Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of drug-containing serum of Chinese herbal compound, Xiongshao Capsule (芎芍胶囊, XS, for activating-blood) and Huanglian Capsule (黄连胶囊, HL, for dispellingtoxin) on the oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced inflammatory factors in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
Methods
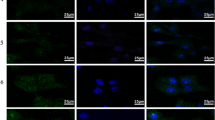
Thirty-two rats were randomly divided into four groups: the blank control group treated with distilled water, the positive control group treated with simvastatin (1.8 mg/kg), the test group I treated with Chinese herbal compound of XS (0.135 g/kg), and the test group II treated with Chinese herbal compound of XS (0.135 g/kg) and HL (0.135 g/kg). All the treatments were administered for 7 successive days by gastrogavage. Rats’ blood serum was harvested 1 h after the last administration to prepare respective drugcontaining serum. HUVECs were exposed to ox-LDL (100 μg/mL) to induce cell injury model and incubated with corresponding drug-containing serum for 24 h. Untreated HUVECs were set for blank control. Levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) in supernatant of cultured HUVECs were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). HUVEC surface expressions of ICAM-1 and E-selectin were determined by flow cytometry.
Results
Levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and sICAM-1 in the supernatant of HUVECs as well as the cell surface expressions of ICAM-1 and E-selectin significantly increased after 24-h ox-LDL stimulation (P<0.01), while the abnormal elevations, except sICAM-1 in the test group I, were all reduced in the treated groups (the positive control and the two test groups) significantly (P<0.01 or P<0.05). Besides, the effect in the test group II seemed somewhat higher than that in the test group I but with no statistical significance (P>0.05).
Conclusion
Drug-containing serum of XS plus HL has a certain inhibitory effect on the vascular endothelial inflammation response induced by ox-LDL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi DZ, Xu H, Yin HJ, Zhang JC, Chen KJ. Combination and transformation of toxin and blood stasis in etiopathogenesis of thrombotic cerebrocardiovascular diseases. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2008;6:1105–1108.
Wen C, Xu H, Huang QF, Chen KJ. Effect of drugs for promoting blood circulation on blood lipids and inflammatory reaction of atherosclerotic plaques in apoE gene deficiency mice. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2005;25:345.
Zhang JC, Chen KJ, Zheng GJ, Zhang WG, Shi DZ, Yin HJ, et al. Regulatory effect of Chinese herbal compound for detoxifying and activating blood circulation on expression of NF-κB and MMP-9 in aorta of apolipoprotein E gene knocked-out mice. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2007;27:40–44.
Jiang YR, Chen KJ, Xu YG, Yang XH, Yin HJ. Effects of Propyl Gallate on adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to human endothelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:47–53.
Ou HC, Lee WJ, Lee IT, Chiu TH, Tsai KL, Lin CY, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract attenuates oxLDL-induced oxidative functional damages in endothelial cells. J Appl Physiol 2009;106:1674–1685.
Landsberger M, Wolff B, Jantzen F, Rosenstengel C, Vogelgesang D, Staudt A, et al. Cerivastatin reduces cytokineinduced surface expression of ICAM-1 via increased shedding in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2007;190:43–52.
Xenos ES, Stevens SL, Freeman MB, Cassada DC, Goldman MH. Nitric oxide mediates the effect of fluvastatin on intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 expression on human endothelial cells. Ann Vasc Surg 2005;19:386–392.
Hopkins AM, Baird AW, Nusrat A. ICAM-1: targeted docking for exogenous as well as endogenous ligands. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2004;56:763–778.
Kaski JC, Fernández-Bergés DJ, Consuegra-Sánchez L, Fernández JM, García-Moll X, Mostaza JM, et al. A comparative study of biomarkers for risk prediction in acute coronary syndrome—results of the SIESTA (Systemic Inflammation Evaluation in non-ST-elevation Acute coronary syndrome) study. Atherosclerosis 2010;212:636–643.
Zhang JC, Chen KJ. Theoretical thinking on relationship between toxic-stasis pathogenicity and atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque. Chin J Integr Tradit Westn Med (Chin) 2008;28:366–368.
Lu XH, Ding SW. Clinical effect and mechanism on treating unstable angina pectoris by Huanglian Jiedu Capsule. J Shandong Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2005;29:457–460.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Developing Plan for Basic Key Items (973 Plan, No. 2006CB504803)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Yr., Miao, Y., Yang, L. et al. Effect of chinese herbal drug-containing serum for activating-blood and dispelling-toxin on ox-LDL-induced inflammatory factors’ expression in endothelial cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 30–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0849-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0849-1