Abstract
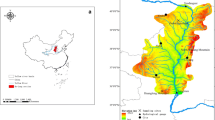
Sediment discharge from the Yellow River originates mainly from the drainage area between Hekouzhen and Longmen, i.e., the Helong area. Spatial-temporal variations of the vegetation cover in this area during the 1981–2007 period have been investigated using GIMMS and SPOT VGT NDVI data. We have also analyzed the interannual variations in vegetation cover and changes in annual runoff and sediment discharge, the consequences from precipitation change and the Grain for Green Project (GGP). The results show that vegetation cover of the Helong area has increased during the 1981–2007 period. The northwestern part the Helong area, where the flat sandy lands are covered by grass, has experienced the largest increase. The region where the vegetation cover has declined is largely found in the southern and southeastern Helong area, which is a gullied hilly area or forested. Although precipitation was relatively low during the 1999–2007 period, the vegetation cover showed a significant increase in the Helong area, due to the implementation of the GGP. During this period, the most significant improvement in the vegetation cover occurred mainly in the gullied hilly areas of the Loess Plateau, such as the drainage basins of the Kuyehe and Tuweihe rivers and the middle and lower reaches of the Wudinghe and Yanhe rivers. A comparison of the average annual maximum NDVI between the earlier (1998–2002) stage and the next five years (2003–2007) of the GGP indicates that the areas with increases of 10% and 20% in NDVI account for 72.5% and 36.4% of the total area, respectively. Interannual variation of annual runoff and sediment discharge shows a declining trend, especially since the 1980s, when the decrease became very obvious. Compared with the 1950–1969 period, the average runoff during the 1980–2007 period was reduced by 34.8×108 m3 and the sediment discharge by 6.4×108 t, accounting for 49.4% and 64.9% of that in the 1950–1969 period, respectively. There is a positive correlation between the annual maximum NDVI and annual runoff and sediment discharge. This correlation was reversed since the implementation of the GGP in 1999 and vegetation cover in the Helong area has increased, associated with the decrease in runoff and sediment discharge. Less precipitation has been an important factor driving the decrease in runoff and sediment discharge during 1999–2007. However, restoration and improvement of the vegetation cover may also have played a significant role in accelerating the decrease in annual runoff and sediment discharge by enhancing evapotranspiration and alleviating soil erosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bochet E, Rubio J L, Poesen J. 1998. Relative efficiency of three representative matorral species in reducing water erosion at the microscale in a semi-arid climate (Valencia, Spain). Geomorphology, 23: 139–150
Calder I R, Hall R L, Bastable H G, H M Gunston, O Shela, A Chirwa, R Kafundu. 1995. The impact of land use change on water resources in sub-Saharan Africa: a modelling study of Lake Malawi. J Hydrol, 170: 123–135
Cammeraat L H, Imeson A C. 1999. The evolution and significance of soil-vegetation patterns following land abandonment and fire in Spain. Catena, 37: 107–127
Casermeiro M A, Molina J A, de la Cruz Caravaca, Costa J H, Hernando Massanet M I, Moreno P S. 2004. Influence of scrubs on runoff and sediment loss in soils of Mediterranean climate. Catena, 57: 91–107
Castro N M D R, Auzet A-V, Chevallier P, Leprun J-C. 1999. Land use change effects on runoff and erosion from plot to catchment scale on the basaltic plateau of Southern Brazil. Hydrol Process, 13: 1621–1628
Chen H, Zhou J X, Cai Q G, Lu Z, Li Z. 2005. Thresholds of geographic environmental elements in sediment yield of drainage basins. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci, 48(2) 230–240
Chen L D, Wei W, Fu B J, Lu Y. 2007. Soil and water conservation on the Loess Plateau in China: review and perspective. Prog Phys Geog, 31(4): 389–403
Dagnachew, Legesse, Vallet-Coulomb C, Gasse F. 2003. Hydrological response of a catchment to climate and land use changes in Tropical Africa: case study South Central Ethiopia. J Hydrol, 275: 67–85
Dai S B, Yang S L, Li M. 2009. The sharp decrease in suspended sediment supply from China’s rivers to the sea: anthropogenic and natural causes. Hydrolog Sci J, 54(1): 135–146
