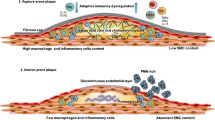
Abstract
The inflammation factors and roles of them in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were explored. The similarity between the theory of pathogenic toxin in Chinese Medicine and the inflammation response theory in ACS was discussed. The exploration of new inflammatory factors may be helpful for Chinese Medicine in the research of ACS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross R. Atherosclerosis an inflammatory disisase. N Engl J Med 1999;340:115–126.
Yang SL, He ZY. The significance of inflammation in acute coronary syndrome. Chin J Critl Care Med (Chin) 2004;24:130–132.
Madjid M, Willerson JT, Casscells SW. Intracoronary thermography for detection of high-risk vulnerable plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 47(8 Suppl):C80–5.
Nin XX, Sun SR. Infection, inflammation and atherosclerosis. Forei Med·Geriat Sci (Chin) 2000;21:173–175.
Go YM, Halvey PJ, Hansen JM, Reed M, Pohl J, Jones DP. Reactive aldehyde modification of thioredoxin-1 activates early steps of inflammation and cell adhesion. Am J Pathol 2007;171:1670–1681.
Van Haelst PL, Tervaert JW, Bijzet J, Baljé-Volkers C, May JF, Langeveld B, et al. Circulating monocytes in patients with acute coronary syndromes lack sufficient interleukin-10 production after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Clin Exp Immunol 2004;138:364–368.
Xie W, Shao N, Ma X, Ling B, Wei Y, Ding Q,et al. Bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide induces up-regulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in rat liver and lungs. Life Sci 2006;79:1820–1827.
Meisinger C, Baumert J, Khuseyinova N, Loewel H, Koenig W. Plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein, a strong predictor for acute coronary heart disease events in apparently healthy, middle-aged men from the general population. Circulation 2005;112:651–657.
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Stampfer JM, Hennekens CH. Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 2000;101:1767–1772.
Bansal S, Ridker PM. Comparison of characteristics of future myocardial infarctions in women with baseline high versus baseline low levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Am J Cardiol 2007;99:1500–1503.
Horne BD, Camp NJ, Carlquist JF, Muhlestein JB, Kolek MJ, Nicholas ZP, et al. Multiple-polymorphism associations of 7 matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase genes with myocardial infarction and angiographic coronary artery disease. Am Heart J 2007;154:718–724.
Yang AL, Jen CJ, Chen HI. Effects of high-cholesterol diet and parallel exercise training on the vascular function of rabbit aortas: a time course study. J Appl Physiol 2003;95:1194–1200.
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Masella M, Marfella R, et al. Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003;289:1799–1804.
Kop WJ, Weissman NJ, Zhu J, Bonsall RW, Doyle M, Stretch MR, et al. Effects of acute mental stress and exercise on inflammatory markers in patients with coronary artery disease and healthy controls. Am J Cardiol 2008;101:767–773.
Gochman E, Reznick AZ, Avizohar O, Ben-Amotz A, Levy Y, et al. Exhaustive exercise modifies oxidative stress in smoking subjects. Am J Med Sci 2007;333:346–353.
Martino F, Pignatelli P, Martino E, Morrone F, Carnevale R, Di Santo S, et al. Early increase of oxidative stress and soluble CD40L in children with hypercholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:1974–1981.
Fuchs D, Vafeiadou K, Hall WL, Daniel H, Williams CM, Schroot JH, et al. Proteomic biomarkers of peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from postmenopausal women undergoing an intervention with soy isoflavones. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;86:1369–1375.
Kodama Y, Kitta Y, Nakamura T, Takano H, Umetani K, Fujioka D, et al. Atorvastatin increases plasma soluble Fmslike tyrosine kinase-1 and decreases vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor in association with improvement of ventricular function in acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:43–50.
Diao JL, Pang GZ, Tong QG, Ma ZM. Effects of suspending statins on the inflammation factors of acute coronary syndrome. J Clin Inter Med (Chin) 2007;24: 700–702.
Solheim S, Arnesen H, Eikvar L, Hurlen M, Seljeflot I. Influence of aspirin on inflammatory markers in patients after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 2003;92:843–845.
Gurbel PA, Bliden KP, Tantry US. Effect of clopidogrel with and without eptifibatide on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and C-reactive protein release after elective stenting: results from the CLEAR PLATELETS 1b study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:2186–2891.
Chen YG, Xu F, Zhang Y, Ji QS, Sun Y, Lu RJ, et al. Effect of aspirin plus clopidogrel on inflammatory markers in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Chin Med J 2006;119:32–36.
Jia FP, Lei H. Inflammation, immune response and acute coronary syndrome. Forei Med Sci (Chin) 2004;31:13–15.
