Abstract
Objective
To objectively assess the effect of Qiming Granule (芪明颗粒) in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy (DR) by fluorescence fundus angiography (FFA).
Methods
In a multi-center, randomized, parallel controlled clinical trial, patients with DR were randomly assigned to the control group (calcium dobesilate capsule) and the test group (Qiming Granule). Changes in the retinal blood circulation time were recorded by FFA after 3 months of medication.
Results
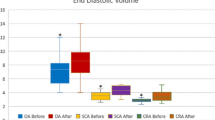
Significant reduction was observed in the retinal arterio-venous circulation time (AVCT) in both groups (P<0.01), the value was 7.635±3.149 s before treatment and 5.165 ±3.382 s after treatment in the treated group, and 7.737±3.413 s and 5.313±3.472 s in the control group respectively. Qiming Granule also reduced the arm-to-retinal circulation time (ARCT, P<0.05). The value was 17.867±3.872 s before treatment and 15.643±4.648 s after treatment in the treated group, and 17.217±3.833 s and 16.312±3.613 s in the control group (P>0.05) respectively. The ARCT in the tested group was reduced, with a statistically significant difference post-medication (P<0.01).
Conclusion
As a Chinese medicine complex prescription, Qiming Granule may alleviate retinal hypoxia and ischemia by increasing retinal blood flow and improving the blood circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan JG, Liao PZ, Wu L, Li YM, Yu YG, Qiu B, et al. Randomized controlled double-blind multicentric clinical trail on non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy treated by Qiming Granule. J Chengdu Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;29(2):1–5.
World Health Organization. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva: Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance; 1999.
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL 3rd, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003;110:1677–1682.
Zhang CF, Zhang HR. Diabetic eye complications and treatment. 1st ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2003:8.
She HN, Xu QY. Changes in the blood rheology of patients with diabetic retinopathy. Recent Adv Ophthalmol (Chin) 1999;19:258–259.
Brunet J, Farine JC, Garay RP, Hannaert P. Angioprotective action of calcium dobesilate against reactive oxygen species-induced capillary permeability in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 1998;358:213–220.
Leite EB, Mota MC, Abreu JR, Cunha-Vaz JG. Effect of calcium dobesilate on the blood-retinal barrier in early diabetic retinopathy. Int Ophthalmol1990;14:81–88.
Li S, Wang B. Treatment combined with Western and Chinese medicine for diabetic retinopathy in 38 cases. Chin J Pract Ophthalmol (Chin) 2006;24:173.
Huang YF. Treatment combined with Western and Chinese medicine for diabetic retinopathy in 70 cases. Sichuan J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2004;22(8);94.
Jin FD. Pharmacological effects of Radix Astragali research and clinical application. J Pract Med Tech (Chin) 2008;15:2702–2704.
Ji ZQ, Gao XX. Experimental study on anti-human platelet aggregation with 63 kinds of regulating lipids Chinese medicine. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1998;17:365–367.
Zhang M, Zheng HY. Effects of puerarin on erythrocyte deformability in brain infarction patient. J Anhui Tradit Chin Med Coll (Chin) 1996;15(5):12.
Liu AQ, Liao PZ, Zheng YL, Duan JG. Effect of Qiming Granule on antioxidatizing reaction in the retinal tissue of diabetic rats. J Tradit Chin Ophthalmol (Chin) 2003;13(3):128–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Programme for the 10th Five-year Plan (No. 2001BA701A13a)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Xx., Duan, Jg., Liao, Pz. et al. Effect of Qiming Granule (芪明颗粒) on retinal blood circulation of diabetic retinopathy: A multicenter clinical trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 15, 384–388 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0384-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0384-5