Abstract
Objective
To identify cancer distribution and treatment requirements, a questionnaire on cancer patients was conducted. It was our objective to validate a series of symptoms commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Methods
The M. D. Anderson Symptom Assessment Inventory (MDASI) was used with 10 more TCM items added. Questions regarding TCM application requested in cancer care were also asked. A multi-center, cross-sectional study was conducted in 340 patients from 4 hospitals in Beijing and Dalian. SPSS and Excel software were adopted for statistical analysis. The questionnaire was self-evaluated with the Cronbach’s alpha score.
Results
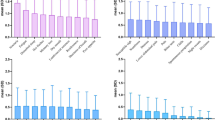
The most common symptoms were fatigue 89.4%, sleep disturbance 74.4%, dry mouth 72.9%, poor appetite 72.9%, and difficulty remembering 71.2%. These symptoms affected work (89.8%), mood (82.6%), and activity (76.8%), resulting in poor quality of life. Eighty percent of the patients wanted to regulate the body with TCM. Almost 100% of the patients were interested in acquiring knowledge regarding the integrated traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine (WM) in the treatment and rehabilitation of cancer. Cronbach’s alpha score indicated that there was acceptable internal consistency within both the MDASI and TCM items, 0.86 for MDASI, 0.78 for TCM, and 0.90 for MDASITCM (23 items).
Conclusions
Fatigue, sleep disturbance, dry mouth, poor appetite, and difficulty remembering are the most common symptoms in cancer patients. These greatly affect the quality of life for these patients. Patients expressed a strong desire for TCM holistic regulation. The MDASI and its TCM-adapted model could be a critical tool for the quantitative study of TCM symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curt G, Bteitbart W, Cella D, et al. Impart of cancer related fatigue on the lives of patients new fi ndings from the fatigue coalition. Oncologist 2005;5:353–360.
Barnes EA, Bruera E. Fatigue in patients with advanced cancer: A review. Intl J Gynecol Cancer 2002;12:424–428.
Zhang LS, Ma K. Investigation on effect of pain on quality of life of cancer patients. Med Pharm Yunnan 2002;23(6):46.
Zhang LS, Liu XL. Modern algesiology. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Scientific and Technological Publishing House, 1999:167–169.
Wang XS, Wang Y, Guo H, et al. Chinese version of the M. D. Anderson Symptom Inventory. Cancer 2004;101:1890–1901.
Cleeland CS, Mendoza TR, Wang XS, et al. Assessing symptom distress in cancer patients. Cancer 2000;89:1634–1646.
Yun YH, Mendoza TR, Heo DS, et al. Development of a cancer pain assessment tool in Korea: a validation study of a Korean version of the brief pain inventory. Oncology 2004;66:439–444.
Yan L, Jiang YQ, Wang Y. Symptom of 249 patients with cancer: a investigation among patients and nurses. Chin J Nursing 2005;40(4): 283–285.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Key Subject Program of Beijing Administration of TCM (No. 2004-061)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Wang, X.S. & Li, Pp. Investigation of common symptoms of cancer and reliability analysis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 13, 195–199 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-007-0195-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-007-0195-5