Richard A, Jeffrey SB, David LB. Effects of antibiotic therapy on outcomes of patients with coronary artery disease. JAMA 2005;293:2641–2647.
Fukushima S, Coppen SR, Varela-Carver A, Yamahara K, Sarathchandra P, Smolenski RT, et al. A novel strategy for myocardial protection by combined antibody therapy inhibiting both P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 via retrograde intracoronary route. Circulation 2006;114:251–256.
Hanefeld M, Marx N, Pfützner A, Baurecht W, Lübben G, Karagiannis E, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of pioglitazone and/or simvastatin in high cardiovascular risk patients with elevated high sensitivity C-reactive protein: the PIOSTAT Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:290–297.
Haim M, Benderly M, Tanne Detc, Matas Z, Boyko V, Fisman EZ, et al. C-reactive protein, bezafibrate, and recurrent coronary events in patients with chronic coronary heart disease. Am Heart J 2007;154:1095–1101.
Smit JJ, Ottervanger JP, Slingerland RJ, Kolkman JJ, Suryapranata H, Hoorntje JC, et al. Comparison of usefulness of C-reactive protein versus white blood cell count to predict outcome after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 2008;101:446–451.
Morrow DA, Braunwald E. Future of biomarkers in acute coronary syndromes: moving toward a multimarker strategy. Circulation 2003;108: 275–281.
Morrow DA, deLemos JA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Demopoulos LA, DiBattiste PM, et al. Evaluation of B-type natriuretic peptide for risk assessment in unstable angina /non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis in TACTICS-TIMI18. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:1264–1272.
Otake H, Shite J, Shinke T, Watanabe S, Tanino Y, Ogasawara D, et al. Relation between plasma adiponectin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and coronary plaque components in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol 2008;101:1–7.
Foussas SG, Zairis MN, Makrygiannis SS, Manousakis SJ, Anastassiadis FA, Apostolatos CS, et al. The significance of circulating levels of both cardiac troponin I and high-sensitivity C reactive protein for the prediction of intravenous thrombolysis outcome in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Heart 2007;93:952–956.
Tello-Montoliu A, Marín F, Roldán V, Mainar L, López MT, Sogorb F, et al. A multimarker risk stratification approach to non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: implications of troponin T, CRP, NT pro-BNP and fibrin D-dimer levels. J Intern Med 2007;262:651–658.
Di Serio F, Amodio G, Ruggieri E, De Sario R, Varraso L, Antonelli G, et al. Proteomic approach to the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome: preliminary results. Clin Chim Acta 2005;357:226–235.
Mateos-Cáceres PJ, García-Méndez A, López Farré A, Macaya C, Núñez A, Gómez J, et al. Proteomic analysis of plasma from patients during an acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 44:1578–1583.
Yi ZG, Wang Q, Zhang SQ. Associated studies between Chinese syndromes of acute coronary syndrome and IL-18, Hs-CRP. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;39(12): 22–23.
Huang YS, Mo HH, Hong YD, Wu H. Heat-clearing and Toxicity-removing Therapy for the Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome: An Observation of 55 Cases. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med 2006;23: 13–16.
Geng LM, Chen FQ. Influence of Jiedu Huoxue Pills on prognosis and levels of CRP and Fig in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Beijing Uni Tradi Chin Med (Clinical Med)(Chin) 2007;14(3): 14–16.
Ge L, Chen XY, Hu YB. Effects of Yiqihuoxuejiedu Decoction on C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor and serum lipid in experimental rabbits with atherosclerosis. Chin J Tradit West Crit Car (Chin) 2007;14:306–308.
Wu H, Liu YD, Wu W, Dong YG, Huang YS. Effects of clearing heat and detoxifying method on Chlamydia pneumonia infection caused atherosclerosis in rabbits. J Guangzhou Uni Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;23:151–155.
Zhang JC, Chen KJ, Zheng GJ, Zhang WG, Shi DZ, Yin HJ, et al. Regulatory effect of Chinese herbal compound fur detoxifying and activating circulation expression of NF-κB and MMP-9 in aorta of apolipoprotein E gene knocked-out mice. Chin J Integr Med (Chin) 2007;21:40–44.
Zhang JC, Chen KJ Liu JG, Zhang WG, Shi DZ, Liu LT, et al. Effect of assorted use of Chinese drugs for detoxifying and activating blood circulation on serum high sensitive C-reactive protein in apolipoprotein E gene knock-out mice. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2008;28:330–333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Foundation of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 0405JP64) and the National Key Basic Research Development Program (973) (No. 2006CB504803)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Zhang, Jc. & Xi, Rx. Clinical significance of inflammation factors in acute coronary syndrome from pathogenic toxin. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 15, 307–312 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0307-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0307-5