Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of modified Xiaochaihu Decoction (小柴胡汤, MXD) on transforming growth factor-β1/Sma- and Mad-related proteins (TGF-β1/Smads) signaling pathway in rats with chronic pancreatitis (CP) induced by dibutyltin dichloride.
Methods
Thirty healthy male Wistar rats were randomly divided into the normal control group, CP group and CP+MXD-treated group. CP was induced by injection of dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC, 7 mg/kg of body weight) into the right caudal vein, and the control rats were treated with vehicle. MXD was given daily by gavage at a dose of 10 g/kg of body weight, starting from the day after CP induction. After 28-day treatment, the n-benzoyl-tyrosyl para-aminobenzoic acid (NBT-PABA) test was carried out to evaluate exocrine pancreatic function. Then, rats were sacrificed, and pancreatic tissues were harvested for histological evaluation. In addition, the mRNA expression of TGF-β1, TGF-β1 type II receptor (TGFβRII), Smad3 and Smad7 was determined in pancreatic tissues by using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results
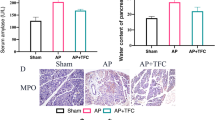
Treatment of CP with MXD improved the PABA recovery, decreased the histological lesion, and reduced the mRNA expression of TGF-β1, TGFβRII and Smad3 (P<0.05). However, MXD had no effect on Smad7 mRNA level.
Conclusions
MXD could protect the pancreas against chronic injury and improve pancreatic exocrine function in DBTC induced rat CP model. Its mechanism may involve inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao GW, Zhang SK, Cui NQ, Li DH. Preventive and therapeutic effects of Kangyi Decoction on chronic pancreatitis in rats. Chin J Surg Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2010;6:565–568.
Talukdar R, Tandon RK. Pancreatic stellate cells: new target in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;23:34–41.
Shimizu M, Hirokawa M, Manabe T. Histological assessment of chronic pancreatitis at necropsy. J Clin Pathol 1996;49:913–915.
Massagne J, Blain SW, Lo RS. TGF beta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorder. Cell 2000;103:295–309.
Miyamoto T, Nakamura H, Nagashio Y, Asaumi H, Harada M, Otsuki M. Overexpression of Smad6 exacerbates pancreatic fibrosis in murine caerulein-induced chronic pancreatic injuries. Pancreas 2010;39:385–391.
Zhang SK, Tsui NC, Li DH, Yao GW, Wang YN. Expression of TGF-ß1/Sma- and Mad-related proteins in rat with chronic pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride. Pancreas 2010;39:252–253.
Dong JJ, Xiao RX, Li YL, Luo YH, Meng RF. Introduce a new test to assess exocrine pancreatic function. J Third Military Med Univ (Chin) 1982;4:90–91.
Cheng JP. Considerations on harmonizing therapy of Xiaochaihu decoction. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;42(10):54–56.
Zhao HF, Ito T, Gibo J, Kawabe K, Oono T, Kaku T, et al. Anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene therapy attenuates experimental chronic pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride in rats. Gut 2005;54:1759–1767.
Chen FP, Chen FJ, Jong MS, Tsai HL, Wang JR, Hwang SJ. Modern use of Chinese herbal formulae from Shang-Han Lun. Chin Med J 2009;122:1889–1894.
Sun H, Che QM, Zhao X, Pu XP. Antifibrotic effects of chronic baicalein administration in a CCl4 liver fibrosis model in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2010;631(1–3):53–60.
Wu K, Zhang XP, Wang XP. The effects and mechanisms of glycyrrhizin on the TNBS-induced pancreatic fibrosis in rat. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2003;19:1424–1427.
Niederau C, Grendell JH. Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1985;88:1973–1995.
He J, Sun X, Qian KQ, Liu X, Wang Z, Chen Y. Protection of cerulein-induced pancreatic fibrosis by pancreasspecific expression of Smad7. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009;1792:56–60.
Qian ZY, Peng Q, Zhang ZW, Zhou LA, Miao Y. Roles of Smad3 and Smad7 in rat pancreatic stellate cells activated by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2010;9:531–536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81102686)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Sk., Cui, Nq., Zhuo, Yz. et al. Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction (小柴胡汤) prevents the progression of chronic pancreatitis in rats possibly by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Sma- and mad-related proteins signaling pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 19, 935–939 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1656-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1656-7