Abstract
Objective
To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection (PDSI) in the treatment of child epidemic parotitis (EP).
Methods
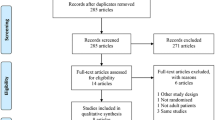
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding PDSI in the treatment of child EP were searched in China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Database, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, PubMed, and Cochrane Library from inception to July 30, 2013. Two reviewers independently retrieved RCTs and extracted information. The Cochrane risk of bias method was used to assess the quality of included studies, and a metaanalysis was conducted with RevMan 5.2 software.
Results
A total of 11 studies with 818 participants were included. The quality of the studies was generally low, among which only one study mentioned the random method. The meta-analysis indicated that PDSI was more effective than the conventional therapy with Western medicine for EP in the outcomes of the total effective rate [relative risk (RR)=1.23, 95% confifidence interval (CI) [1.14, 1.33], P<0.01], the time of temperature return to normal, the time of detumescence [mean difference (MD)=–2.10, 95% CI [–2.78,–1.41], P<0.01], and the incidence of complications (RR=0.14, 95% CI [0.03, 0.72], P=0.02). There were 6 adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in this systematic review, 2 of which were mainly represented rash and diarrhea in the experiment group, while another 4 ADRs occurred in the control group.
Conclusions
Based on the systematic review, PDSI was effectiveness and relatively safety in the treatment of child EP. But further rigorously designed trials are warranted to determine its effectiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li BZ, Fang YL. Study on efficacy of 42 cases of Tanreqing Injection in treating epidemic parotitis. China Modern Med (Chin) 2010;17:55–56.
Ying Y, Deng HJ, Wu HF, Yang ZQ, Jing LP, Zhao LL, et al. Survey on the epidemic parotitis outbreak in the school of floating children. Shanghai J Prevent Med (Chin) 2009;17:115–116.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overview of mumps. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/mumps/index.html, 2010-03-14.
Wu RP, Hu YM, Jiang ZF, eds. ZHU Fu-tang practice of pediatrics. 6th ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House; 1995:749–753.
Duan SC, Liu XY, Zhu QR, eds. Pediatric infectious diseases. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press; 2003:105.
Ni SF. Experience of 69 cases of the treatment of epidemic parotitis. Guide China Med (Chin) 2009;7:83–84.
Zhou YQ, Wu GM. Progress of Chinese medicine treatment of mumps. Chin Corresp Commun (Chin) 1996:6–8.
State Drug Administration of China. The catalog of essential Chinese patent drugs in the emergency department (room) of national Chinese medicine hospitals. J Emerg Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1992;2:4.
Xu R, Xu XL. Clinical use of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. J Modern Clin Med (Chin) 2005;31:278–280.
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343:d5928.
Zheng MH, ed. Applications and example analyzation of the meta-analysis software. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House; 2013:4.
Xue HR, Zhu P, Yan YJ. 30 cases epidemic parotitis treated with Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. J Med Theory Pract (Chin) 2000;13:618.
Zhang GL, Guo SX, Jiang YL, Xiang YL. Observation of 48 cases of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection for the treatment of epidemic parotitis. Modern J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2001;10:1775.
Wu WL, Ji XF, Liu CB. Efficacy of 50 cases epidemic parotitis treated with Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2001;12:356.
Wang RG. Observation on efficacy of epidemic parotitis treated with Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. J Jining Med Coll (Chin) 2002;25:55.
Li XT. 22 cases of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection for the treatment of epidemic parotitis. Henan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2003;23:64.
Wang MC, Wang J. Observation of the efficacy of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection in treatment of epidemic parotitis. Jiangsu Health Care (Chin) 2005;9:54.
Cui WG, Yang CP. 30 cases of the efficacy of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection in treatment of epidemic parotitis. J Taishan Med Coll (Chin) 2002;23:240.
You JY. Observation on the efficacy of epidemic parotitis treated with Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. Med J Liaoning (Chin) 2001;15:206.
Fu PX. Observation on the efficacy of 32 cases of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection in treatment of epidemic parotitis. Jiangxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;33:29–30.
Gong FB. The efficiency of andrographolide in treating of child mumps epidemic parotitis. J Pediatr Pharm (Chin) 2005;11:54–55.
Kong DL, Li YC. Observation on the efficacy of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection in treating 50 cases with epidemic parotitis. Asia-Pacific Tradit Med (Chin) 2006:66.
Lu XW, Meng LL, Wu LP. The clinical treatment scheme optimization study of epidemic parotitis. J Pediatr Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;5:10–13.
Brillanti S, Garson J, Foli M, Whitby K, Deaville R, Masci C, et al. A pilot study of the combination therapy with ribavirin plus interferon alfa for interferon alfa-resistant chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1994;107:812–817.
Xu ZY, ed. Infectious diseases. 2nd ed. Shanghai: Shanghai Medical University Press; 1996:267–270.
Gao ZQ, Wang JH. The treatment of epidemic parotitis with Chinese patent drug. Henan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;22:4.
Zhang TM. Clinical Chinese pharmacy. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2004:179–180.
Deng WL, Liu JY, Nie RF. Comparison of the pharmacological effects of 13 Andrographis Injection (I)—antipyretic and antiinflammatory effects and toxicity. Bull Chin Mater Med (Chin) 1985;10:38–42.
Wang L, Liu HW, Song T, Ren YH. The research and clinical use of Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. Inform Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1998;15:9–10.
Zhang YP. Experience of Chinese herb injection in treatment for pedopneumonia. Zhejiang J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2000;2:55.
Wang YH. The adverse drug reactions in pediatric caused by Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection. Gansu Sci Technol (Chin) 2003;19:110–111.
National Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring Center. The third issue of "Adverse Drug Reaction Information Bulletin". Available at: http://www.cdr.gov.cn/xxtb_255/ypblfyxxtb/200806/t20080626_2817.html, 2003-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Jr., Zhang, Xm. & Zhang, B. Potassium Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Injection for the treatment of child epidemic parotitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 866–873 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1895-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1895-2