Abstract
Objective
To analyze and investigate the rules for drug utilization of Chinese medicine for the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris with blood-heat syndrome.
Methods
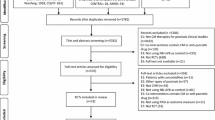
The literatures that met the following inclusion criteria were screened out from China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) from January 1998 to December 2008, including the compositions and dosages of the recipes reported completely and accurately, the sample size being ⩾ 30 cases and the total effective rate being ⩾ 70%.
Results
In total, 289 papers meeting the inclusion criteria were retrieved, involving 301 recipes; in which 111 recipes consisting of 145 individual drugs were the function for clearing the heat, accounting for 52.84%. The three drugs with the highest utilized frequency were Radix Rehmanniae, Radix Arnebiae seu Lithospermi and Cortex Moutan. Meridian adscription of the drugs was mainly the Gan (肝)-meridian.
Conclusion
There were rules for the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris of blood-heat syndrome with Chinese medicine prescriptions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhai YC, ed. Surgery of traditional Chinese medicine. 1st ed. Shanghai: Shanghia University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Press; 2002:221.
Song GY. Clinical observation on treatment of 56 cases of psoriasis vulgaris viewing from blood. Guangxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1999;22(5):32–33.
Bai YP, Zeng JJ, Yang DQ. Causal analysis of blood heat syndrome in psoriasis vulgaris. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2007;22:537–540.
Zhou L, Fu C, Xie ZW. Study of medication rules for psoriasis vulgaris by traditional Chinese medicine. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2004;25:1136–1137.
Cui SD, ed. Dictionary of Chinese herbal medicine. 1st ed. Harbin: Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press; 1989:1–1163.
Shen PA, ed. Pharmacology of clinical application of Chinese materia medica. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2006:125–126, 267–268, 393–394.
Huang CL, Zhu XX, eds. Handbook of pharmacology and clinic of Chinese materia medica. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2006:94.
Liu XM, Sun XK, Qi X, Lin XR. Effect of 20 Chinese herbals on epithelial cell, differentiation of epidermal cell and plasma endothelin-1 in mice. Chin J Dermatol (Chin) 2001;34:282–283.
Wang P, Zhang P, Deng BX, Sun LY. Treatment method and clinical research on the treatment of psoriasis using syndrome differentiation by ZHANG Zhi-li (I). Chin J Dermatol Venerol Tradit West Med 2004;3:191–193.
Tang L, Zhao YX. Causative factor of psoriasis. Chin J Dermatol Venerol Tradit West Med (Chin) 2009;8:392–394.
Xu N, Wu SL, Ma SY. Experimental study on blood-cooling and toxin-relieving herbs in treating psoriasis. J Shanghai Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2003;18:61–62.
Zhang YB, Qu X, Niu FL. Affects of 8 kinds of Chinese herbs on the growth and interleukin-8 production of keratinocytes stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-α. Chin J Dermatol Venerol Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;5:18–20.
Wu YJ, Liu HX, Yao L, Dang SX, Shang PS, Tang XR. Research on drug application principles of treating psoriasis in TCM. Beijing Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;28:701–702.
Liu LF. Observation of psychological analysis and nursing effect of psoriasis patients. Contemp Med (Chin) 2010;16:18–19.
Farber EM, Nickoloff BJ, Recht B, Fraki JE. Stress, symmetry, and psoriasis: possible role of neuropeptides. J Am Acad Dermatol 1986;14:305–311.
Zhang YW, Li Q. Psychological assessment on patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Chin J Dermatol Venerol Tradit West Med (Chin) 2009;2:51–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Science Technology Research and Development Program in the 11th Five-year Plan of China (No. 2008BAI53B044)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Yq., Liu, Jl., Bai, Yp. et al. Literature research of Chinese medicine recipes for the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris with blood-heat syndrome type. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 150–153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0645-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0645-y