Abstract
Objective
To investigate effects of Dahuang Zhechong Pill (大黄{ie371-1}虫丸, DHZCP) on the cell cycle and the related signal pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) with the method of serum pharmacology.
Methods
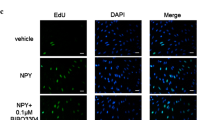
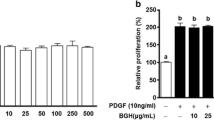
DNA synthesis in VSMCs was examined by detecting 5′-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine incorporation with the immunocytochemical method. The cycle of VSMCs was evaluated with flow cytometry. Expressions of cyclin D1, p27, protein kinase Cα (PKCα), and phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) were quantified by Western blot method.
Results
DHZCP containing serum significantly inhibited DNA synthesis of PDGF-stimulated VSMCs, arrested the cells in G G1 phase, modulated the protein expressions of cyclin D D1 and p27, and suppressed the activation of PKCα and ERK1/2.
Conclusion
DHZCP containing serum inhibits VSMCs proliferation via modulating the expressions of cell cycle proteins to arrest the cell in G G1 phase, which is attributed to, at least in part, suppressing PKCα-ERK1/2 signaling in VSMCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan JJ, Chen XY. The progress of experiment study on Dahuang Zhechong Pill. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae (Chin) 2000;6:60–61.
Li WL, Wu SP. Clinical effect of Dahuang Zhechong Pill on chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis. Chin Pharmacy (Chin) 2008;19:1658–1659.
Yuan HX. Clinical application of Dahuang Zhechong Pill in gynecology. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2009;7:168–170.
Chen JF. Efficancy of Dahuang Zhechong Pill in treatment of 50 cases of patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;20:331–332.
Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature 1993;362:801–809.
Libby P. Inflammat ion in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002;420:868–874.
Ross R. Cell biology of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Physiol 1995;57:791–804.
Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Li B, Sun J, Harp JB, Ling BN. Role of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription and mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in angiotensin II- and platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 1997;272:24684–24690.
Andrés V. Control of vascular cell proliferation and migration by cyclin-dependent kinase signalling: new perspectives and therapeutic potential. Cardiovasc Res 2004;63:11–21.
Boehm M, Nabel EG. Cell cycle and cell migration: new pieces to the puzzle. Circulation 2001;103:2879–2881.
Li JL, Liu JT, Gou W, Li XK, Liu CH. Effect of Dahuang Zhechong Pill on vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic rabbits. Chin Tradit Patent Med (Chin) 2006;28:1470–1472.
Ji YY, Liu JT, Li JL, Wang ZD, Liu CH, Ding CJ, et al. Effect of the disassembled recipes of Dahuang Zhechong Pill on proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic rabbits. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;26:913–917.
Zhang YH, Liu JT, Wen BY, Xiao XH. In vitro inhibition of proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by serum of rats treated with Dahuang Zhechong Pill. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;112:375–379.
Tashino S. “Serum pharmacology ” and “ serum pharmaceutical chemistry”: from pharmacology of Chinese traditional medicines to start a new measurement of drug concentration in blood. Ther Drug Monit Res (Jpn) 1988;5:54–64.
Skalli O. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol 1986;103:2787–2796.
Gratzner HG. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: a new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science 1982;218:474–475.
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bedner E, Smolewski P. Flow cytometry in analysis of cell cycle and apoptosis. Semin Hematol 2001;38:179–193.
Blake MS, Johnston KH, Russell-Jones GJ, Gotschlich EC. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem 1984;136:175–179.
Meng YC, Ding X, Ben CE. The application view of Chinese traditional medicine serum pharmacology. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1999;22:42–43.
Sherr CJ. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 1994;79:551–555.
Morgan DO. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature 1995;374:131–134.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Gene Dev 1999;13:1501–1512.
Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM. Reactive oxygen species and vascular cell apoptosis in response to angiotensin II and pro-atherosclerotic factors. Regul Peptides 2000;90:19–25.
Nelson PR, Yamamura S, Mureebe L, Itoh H, Kent KC. Smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation are mediated by distinct phases of activation of the intracellular messenger mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Vasc Surg 1998;27:117–125.
Lavoie JN, Allemain GL, Brunet A, Muller R, Pouyssegur J. Cyclin D1 expression is regulated positively by the p42/p44MAPK and negatively by the p38/HOGMAPK pathway. J Biol Chem 1996;271:20608–20616.
Sakakibara K, Kubota K, Worku B, Ryer EJ, Miller JP, Koff A, et al. PDGF-BB regulates p27 expression through ERK-dependent RNA turn-over in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2005;280:25470–25477.
Villanueva J, Yung Y, Walker JL, Assoian RK. ERK activity and G1 phase progression: identifying dispensable versus essential activities and primary versus secondary targets. Mol Biol Cell 2007;18:1457–1463.
Taylor AM, McNamara CA. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell growth: targeting the final common pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23:1717–1720.
Marais R, Light Y, Mason C, Paterson H, Olson MF, Marshall CJ. Requirement of Ras-GTP-Raf complexes for activation of Raf-1 by protein kinase C. Science 1998;280:109–112.
Schönwasser DC, Marais RM, Marshall CJ, Parker PJ. Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by conventional, novel, and atypical protein kinase C isotypes. Mol Cell Biol 1998;18:790–798.
Saito Y, Hojo Y, Tanimoto T, Abe J, Berk BC. Protein kinase C-α and protein kinase C-ɛ are required for Grb2-associated binder-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in response to platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem 2002;277:23216–23222.
Leszczynski D, Joenväärä S, Foegh ML. Protein kinase C-α regulates proliferation but apoptosis in rat coronary vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 1996;58:599–606.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30572347)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Liu, Jt., Ji, Yy. et al. Dahuang Zhechong Pill (大黄虫丸) containing serum inhibited platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation by inducing G1 arrest partly via suppressing protein kinase C α-Extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 371–377 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0696-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0696-0