Descheemaeker K, Nyssen J, Poesen J, Raes D, Haile M, Muys B, Deckers S. 2006. Runoff on slopes with restoring vegetation: A case study from the Tigray highlands, Ethiopia. J Hydrol, 331: 219–241
Descroix L, Viramontes D, Vauclin M. 2001. Influence of soil surface features and vegetation on runoff and erosion in the Western Sierra Madre (Durango, Northwest Mexico). Catena, 43: 115–135
Dunjo G, Pardini G, Gispert M. 2003. Land use change effects on abandoned terraced soils in a Mediterranean catchment, NE Spain. Catena, 52: 23–37
Fang J Y, Piao S L, He J S, Fang J Y, Piao S L, He J S, Ma W H, 2003. Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity in China in the past 20 years in China. Sci China Ser C, 33(6): 554–565
Fu G, Charles S P, Viney N R, Chen S, Wu J Q. 2007. Impacts of climate variability on stream-flow in the Yellow River. Hydrol Process, 21(25): 3431–3439
Gyssels G, Poesen J, Bochet E, Li Y. 2005. Impact of plant roots on the resistance of soils to erosion by water: a review. Prog Phys Geog, 29: 198–217
Holben B N. 1986. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int J Remote Sens, 7: 1417–1434
Huang M, Zhang L. 2004. Hydrological responses to conservation practices in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol Process, 18: 1885–1898
Hydrology and Water Resources Bureau of Middle Yellow River (YRCC). 2005. Hydrology of the middle Yellow River from Hekouzhen to Longmen. Zhengzhou: Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, pp. 1
Kang L L, Wang C G, Zhang Y L, Kang L L, Wang C G, Zhang Y L, Chen J N. 2004. Precipitation variations in the Middle Yellow River in the Last 50 years and its influence on the flow. Yellow River, 26(8): 26–28 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kang S, Zhang L, Song X, Zhang S, Liu X, Liang Y, Zheng S. 2001. Runoff and sediment loss responses to rainfall and land use in two agricultural catchments on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol Process, 15: 977–988
Kosmas C, Danalatos N G, Gerontidis St. 2000. The effect of land parameters on vegetation performance and degree of erosion under Mediterranean conditions. Catena, 40: 3–17
Kosmas D, Danalatos N, Cammeraat L H, Chabart M. 1997. The effect of land use on runoff and soil erosion rates under Mediterranean conditions. Catena, 29: 45–59
Li Z F, Li X M, Cai Y L, Li Z F, Li X M, Cai Y L, Wang Y.2007. Study of land cover change in Yulin district based on Spot Vegetation. J Arid Land Resour Environ, 21(2): 56–59 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liang S H, Chen J, Jin X M, Wang L, Gong B. 2007. Regularity of vegetation coverage changes in the Tibetan Plateau over the last 21 years. Adv Earth Sci, 22(1): 33–40 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ludwig J A, Wilcox B P, Breshears D D, Tongway D J, Imeson A C. 2005. Vegetation patches and runoff-erosion as interacting ecohydrological processes in semiarid landscapes. Ecology, 86: 288–297
Ma M G, Dong L X, Wang X M. 2003.Study on the dynamically monitoring and simulating the vegetation cover in northwest China in the past 21 years. J Glaciol Geocryol, 25(2): 232–236
Mapa R B. 1995. Effect of reforestation using Tectona grandis on infiltration and soil water retention. Forest Ecol Manage, 77: 119–125
McVicar T R, Li L T, Van Niel T G, Hutchinson M F, Li L T. 2007. Developing a decision support tool for China’s re-vegetation program: Simulating regional impacts of afforestation on average annual streamflow in the Loess Plateau. Forest Ecol Manage, 251: 65–81
Moreno-de M, Merino-Martín L, Nicolau J M. 2009. Effect of vegetation cover on the hydrology of reclaimed mining soils under Mediterranean-Continental climate. Catena, 77(1): 39–47
Morgan R P C. 1995. Soil erosion and conservation. Harlow: Longman
Mu X M, Ba S C L, Zhang L, Gao P, Wang F. 2007. Impact of soil conservation measures on runoff and sediment in Hekou-Longmen region of the Yellow River. J Sediment Res, 2: 36–41
Myneni R B, Keeling C D, Tucker C J, Asrar G, Nemani R R. 1997. Increased plant growth in the Northern high latitudes from 1981–1999. Nature, 386: 698–702
Herron N, Davis R, Jones R. 2002. The effects of large-scale afforestation and climate change on water allocation in the Macquarie River catchment, NSW, Australia. J Environ Manage, 65: 369–381.
