Abstract
Objective
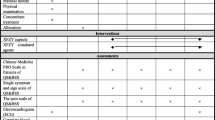
To establish the diagnosis scale of blood stasis syndrome (BSS) and explore the idea and method of using scale to research the quantitative diagnosis of Chinese medicine (CM) syndrome.
Methods
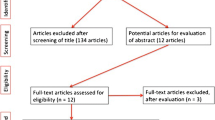
Combining the modern epidemiology, consulting the access of quality of life scale, and colligating multi-angle methods to make the scale.
Results
The scale had relatively good reliability and validity and could be used to estimate the degree of stasis and analyse the curative effect.
Conclusions
It was a reference for CM syndrome diagnosis that combines screening methods of scale entry with quantitative diagnosis to establish the quantitative diagnosis scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen HZ, ed. Internal medicine. 3th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 1995:263–264.
Qian RL. New criteria for diagnosis and type of diabetes mellitus. Chin J Diabetes (Chin) 2000;8(1):5–6.
Chen HZ, ed. Internal medicine. 20th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2005:1525–1541.
Sun YQ, ed. Obstetrics and gynecology. 4th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2000:59–60.
Specialty Committee of Activating Blood and Removing Stasis, Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine. Diagnostic standards of blood stasis syndrome. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 1987;7(3):cover 2.
He J, Gao ES, Lou CH. Study of the weight coefficient and standardization method in synthesized estimation. Chin J Statistics (Chin) 2001;17:1048–1050.
Wu Y, Hu YS, Fan WK. Reliability and validity study of the rehabilitation medicine assessment of function scale. Chin Clin Rehabil (Chin) 2002;6:310,317.
Lai SL. The dependability analysis in clinic observation of formula and herbs. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm (Chin) 1991;1(2):51.
Liang HC, ed. Social medicine. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press; 1988:157–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Grants from 973 Programme of China (No. 2003CB517103); National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90709048)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Kw., Chu, Fy. & Wang, J. A clinical epidemiological study of the quantitative diagnosis scale of blood stasis syndrome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 200–204 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0667-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0667-5