Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of Musa sapientum L. (MS) bark juice in diabetic gastroparesis and its effect on pharmacokinetic of metformin (MET).
Methods
Diabetes was induced in rats by administering alloxan (120 mg/kg) saline solution and maintained for 8 week. All the 18 Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups (n =6 in each group): normal control, diabetic control and MS bark juice. Assessment of diabetes was done by glucose oxidase-peroxidase method on the 3rd day of alloxan administration. The effects of MS bark juice (100 mL/kg) on gastric emptying time, intestinal transit time, contractility of fundus and pylorus as well as gastric acid secretion in chronic diabetic rats were observed after 8 weeks of alloxan administration. The effect of MS bark juice on the pharmacokinetic of orally administered single dose of MET (350 mg/kg) was evaluated on the 57th day of protocol. Any drugs that may reduce the blood glucose level or influence the fibrinolytic system were not used in this study.
Results
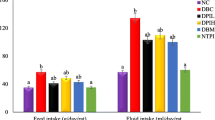
The MS bark juice significantly reduced the blood glucose level in the diabetic rats (P<0.01). There was significant decrease in the pylorus motility and increase in the gastric emptying time, intestinal transit time, contractility of fundus, gastric acid secretion in the MS bark juice treated group (P<0.01). There was significant decrease in the time at which drug at a maximum concentration, half life of drug and increase in the maximum concentration of drug in the plasma of MET in MS bark juice treated group as compared to diabetic control group (P<0.01).
Conclusion
MS bark juice effectively manages diabetic gastroparesis and thereby improves the bioavailabilty of MET when administered with MS bark juice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization, Diabetes Programme, Department of Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion. Facts and Figures sheet Diabetes, Geneva, Switzerland: 2006.
Thakur M, Bhargava S, Praznik W, Loeppert R, Dixit V. Effect of Chlorophytum Borivilianum Santapau and Fernandes on sexual dysfunction in hyperglycemic male rats. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:448–453.
Wang JS, Ying HJ, Guo CY, Huang Y, Xia CD, Liu Q. Influence of high blood glucose fluctuation on endothelial function of type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and effects of Panax Quinquefolius saponin of stem and leaf. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:217–222.
Sies H, ed. Antioxidants in disease mechanisms and therapy. San Diego, CA, Academic Press;1997:3–6.
Ordög T, Takayama I, Cheung WK, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Remodeling of networks of interstitial cells of Cajal in a murine model of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes 2000;49: 1731–1739.
Kashyap P, Farrugia G. Diabetic gastroparesis: what we have learned and had to unlearn in the past 5 years. Gut 2010;59:1716–1726.
Tang DM, Friedenberg FK. Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon 2011;57:74–101.
Choi KM, Gibbons SJ, Nguyen TV, Stoltz GJ, Lurken MS, Ordog T, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 protects interstitial cells of Cajal from oxidative stress and reverses diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2008;135:2055–2064.
Watkins CC, Sawa A, Jaffrey S, Blackshaw S, Barrow RK, Snyder SH, et al. Insulin restores neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression and function that is lost in diabetic gastropathy. J Clin Invest 2000;106:373–384.
Vittal H, Farrugia G, Gomez G, Pasricha PJ. Mechanisms of disease: the pathological basis of gastroparesis—a review of experimental and clinical studies. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;4:336–346.
Hasler WL. Gastroparesis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;8:438–453.
Forster J, Damjanov I, Lin Z, Sarosiek I, Wetzel P, McCallum RW. Absence of the interstitial cells of Cajal in patients with gastroparesis and correlation with clinical findings. J Gastrointest Surg 2005;9:102–108.
Fetrow CW, Avila JR, eds. Professionals handbook of complementary and alternative medicine. New York: Springhouse Corporation; 1999:36–40.
Dhanabal SP, Sureshkumar M, Ramanathan M, Suresh B. Hypoglycemic effect of ethanolic extract of Musa sapientum on alloxan induced diabetes mellitus in rats and its relation with antioxidant potential. J Herbal Pharmacother 2005;5:7–19.
Someya S, Yoshiki Y, Okubo K. Antioxidant compounds from bananas (Musa Cavendish). Food Chem 2002;79:351–354.
Dubby JJ, Campbell RK, Setter SM, White JR, Rasmussen KA. Diabetic neuropathy: an intensive review. Am J Health Sys Pharm 2004;16:160–173.
Bittinger M, Barnert J, Wienbeck M. Autonomic dysfunction and the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Auton Res 1999;9:75–81.
Perusicova J. Gastrointestinal complication in diabetic mellitus. Vnitr Lek: 2004;50:388.
Horowitz M, Fraser R. Disordered gastric motor function in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1994;37:543–551.
Nilsson PH. Diabetic gastroparesis: a review. J Diabe Complic 1996;10:113–122.
Beaven K. Gastroparesis and jejunal feeding. J Renal Nutrition 1999;9:202–205.
Tripathi AS, Dewani AP, Sheikh I, Shelke PG, Bakal RL, Mazumder PM, et al. Development and validation of RPHPLC method for simultaneous estimation of glimepiride and sildenafil citrate in rat plasma—application to pharmacokinetic studies. Drug Res 2013;63:510–515.
Gwilt PR, Nahhas PR, Tracewell WG. The effects of diabetes mellitus on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet 1991;20:477–490.
Lincoln J, Bokor JT, Crowe R, Griffith SG, Haven AJ, Burnstock G. Myenteric plexus in streptozotocin-treated rats. Neurochemical and histochemical evidence for diabetic neuropathy in the gut. Gastroenterology 1984;86:654–661.
Belai A, Burnstock G. Changes in adrenergic and peptidergic nerves in the submucous plexus of streptozocindiabetic rat ileum. Gastroenterology 1990;98:1427–1436.
Nowak TV, Harrington B, Kalbfleisch JH, Amatruda JM. Evidence for abnormal cholinergic neuromuscular transmission in diabetic rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 1986;91:124–132.
Zandecki M, Vanden Berghe P, Depoortere I, Geboes K, Peeters T, Janssens J, et al. Characterization of myenteric neuropathy in the jejunum of spontaneously diabetic BBrats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2008;20:818–828.
Yoneda S, Kadowaki M, Kuramoto H, Fukui H, Takaki M. Enhanced colonic peristalsis by impairment of nitrergic enteric neurons in spontaneously diabetic rats. Auton Neurosci 2001;92:65–71.
Darvhekar VM, Tripathi AS, Jyotishi SG, Mazumder PM. Evaluation of diabetic gastroparesis effect of Musa sapientum L. bark juice by reducing the level of oxidative stress. Orient Pharm Exp Med 2013;13:29–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darvhekar, V., Tripathi, A.S., Jyotishi, S.G. et al. Influence of Musa sapientum L. on pharmacokinetic of metformin in diabetic gastroparesis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 783–788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2520-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2520-3