Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of “Three-Typed Syndrome Differentiation” (TTSD) in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
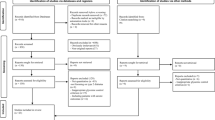
A systematic review and meta-analysis was done based on the clinical diabetes treatment literature of the “TTSD”. Overseas databases like the PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials, and China databases like China Biology Medicine Disc (CBM), Chinese national Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database, and VIP database, without limitation on language, were included with the time limitation from Jan 1982 to Dec 2012 by retrieval of relative original clinical research articles.
Results
Nineteen articles where contains 1,840 diabetes patients were obtained, in which no adverse reactions were reported. Of these, 14 literatures involved the effect of fasting blood glucose (FBG), 10 involved that of postprandial 2-h blood glucose (P2hBG), and 19 involved the overall efficacy based on the national Chinese medicine (CM) diagnosis and treatment standard of diabetes. All the meta-analysis results prefer to the “TTSD” groups (CM+Western medicine Based on TTSD). The results show that, beside the efficacy of Western medicine, the concentrations of FBG and P2hBG in “TTSD” groups continue to drop with statistical significance. For “TTSD” groups, the FBG subsequently dropped 1.03 mmol/L, 95%CI [1.24,0.82] P <0.00001), the P2hBG subsequently dropped 1.09 mmol/L, 95% CI [1.61, 0.57] (P <0.0001), and the overall efficacies benefit 3.46 times those of Western medicine alone, 95% CI [2.67,4.48] (P <0.00001).
Conclusions
The CM by the diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes based on TTSD might be safe and effective, and could better improve both blood glucose and the overall status of patients, including symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang WY, Lu JM, Weng JP, Jia WP, Ji LN, Xiao JZ, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1090–1101.
Diabetes group of Guang’anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences. Pilot study on syndrome differentiation and treatment of diabetes. Beijing J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1980;2:217.
Zhang YR, Lin L, Zhang HE, Li BZ, Fu JS, Gao QJ, et al. Pilot study on syndrome differentiation of diabetes in adults in traditional Chinese medicine. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1982;5:40–42.
Pharmaceutical Council of Traditional Chinese medicine of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. The technological guiding principles in clinical research in developing new drugs (traditonal Chinese medical formula) in treatment of Xiao-Ke disease (diabetes). J Chin Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1990;10:56–57.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. The clinical research guiding principles of new traditonal Chinese medical formula (Volume one). 1993:215–218.
Yan XF, Ni Q, Meng FX. Study on the application of three-typed differentiation syndrome and its influence on the treatment of diabetes with traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Inform Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2005;12(6):95–98.
Cai JW. Observation of traditional Chinese medicine on the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;23:419–420.
Deng HQ, Pan ZX. Clinical observation of Jin-jin-yu-ye Decoction in treating diabetes. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;2:21–22.
Fan JR, Wang XK, Yao XY, Chen LP. The clinical observation on Qinggan Xiexin Capsule (清肝泻心胶囊) in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 30 cases. J Chin Med Sci Technol (Chin) 2002;9:17
Guo XF. Clinical study on Xiaodan Prescription (消瘅方) in the treatment of type 2 diabetes with 50 cases. Hunan J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 200 2004;20:59–60.
Huang Y, Li YM. Clinical study of Sihuang Xiaoke Decoction (四黄消渴饮) on the treatment of type II diabetes with 80 cases. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;20:2
Huo BY, Huo PA. Clinical observation of Jiangtang No.1 in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;9:14–15.
Jiao YX, Dong XR, Jiang Q. Clinical observation of “Xihuang-jiang-tang Capsule” in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2003;31:41.
Li RG. 47 cases of treating diabetes with Kidney-nourishing and antidiabetic decoction. Hunan Guiding J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2001;7:175.
Liu TY. Clinical observation of “smoothing-Liver and regulating-qi” method in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 63 cases. J Tradit Chin Med correspond communicat (Chin) 2000;19:51.
Qing ZQ. Clinical observation of Shenqi Yuxiao Decoction (参氏愈消汤) in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 60 cases. Attachment with 30 cases treated with gliclazide as the control. Zhejiang J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;5:190
Shi H, Lin QC, Chen GQ, Feng Y, Lin YP. Clinical observation of “Shi-hu mixture” in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm (Chin) 2002;13:348–350.
Sun J. Clinical observation of “Shen-lian Compound Tablet” in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 90 cases. J Chin Sci Tech Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;8:192–193.
Wang MX, Wang XK, Dai XL. Clinical study of “clearing-Liver, purgarting-heart, nourishing-Yin and moisting driness” method on treating type II diabetes mellitus. Gansu J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;15:25–26.
Wei JL, Shi HL. Clinical observation of decoction for reducing blood sugar and regulating lipid in the treatment of diabetes innocens. J Henan Univ Chin Med (Chin) 2003;18:51–52.
Wu LE, Yang JP. Clinical observation of “replenishing-the-Spleen-yin” method in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 116 cases. Hubei J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;23:17.
Yan HH, Zou BY. Clinical observation of “Yi-qi-zi-yin-huoxue Decoction” in treating type II diabetes mellitus with 50 cases. Hunan Guiding J TCMP (Chin) 2001;7:16–17.
Yuan L. Dongling antidiabetic Capsule for diabetes: a report of 60 cases. Hunan Guiding J Tradit Chin Med Pharam (Chin) 2001;7:173–174.
Zhang W, Ye HY. The Clinical effect of Yi-qi-yang-yin Fang for treating NIDDM. LI Shi-zhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2002;13:479–480.
Zhao YH. Clinical observation of “Gu-ben-bu-shen-jiangtang decoction” in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus with 62 cases. Hunan J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2004;20:60–61.
New theory of diabetes in Traditional Chinese medicine—interview of Prof. Tong Xiao-lin of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (sept. 29th, 2005): http://www.100md.com/html/DirDu/2005/09/29/76/99/76.htm
Su H, Tong XL, Wang WJ. The academic viewpoint and experience of peofessor Tong Xiao-lin in treating diabetes with Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Chin Guide Med (Chin) 2008;6:198–199.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Xf., Ni, Q., Wei, Jp. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment based on the “three-typed syndrome differentiation” theory in Chinese medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 20, 633–640 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1462-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1462-2