Abstract
Objective
To investigate the efficacy of Aidi Injection (艾迪注射液) on overexpression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) induced by vinorelbine and cisplatin (NP) regimen in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and study the difference between intravenous administration and targeting intratumor administration of Aidi Injection with thoracoscope.
Methods
Totally 150 patients with NSCLC were randomly assigned to the control group, the intravenous group and the intratumor group by the random envelope method, 50 cases in each group. The patients were treated with NP regimen (2 cycles), NP regimen (2 cycles) plus Aidi intravenous injection, or NP regimen (2 cycles) plus Aidi intratumor injection with thoracoscope, respectively for 6 weeks. The clinical effificacy was observed based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) rules, the expression of P-gp in the tumor tissue was tested before, 3 and 6 weeks after treatment, the safety was evaluated by monitoring the toxicity in the process of treatment, and the progression-free survival (PFS) was measured.
Results
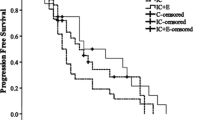
Fifteen cases dropped out because of the irreconcilable conditions which had no relationship with the treatment, 4 in the control group, 5 in the intravenous group, and 6 in the intratumor group, respectively. Compared with the control group, the response rates (complete remission + partial response) and the disease control rates (complete remission + partial response + stable disease) were significantly higher, the P-gp expressions were significantly decreased after 3 and 6 weeks of treatment, and the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of PFS were significantly longer in the intravenous and intratumor groups (P<0.05 or P<0.01), and the intratumor group showed better effects than the intravenous group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the control group, the occurrences of rash, nausea and leukocytopenia were signifificantly decreased in the intravenous and intratumor groups (P<0.05), but without signifificant difference between the intravenous and intratumor groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion
Aidi Injection not only improves the effificacy of NP regime, but also has the function of reducing adverse events and preventing against overexpression of P-gp induced by chemotherapy of NP regimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger W, Setinek U, Hollaus P, Zidek T, Steiner E, Elbling L, et al. Multidrug resistance markers P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein 1, and lung resistance protein in non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic implications. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2005;131:355–363.
Zhu WY, Huang YY, Liu XG, He JY, Chen DD, Zeng F, et al. Prognostic evaluation of CapG, gelsolin, P-gp, GSTP1, and topo-II proteins in non-small cell lung cancer. Anatl Rec 2012;295:208–214.
Masanek U, Pommerenke E, Mattern J, Volm M. Resistance proteins in human kidney, breast, ovarian and lung carcinoma—a comparative analysis. Oncol Reps 1995;2:41–44.
Kelly RJ, Draper D, Chen CC, Robey RW, Figg WD, Piekarz RL, et al. A pharmacodynamic study of docetaxel in combination with the P-glycoprotein antagonist, tariquidar (XR9576) in patients with lung, ovarian, and cervical cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:569–580.
Hong Z, Pan LX, Chen J, Feng JF, Huang FL, Zheng XL. Traditional Chinese medicine Aidi Parenteral Solution with NP regimen for reversal of multidrug resistance in nonsmall cell lung cancer with P-gp overexpression. J Clin Med Pract (Chin) 2005;9:30–33.
Xu HX, Huang XE, Li Ying, Li CG, Tang JH. A clinical study on safety and efficacy of Aidi Injection combined with chemotherapy. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prevent 2011;12:2233–2236.
Ma WH, Duan KN, Feng M, She B, Chen Y, Zhang RM. Aidi Injection as an adjunct therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2009;7:315–325.
Sun XF, Pei YT, Yin QW, Wu MS, Yang GT. Application of Aidi Injection in the bronchial artery infused neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III A non-small cell lung cancer before surgical operation. Chin J Integr Med 2010;16:537–541.
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, eds. WHO classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004:26–67.
Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 2010;17:1471–1474.
Sohaib A. RECIST rules. Cancer Imaging 2012;12:345–346.
Nishino M, Jackman DM, Hatabu H, Yeap BY, Cioffredi LA, Yap JT, et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) guidelines for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: comparison with original RECIST and impact on assessment of tumor response to targeted therapy. Am J Roentgenol 2010;195:221–228.
Zhou DH, Lin LZ, Zhou YQ, Luo RC, Liu KF, Jia YJ, et al. Prognostic analysis of stage III–IV non-small cell lung cancer patients treated by traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Cancer (Chin) 2005;24:1252–1256.
Ng CS, Wan IY, Yim AP. Impact of video-assisted thoracoscopic major lung resection on immune function. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2009;17:426–432.
Kang MQ, Cao YP, Deng F, Zhu Y, Wang MH, Lin RB. Impact of intrapleural hyperthermic perfusion on immunologic reaction state of cytokines Th1/Th2 of lung carcinoma patients with malignant pleural effusion. Chin J Cancer (Chin) 2008;27:210–213.
Chen Z, Zhang M, Li X, Xu Q, Yang S. Simultaneous determination of five glycosides in Aidi Injection by RP-HPLC-ELSD. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2011;36:706–708.
Li JJ, Liang S, Zhuang S, Li CY. Research progress of Adie Injection. J Changchun Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2016;32:271–273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the 2011 National Key Specialty Construction of Clinical Projects of China, Science and Technology Projects of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau in Jiangsu Province of China (No. LB13042)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Jj., Liu, Hp. Efficacy of Aidi Injection (艾迪注射液) on overexpression of P-glycoprotein induced by vinorelbine and cisplatin regimen in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 504–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2511-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2511-4