Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether the serum levels of inflammation-related cytokines might be different between the healthy individuals and the psoriatic patients diagnosed of three varied Chinese medicine (CM) syndromes [blood-stasis syndrome (BSS), blood-dryness syndrome (BDS) and wind-heat syndrome (WHS)].
Methods
A total of 62 psoriatic patients were recruited and assigned to 3 groups according to their CM syndromes, including 27 patients of BSS, 21 of BDS and 14 of WHS. Another 20 sex- and age-matched healthy subjects were enrolled into the control group. Serum concentrations of multiple cytokines, including monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), soluble CD4O ligand (SCD40L), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), epidermal growth factor (EGF), interleukin-8 (IL-8), interleukin-17 (IL-17), interferon γ inducible protein-10 (IP-10) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), were measured by a multiplexed flow cytometric assay.
Results
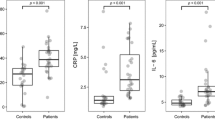
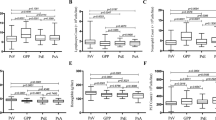
The circulating levels of MIP-1α, TNF-α, IL-8, and IP-10 were significantly increased in the psoriatic patients compared with the healthy controls (P<0.01). Male and female patients tended to have higher serum levels of MCP-1 and IP-10, respectively (P<0.05). Interestingly, compared with the control group, 6 out of the 9 cytokines (MCP-1, MIP-1α, TNF-α, EGF, IL-8 and IP-10) were substantially increased in the BSS group (P<0.05 or P<0.01), whereas only MIP-1α and IL-8 levels were elevated in the BDS group (P<0.05 or P<0.01) concurrent with lowered concentrations of SCD40L and IL-17 (P<0.05). In the WHS group, MIP-1α was the only cytokine whose level was evidently increased (P<0.01), in contrast to IL-17 which was decreased as compared with the control (P<0.05). The psoriatic patients overall owned higher levels of MIP-1α and IL-8 in the circulation which were comparable among the 3 groups of CM syndromes (P<0.01). In contrast, TNF-α level of the BSS group was the highest among the three (P<0.01), followed by the BDS and the WHS groups.
Conclusions
The expression profiles of cytokines in the circulation might not be necessarily identical for psoriatic patients with different CM syndromes. Accordingly, the serum concentrations of certain cytokines could potentially be used as the ancillary indices for the clinical classification of psoriatic CM syndromes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu W, Zhao G, Liu YF. Proliferation response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to streptococcus M6 protein in patients with psoriasis. J Fourth Milit Med Univ (Chin) 2003;24:1213–1215.
Skov L, Kragballe K, Zachariae C, Obitz ER, Holm EA, Jemec GB, et al. HuMax-CD4: a fully human monoclonal anti-CD4 antibody for the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. Arch Dermatol 2003;139:1433–1439.
Bos WE, Thio HB, Neumann HA, van der Fits L, Prens EP. The pathogenesis of inflammatory dermatoses, expecially psoriasis. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2006;150:179–183.
Krueger GG, Langley RG, Leonardi C, Yeilding N, Guzzo C, Wang Y, et al. A human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2007;356:580–592.
Sano S, Chan KS, Carbajal S, Clifford J, Peavey M, Kiguchi K, et al. Stat3 links activated keratinocytes and immunocytes required for development of psoriasis in a novel transgenic mouse model. Nat Med 2005;11:43–49.
Deng BX, Jiang CY, Wang P, liu WL, Qu X, Zhao YM, et al. Rule of distribution and development of TCM syndromes of psoriasis. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;47:770–772.
Zhang GZ, Wang P, Wang JS, Jiang CY, Deng BX, Li P, et al. Study on the distribution and development rules of TCM syndromes of 2651 psoriasis vulgaris cases. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;49:894–896.
An JY, Jin L. Traditional Chinese medicine progress research of psoriasis with blood-stage treatment. Chin J Dermatovenerol Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2009;8:59–61.
Psoriasis Study Group, Skin Venereal Diseases Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for the treatment of psoriasis (2008). Chin J Dermatol (Chin) 2009;42:213–214.
Zheng XY, ed. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of traditional Chinese medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2002:229–300.
Wang L, Yang L, Gao L, Gao TW, Li W, Liu YF. A functional promoter polymorphism in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is associated with psoriasis. Int J Immunogenet 2008;35:45–49.
Kaur S, Zilmer K, Leping V, Zilmer M. Comparative study of systemic inflammatory responses in psoriasis vulgaris and mild to moderate allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatology 2012;225:54–61.
Szodoray P, Alex P, Chappell-Woodward CM, Madland TM, Knowlton N, Dozmorov I, et al. Circulating cytokines in Norwegian patients with psoriatic arthritis determined by a multiplex cytokine array system. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2007;46:417–425.
Chen JS, Zheng M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in patients with psoriasis. Chin J Dermatol (Chin) 2002;35:111–113.
Jin L, Jiang YS, Cai NN, Wang P. Expression of VEGF in skin lesions and serum level in patients of psoriasis vulgaris with TCM differentiation-types. Chin J Derm Venereol (Chin) 2006;20:406–408.
Perera GK, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. Psoriasis. Annu Rev Pathol 2012;7:385–422.
Arican O, Aral M, Sasmaz S, Ciragil P. Serum levels of TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in patients with active psoriasis and correlation with disease severity. Mediators Inflamm 2005;2005:273–279.
Takahashi H, Tsuji H, Hashimoto Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Iizuka H. Serum cytokines and growth factor levels in Japanese patients with psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol 2010;35:645–649.
Cai Y, Shen X, Ding C, Qi C, Li K, Li X, et al. Pivotal role of dermal IL-17-producing γδ T cells in skin inflammation. Immunity 2011;35:596–610.
Erturan I, Köroğlu BK, Adiloğlu A, Ceyhan AM, Akkaya VB, Tamer N, et al. Evaluation of serum SCD40L and homocysteine levels with subclinical atherosclerosis indicators in patients with psoriasis: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol 2014;53:503–509.
Gerdes S, Osadtschy S, Buhles N, Baurecht H, Mrowietz U. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 2014;23:322–325.
Witowski J, Ksiazek K, Jörres A. Interleukin-17: a mediator of inflammatory responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 2004;61:567–579.
Zhang P, Zhang R, Zhou XY. The expression and significant of IL-17 in psoriatic lesions. Chin J Dermatovenereol (Chin) 2010;24:13–15.
Krueger JG, Bowcock A. Psoriasis pathophysiology: current concepts of pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:ii30–36.
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 1999;13:9–22.
Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L, Rocha S, Quintanilha A, et al. Interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17, IL-23, IL-8, vascular endothelial growth factor and tumour necrosis factor-α levels in patients with psoriasis before, during and after psoralen-ultraviolet A and narrowband ultraviolet B therapy. Br J Dermatol 2010;163:1282–1290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Financial Industry Technology Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, China (No. 201105)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xuan, Ml., Lu, Cj., Han, L. et al. Circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines in patients with psoriasis vulgaris of different Chinese medicine syndromes. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 108–114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1792-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1792-0