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao YM, Sheng ZY, Huang LF. The effect of a novel cytokine, high mobility group box 1 protein, on the development of traumatic sepsis. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:13–15.
Liu QQ. Based on the four segments and treatment by syndrome differentiation to lower the mortality of sepsis. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:16–18.
Lin SJ, Cheng YY, Chang CH, Lee CH, Huang YC, Su YC. Traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis "yang-xu zheng": significant prognostic predictor for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013;759748.
Ma ST, Feng CT, Zhang XL, Dai GL, Li CY, Cheng XG, et al. The multi-target capabilities of the compounds in a CM used to treat sepsis and their in silico pharmacology. Complement Ther Med 2013;21:35–41.
Chen XW, Liao XF, Wan L, Huang J. The clinic observation on the role of Xingnaojing Injection solution in treating burn sepsis. J Chin Physician (Chin) 2005;7:68–69.
He W, Zheng J. Effects of Xingnaojing injection in adjuvant treatment 50 patients with viral encephalitis. Chin J New Drugs Clin Rem (Chin) 2005;24:654–656.
Shen SY, Cai DF, Chen WH, Liu J, Chen H, Ying J. Effect of Xingnaojing injection on hippocampal N-methyl-Daspartic acid receptors of focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Chin J Integr Med 2003;9:49–52.
Yao Z, Lu Y, Du S, Chen X, Wang Y. Study on pharmacokinetics of jasminoidin in rabbits administered Xingnaojing naristillae by nasal medication. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2010;35:1871–1873.
Du S, Zhang Q, Lu Y, Zhai Y, Wu Q. Study of components in Xingnaojing affecting intestine absorption of gardenia extract. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2010;35:297–300.
Wei N, Ma C, Duan T. Determination of muscone in Xingnaojing injection by gas chromatography with solid phase micro-extraction. Chin J Chromatogr (Chin) 2005;23:565.
Li S, Zhang B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med 2013;11:110–120.
Okada T, Fujiyoshi Y, Silow M, Navarro J, Landau EM, Shichida Y. Functional role of internal water molecules in rhodopsin revealed by X-ray crystallography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002;99:5982–5987.
Rasmussen SG, Choi HJ, Rosenbaum DM, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Edwards PC, et al. Crystal structure of the human beta2 adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 2007;450:383–7.
Weberpals M, Hermes M, Hermann S, Kummer MP, Terwel D, Semmler A, et al. NOS2 gene deficiency protects from sepsis-induced long-term cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 2009;45:14177–14184.
Dou H, Song Y, Liu X, Yang L, Jiang N, Chen D, et al. A novel benzenediamine derivate rescued mice from experimental sepsis by attenuating proinflammatory mediators via IRAK4. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2014;51:191–200.
Dubois B, Starckx S, Pagenstecher A, Oord J, Arnold B, Opdenakker G. Gelatinase B deficiency protects against endotoxin shock. Eur J Immunol 2002;32:2163–2171.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81403268 and No. 81403114), the Public Welfare Technology Application Research Linkage Project of Anhui Province (No. 1704f0704062), the Talent Fund of Anhui Science and Technology University (No. SPWD201602) and Education Department of Anhui Province (No. gxfx2017076)
Electronic supplementary material
11655_2017_2421_MOESM1_ESM.doc
In Silico System Pharmacology for the Potential Bioactive Ingredients Contained in Xingnaojing Injection (醒脑静注射液) and Its Material Basis for Sepsis Treatment
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, St., Feng, Ct., Xiong, Yx. et al. In Silico System Pharmacology for the Potential Bioactive Ingredients Contained in Xingnaojing Injection (醒脑静注射液) and Its Material Basis for Sepsis Treatment. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 24, 944–949 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2421-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2421-0