Pinzon J. 2002. Using HHT to successfully uncouple seasonal and interannual components in remotely sensed data. Conference Proceedings Jul 14–18. Orlando, Florida, 287–292
Ran D C, Liu L W, Zhao L Y, Bai Z G, Liu B, Wang H. 2000. Soil and Water Conservation and Runoff and Sediment Variation in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River. Zhengzhou: Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 124–137
Shi F C. 2006. Reasons for variations of rainfall-runoff relationship of Hekouzhen-Longmen reach. Yellow River, 28(4): 24–25 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song Y, Ma M G. 2007. Study on vegetation cover change in northeast China based on SPOT vegetation data. Deserts China, 27(1): 89–94 (in Chinese with English abstract)
State Forestry Administration (SFA). Forestry and ecological construction bulletin of China, 2008 (official document)
Sun G, Zuo C Q, Liu S Y, M L Liu, McNulty S G, Vose J M. 2008. Watershed evapotranspiration increased due to changes in vegetation composition and structure under a subtropical climate. J Am Water Resour Assoc, 44(5): 1164–1175
Sun G, Zhou G Y, Zhang Z Q, Wei X, McNulty S G, Vose J M. 2006. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J Hydrol, 328: 548–558
Trimble S W. 1990. Geomorphic effects of vegetation cover and management: some time and space considerations in prediction of erosion and sediment yield. In: Thornes J B ed. Vegetation and Erosion Processes and Environments. John Wiley and Sons
Tucker C J, Pinzon J E, Brown M E, Slayback D A, Pak E W, Mahoney R, Vermote E F, Saleous N E. 2005. An Extended AVHRR 8 — km NDVI Data Set Compatible with MODIS and SPOT Vegetation NDVI Data. Int J Remote Sens, 26(20): 4485–4498
Tucker C J, Vanpra et C L, Sharman M J, Van Ittersum G. 1985. Satellite remote sensing of total herbaceous biomass production in the Senegalese Sahel: 1980–1984. Remote Sens Environ, 17: 233–249
Vacca A, Loddo S, Ollesch G, Puddu R, Serra G, Tomasi D, Aru A. 2000. Measurement of runoff and soil erosion in three areas under different land use in Sardinia (Italy). Catena, 40: 69–92
Vallauri D, Aronson J, Dudley N, Vallejo R. 2005. Monitoring and evaluating forest restoration success. In: Mansourian S, Vallauri D, Dudley N eds. Forest Restoration in Landscapes: Beyond Planting Trees. New York: Springer (in Cooperation with WWF), pp. 150–156
Wang H, Yang A M, Zhou Z H, Yang D H. 2005. Studies on effect of soil and water conservation on hydrology and water resources based on distributed hydrological model. Sci Soil Water Conserv, 3(4): 6–10 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang S J. 2007. Comparison of sediment and runoff yield processes between different geomorphic regions in the Wudinghe River Basin. Geogr Res, 26(3): 508–517 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y H, Yu P T, Xiong W, Z X Shen, Guo M C, Shi Z J, Du A P, Wang L M. 2008. Water yield reduction after afforestation and related process in the semiarid Liupan Mountains, Northwest China. J Am Water Resour Assoc, 44(5): 1086–1097
Wang S Y, Huang Y J, Chen Z X. 2005. Remote sensing study of returning farmland to forest or grassland in the Yellow River Basin. J Tsinghua Univ Sci Tech, 45(3): 306–309
