Abstract
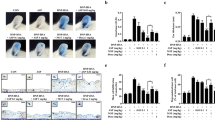
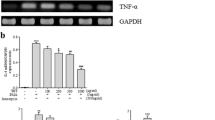
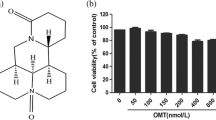
The histamine receptor antagonists in the treatment of allergic disease have limitations. The treatments of Chinese herbs have some curative effects on allergic skin lesions. Present research indicates that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway might be equally important in allergic reactions. It was found that the inhibition of MAPK signaling pathways might relieve allergy symptoms, and some herbs can inhibit the MAPK pathway, which yields anti-allergy effects. Chinese medicines (CMs) have immense potential in the development of treatments for allergic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zuberbier T, Aberer W, Asero R, Bindslev JC, Brzoza Z, Canonica GW, et al. The EAACI/GA(2) LEN/EDF/WAO Guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria: the 2013 revision and update. Allergy 2014;69:868–887.
Li T, Wang H, Chen H, Liu XG, Yang JN, Cajo B, et al. The preliminary study of pseudolaric acid B on specific immune response. Chin Pharm Bull (Chin) 2013;29:184–189.
Azzolina A, Guarneri P, Lampiasi N. Involvement of p38 and JNK MAPKs pathways in substance P-induced production of TNF-alpha by peritoneal mast cells. Cytokine 2002;18:72–80.
Chen ZJ, Li QS, Li YS, Yu ZF, Yuan JL, Li YK. Pharmacodynamics study on Radix saposhnikoviae (RL) and Feutus tribuli (FI). Chin Tradit Patent Med (Chin) 2003;25:737–739.
Hu HW, Xu XG, Zhang XS, Sun R. Research of extraction and separation technology and anti-allergic effect about fargesin. Chin J Pharm (Chin) 2014;11:261–263.
Xiang FZ, Mei W, Yu YX, Su Z. Effect of composite Salvia Miltirrhiza on hemorrheology of chronic urticaria. Clin Med J China (Chin) 2003;10:602–603.
Yang YJ, An SF, Liang HL. The progress of traditional Chinese medicine experiment research in anti-anaphylaxis. Forum Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;30:67–70.
Asero R. Chronic unremitting urticaria: is the use of antihistamines above the licensed dose effective? A preliminary study of cetirizine at licensed and abovelicensed doses. Clin Exp Dermatol 2007;32:34–38.
Zhu HY, Wu XB, Jin XG, Cui MY, Li TF, Wang MY. The effect of Wumei to mast cell degranulation and the related signaling pathways. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2015;26:2096–2098.
Pelaia G, Cuda G, Vatrella A, Gallelli L, Caraglia M, Marra M, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and asthma. J Cell Physiol 2005;202:642–653.
Marchand F, Mecheri S, Guilloux L, Iannascoli B, Weyer A, Blank U. Human serum IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation shows poor correlation to allergen-specific IgE content. Allergy 2003;58:1037–1043.
Williams CM, Galli SJ. The diverse potential effector and immunoregulatory roles of mast cells in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;105:847–859.
Bradding P, Walls AF, Holgate ST. The role of the mast cell in the pathophysiology of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;117:1277–1284.
Gurish MF, Austen KF. The diverse roles of mast cells. J Exp Med 2001;194:F1–F5.
Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 2002;298:1911–1912.
Gilfillan AM, Tkaczyk C. Integrated signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol 2006;6:218–230.
Gschwandtner M, Schäkel K, Werfel T, Gutzmer R. Histamine H(4) receptor activation on human slan-dendritic cells down-regulates their pro-inflammatory capacity. Immunology 2011;132:49–56.
Zhang HY, Yang J, Long XN, He SH. Signal transduction pathway for TNF-induced IL-6 release from mast cells. J Cell Mol Immunol (Chin) 2011;27:829–831.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Müller-Newen G, Schaper F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J 2003;374:1–20.
Zhang HY, Wang SL, Lin LY, LIN Q, Bei N, He SH. Relationship between IL-13 release of mase cells induced by IL-12 and ERK signaling pathway. J Jilin Univ (Med, Chin) 2009;35:322–325
Jin GR, Hong H, Jin GY, Li YZ, Li GS, Yan GH. Anthocyanidin inhibits immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic response in mast cells. Acta Pharm Sin (Chin) 2012;47:34–38.
Huang F, Deng HM, Tong XY. Effect of extracts of ginkgobiloba leaves on activation of RBL-2H3 cell. Chin J Pathophysiol (Chin) 2009;25:1816–1820.
Liang Z, Wu R, Xie W, Geng H, Zhao L, Xie CF, et al. Curcumin suppresses MAPK pathways to reverse tobacco smoke-induced gastric epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mice. Phytother Res 2015;29:1665–1671.
Zhang ZR, Xu LJ, Sui SQ. Effect of methanol extract of Linghuai Pills on allergic contact dermatitis in mice. Pharm Today (Chin) 2014;24:243–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xf., Pan, Wd., Yao, Yl. et al. Recent highlights of Chinese herbs in treatment of allergic disease: Acting via mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 570–573 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2526-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2526-x