Abstract
Objective
To study the principle of clearing Fei (肺), cooling blood, and detoxification as well as nourishing yin and moisening Fei (abbr. as CCD-NM) in regulating the levels of peripheral T-lymphocyte subsets Th and Tc cells to explore its mechanism for lowering the incidence of infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods
Sixty SLE patients without complicated infection were assigned to the treatment group and the control group, 30 in each group. The control group was treated with Western medicine alone, while the treatment group was treated with the same program of Western medicine, but additionally administered with either Langchuang No.1 (狼疮I号) or 2 (狼疮II号), serial concerted Chinese recipes, applied respectively in patients in the active stage or in the resting stage. The total time of treatment for both groups was 1 year. Further, a healthy control group was set up with 20 healthy subjects. The expressions of Th1, Th2, and Tc1 and Tc2 cells in peripheral blood were detected and compared with those in the healthy control group.
Results
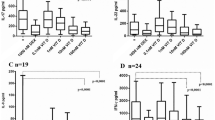
(1) As compared with the healthy control group, ratios of Th1/Th2 and Tc1/Tc2 in SLE patients, whether complicated with infection or not, were significantly lower (P<0.05 or P<0.01). (2) Comparison between patients with complications and those uncomplicated with infection showed that the two ratios and Th1 expression were lower and Tc2 was higher in the former than those in the latter (all P<0.05). (3) Ratios of Th1/Th2 and Tc1/Tc2 increased after treatment in patients of both the treatment group and the control group (P<0.05 and P<0.01), but the changes in the treatment group were more significant (P<0.05).
Conclusion
The principle of CCD-NM could regulate the Th and Tc subsets toward equilibrium in SLE patients, which might be one of the mechanisms of action for alleviating complicated infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 1. 5-year period. A multicenter prospective study of 1000 patients. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1999;78:167–175.
Mok CC, Lee KW, Ho CT, et al. A prospective study of survival and prognostic indicators of systemic lupus erythematosus in a southern Chinese population. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000;39(4):399–406.
Tao XJ, Zheng HX, Yu JN, et al. Clinical research on effect of TCM treatment beginning with Fei in treating systemic lupus erythematosus for reducing incidence of complicated infection. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2007;27(1):33–36.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Arthritis Rheum 1982;25:1271–1277.
Hay E, Cordon C, Emery P, et al. Assessment of lupus. Where are we now? Ann Rheum Dis 1993;52:169–172.
Varadhachary AS, Peter ME, Perdow SN, et al. Seletive up-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase activity in Th2 cells inhibits caspase-8 cleavage at the death-inducing complex: a mechanism for Th2 resistance from Fasmediated apoptosis. J Immunol 1999;163:4772–4779.
Li ZJ, Wang CL, Fan XY, et al. Clinical study on the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus complicated by infections. Chin J Rheumatol (Chin) 2000;4(3):165–168.
Xu G, Liu ML, Yu KM. A prospective study of nosocomial infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chin J Rheumatol (Chin) 2003;7(4):216–219.
Xu G, Xu Q, Yu LM. An analysis of nosocomial infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chin J Nosocomiol (Chin) 2000;10(5):362–364.
Yu Y, Chen J, Xie FA, et al. Clinical investigation of nosocomial infection cases with lupus nephritis. Chin J Nosocomiol (Chin) 2000;10(3):174–176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Funds of Hangzhou Municipal Medical Key Subjects (No. 2005633Q14)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Xj., Zheng, Hx., Yu, Jn. et al. Regulatory effect of Langchuang serial recipes on T-lymphocyte subsets Th and Tc in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 14, 180–184 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-008-0180-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-008-0180-7