Abstract
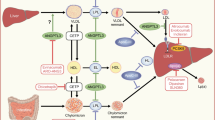
With further researches on blood lipids and atherosclerosis, especially after the conception of “residual cardiovascular risk”, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) becomes a new therapeutic target against atherosclerosis. However, the failure of ILLUMINATE study that was targeted at raising HDL-C level disappointed cardiologists all over the world, which indicates the limitation of HDL-C concentration in representing HDL function. The updated understanding of HDL from “quantity” to “quality” brings a new cut-in point for integrative Chinese and Western medicine in preventing and treating dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. In addition to highlighting statins in directly intervening low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, we should make full use of the superiority of Chinese medicine in overall regulation and individualized treatment to promote the self-healing capacity of the patients, which further regulates abnormity of both concentration and function of the whole blood lipid family to equilibrium. This new strategy for modulating dyslipidemia with mutual complement of advantages from Western and Chinese medicines will no doubt play an important role in future therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barter PJ, Caulfield M, Eriksson M, Grundy SM, Kastelein JP, Komajda M, et al. Effects of torcetrapib in patients at high risk for coronary events. N Engl J Med 2007; 357:2109–2122.
Kastelein JJP, Akdim F, Stroes ESG, Zwinderman AH, Bots ML, Stalenhoef AF, et al. Simvastatin with or without ezetimibe in familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1431–1443.
Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med 1977;62:707–714.
Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 1989;79:8–15.
Florentin M, Liberopoulos EN, Wierzbicki AS, Mikhailidis DP. Multiple actions of high-density lipoprotein. Curr Opin Cardiol 2008;23:370–378.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486–2497.
Nissen SE, Tardif JC, Nicholls ST, Revkin JH, Shear CL, Duggan WT. Effect of torcetrapib on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1304–1316.
Kastelein JJ, van Leuven SI, Burgess L, Evans GW, Kuivenhoven JA, Barter PJ, Revkin JH, Shear CL, Duggan WT. Effect of torcetrapib on carotid atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1620–1630.
Bots ML, Visseren FL, Evans GW, Riley WA, Revkin JH, Tegeler CH, et al. Torcetrapib and carotid intima-media thickness in mixed dyslipidaemia (RADIANCE 2 study): a randomized, double-blind trial. Lancet 2007;370:153–160.
Ansell BJ, Fonarow GC, Fogelman AM. The paradox of dysfunctional high density lipoprotein. Curr Opin Lipidol 2007;18:427–434.
Feng H, Li XA. Dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2009;16:156–162.
Kontush A, Guérin M, Chapman MJ. Spotlight on HDL-raising therapies: insights from the torcetrapib trials. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2008;5:329–336.
Huang X, Chen KJ. Hypothesis of syndrome- and treatment-based pharmacokinetics: the theory and practice. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1997;38:745–747.
Xu H, Chen KJ. Aggressive lipid-lowering and individualized lipid-regulating. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2008;28:476–480.
Zheng F, Zhou MX, Xu H, Chen KJ. Effects of herbs with function of activating blood circulation and detoxication on serum inflammatory markers and blood lipids in stable patients with coronary heart disease. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2009;24:1153–1157.
Wen C, Xu H, Huang QF, Chen KJ. Effect of drugs for promoting blood circulation on blood lipids and inflammatory reaction of atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE gene deficiency mice. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2005;25:345–349.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Beijing Project of Science & Technology Plan (No. D08050703020801); National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30973702); Major Discipline Project of China-Japan Friendship Hospital
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, C., Xu, H. The new strategy for modulating dyslipidemia: Consideration from updated understanding on high-density lipoprotein. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 467–470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0632-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0632-3