Wei H B, Li R, Yang Q K. 2002. Research advances of vegetation effect on soil and Water Conservation. Acta Phytoecol Sin, 26(4): 489–496 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei J J, Li X P, Yang Q K, Liang W. 2007. Land use changes based on CBERS Data in lower reaches of Yanhe River in the Loess Plateau of China. Bull Soil Water Conserv, 27(2): 87–90 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu B F, Li M M, Yang C Z, et al. 2005. Environment monitoring over 1997–2002 with remote sensing in national environmental project sites. J Remote Sens, 9(1): 32–38 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xin Z B, Xu J X. 2007. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation cover and its response to climate change. Progress Nat Sci, 17(6): 770–778
Xin Z B, Xu J X, Ma Y X. 2009. Spatiotemporal variation of erosive rainfall in Chinese Loess Plateau in the period 1956–2005. Sci Geogr Sin, 29(1): 98–104 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xin Z B, Xu J X, Zheng W. 2008. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover on the Chinese Loess Plateau (1981–2006): Impacts of climate changes and human activities. Sci China Ser D, 51(1): 67–78
Xu J X. 2005. Precipitation-vegetation coupling and its influence on erosion on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena, 64: 103–116
Xu J X. 2004. Temporal variation of river flow renewability in the middle Yellow River and the influencing factors. Progress Nat Sci, 14(7): 787–791
Xu J X, Ma Y X. 2009. Response of the hydrological regime of the Yellow River to the changing monsoon intensity and human activity. Hydrol Sci J, 54(1): 90–100
Xu X K, Chen H, Zhang F. 2007. Temporal and spatial change of vegetation cover in the northwest of China and factors analysis influencing on vegetations variation. Environ Sci ence, 28(1): 41–47 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu Z G, Bennett M T, Tao R, Xu J T. 2004. China’s sloping land conversion programme four year on: current situation and pending issues. Int Forest Rev, 6: 317–326
Yang T, Zhang Q, Chen Y D, Tao X, Xu C Y, Chen X. 2008. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration caused by dam construction in the middle and lower Yellow River, China. Hydrol Process, 22(18): 3829–3843
Zhang X P, Zhang L, McVicar T R, Van Niel T G, Li L T, Li R, Yang Q K, Wei L. 2008. Modeling the impact of afforestation on average annual streamflow in the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol Process, 22(12): 1996–2004
Zhang B, Yang Y, Zepp H. 2004. Effect of vegetation restoration on soil and water erosion and nutrient losses of a severely eroded clayey Plinthudult in southeastern China. Catena, 57: 77–90
Zhang L, Dawes W, Walker G R. 2001. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour Res, 37(3): 701–708
Zhou G Y, Morris J D, Yan J H, Yu Z Y, Peng S L. 2002. Hydrological impacts of reafforestation with eucalypts and indigenous species: a case study in southern China. Forest Ecol Manage, 167: 209–222
Zhou L, Kaufmann R K, Tian Y, Myneni R B, Tucker C J. 2003. Relation between interannual variations in satellite measures of northern forest greenness and climate between 1982 and 1999. J Geophys Res, 108(1): 1029–2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Zb., Yu, Xx. Impact of vegetation restoration on hydrological processes in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, China. For. Stud. China 11, 209–218 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-009-0037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-009-0037-y