Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of Huannao Yicong Prescription (还脑益聪方, HNYC, a Chinese medical compound) extract on β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) metabolic signal transductionrelated protein kinase C (PKC), tyrosine amyloid protein kinase (TrKA), and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) in brain tissue of transgenic mouse dementia model induced by APP.
Methods
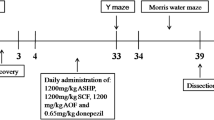
Sixty dementia model transgenic 3-month-old mice induced by APP695V717I were randomly allocated in four groups: the model group (A), the Donepezil (0.65×10−3 g·kg−1·−1)-treated group (B), and the two HNYC-treated groups (C and D) with high dosage (2.8 g·kg-1·−1) and low dosage (1.4 g·kg−1·−1) of HNYC extract, respectively, 15 mice in each group. Besides, a normal control group was set up with 15 C57BL/6J mice with the same age and genetic background as the model mice. The drugs for treatment were administered once a day by dissolving in equal-volume distilled water through gastric infusion, continued for 6 months, to mice in group A and to normal control group equal-volume distilled water was administered instead. Spatial learning and memory capacity of mice were observed by Morris water maze; their one-time escape response memory capacity was tested by diving platform; and changes of PKC, TrkA, and GSK-3 levels in hippocampus and cortex of brain were detected by Western blotting.
Results
HNYC extract showed significant effects on increasing the time of model mice for swimming through the flat roof and the swimming time and path in the fourth quadrant P<0.05 or P<0.01). Diving platform test showed that the latent times in Groups B and C were longer than that in Group A significantly (P <0.05 and P<0.01). Compared with the normal control group, PKC and TrkA protein expression levels in hippocampus and cortex of model mice’s brain lowered significantly (P<0.01), while GSK-3 protein expression increased significantly (P<0.01); compared with Group A (the model group), hippocampal and cortical levels of PKC protein expression in the intervened groups (B-D) as well as those of TrkA in Group C were higher (P<0.01 or P<0.05), while hippocampal levels of GSK-3 in intervened groups were lower (P<0.01).
Conclusion
HNYC extract could obviously increase the protein expressions of PKC and TrkA and decrease the expression of GSK-3 protein in brain tissue of transgenetic mice model of dementia, and regulate APP metabolic signal transduction path, and thus to suppress the production of Aβ, which is one of the dominant mechanisms for improving learning/memory capacity of dementia model animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
State Pharmacopoeia Committee. People’s Republic of China Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2005:123,28,214.
Xu SY, Bian RL, Chen X. Methodology of pharmacological experiments. 3rd ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2002:828–829.
Chen Q. Methodology of pharmacological studies on Chinese medicine. 2nd ed. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House; 2006:910.
Xu SZ, Bullock L, Shan CJ, Cornelius K, Rajanna B. PKC isoforms were reduced by lead in the developing rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 2005;23:53–64.
Takihino K, Johan F, Willyl B. Los s of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor sites and decreased PKC levels correlate with staging of Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary pathology. Brain Res 1998;796:209–221.
Guan J, Liu JG, Li H, Liu MF, Cai LL, Yao MJ, et al. Effect of extracts from Huannao Yicong Prescription on expression of cerebral amyloid beta, amyloid precursor protein and secretases in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm (Chin) 2011;22:236–240.
Geng JS, Zhou AL, Mao JH, Zhu Y, Shi HY, Hu YE. Effects of Naoyikang on both learning and memory ability and expression of NGF-TrkA mRNA in rats with Alzheimer’s disease. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2009;29:152–155.
Meng Y, Wang R, Liu MX, Sheng SL. Study on the factors related with mechanism of neuron apoptosis in Alzheimer disease. Chin J Geriatrics (Chin) 2006;25:245–247.
Ma YX, Yu ZW. Contemporary dementia medicine. Beijing: Scientific and Technical Documents Publishing House; 2008:817.
Steinbrecher KA, Wilson W 3rd, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta functions to specify genespecific, NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol 2005;25:8444–8455.
De Ferrari GV, Inestrosa NC. Wnt signaling function in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Rev 2000;33:1–12.
Terwel D, Muyllaert D, Dewachter I, Borqhqraef P, Croes S, Devijver H, et al. Amyloid activates GSK-3beta to aggravate neuronal tauopathy in bigenic mice. Am J Pathol 2008;172:786–798.
Anderton BH, Dayanandan R, Killick R, Lovestone S. Does dysregulation of the Notch and wingless/Wnt pathways underlie the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease? Mol Med Today 2000;6(2):54–59.
Lim HJ, Cho JS, Oh JH, Shim SB, Hwang DY, Jee SW, et al. NSE-controlled carboxyl-terminus of APP gene overexpressing in transgenic mice induces altered expressions in behavior, Abeta-42, and GSK3beta binding proteins. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2005;25:833–850.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30873338) and the Major New Drug Projects of the Ministry of Science and Technology of P. R. China (No. 2009ZX09103-391)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, Mf., Liu, Jg. et al. Effect of Huannao Yicong Prescription (还脑益聪方) extract on β-Amyloid precursor protein metabolic signal transduction-related protein in brain tissue of dementia model transgenic mouse. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 683–689 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1204-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1204-x