Abstract
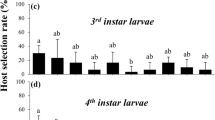
The Asian longhorned beetle (ALB), Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky) is a polyphagous woodborer of hardwood trees. In order to well understand the oviposition preference of A. glabripennis emerging from different larval host tree species, we selected five common host tree species in the field and evaluated its oviposition preferences. The five host tree species are Acer negundo (AN), Salix matsudana f. lobato-glandulosa (SM), Populus nigra L. var. thevestina (Dode) Bean (PN), P. simonii × P. pyramidalis cv. Opera 8277 (PS) and P. alba var. pyramidalis (PA). Results show that adult beetles emerging from these five tree species almost have the same oviposition phenomenon. All adult beetles, except those emerging from PS, chewed the highest potential sites and laid most eggs on AN trees. Adult beetles emerging from AN, PN, PS and PA did not chew any sites nor laid any eggs on PA trees. These results showed that adult A. glabripennis emerging from the five host tree species did not show any clear oviposition preference for their larval host tree species in the field but they did present the most obvious preference for AN and the lowest preference for PA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haack R A, Law K R, Mastro V C, Ossenbruggen H S, Ram B. J. 1997. New York’s battle with the Asian long-horned beetle. J For, 95(12): 11–15
Haack R A. 2003. Research on Anoplophora glabripennis in the United States. Nachrichtenbl Deut Pflanzenschutzd, 55: 68–70
Haack, R. A. 2006. Exotic bark-and wood-boring Coleoptera in the United States: recent establishments and interceptions. Can J For Res, 36: 269–288
Hanks L M. 1999. Influence of the larval host plant on reproductive strategies of cerambycid beetles. Ann Rev Entomol, 44: 483–505
Keena M A. 2002. Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) fecundity and longevity under laboratory conditions: comparison of population from New York Illinois on Acer saccharum. J Environ Entomol, 31: 490–498
Keena M A. 2005. Pourable artifical diet for rearing Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and method to optimize larval survival and synchronize development. Ann Entomol Soc Am, 98: 536–547
Keena M A. 2006. Effects of temperature on Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) adult survival, reproduction and egg hatch. J Environ Entomol, 35(4): 912–921
Lingafelter S W, Hoebeke E R. 2002. Reversion Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Washington DC: Entomological Society of Washington, DC
Ludwig S W, Lazrarus L, McCullough D G, Hoover K, Montero S, Sellmer, J C. 2002. Methods to evaluate host tree suitability to the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis. J Environ Hort, 20: 175–180
Luo Y Q, Huang J F, Li J G. 1999. Strategy on applied technology and basic studies of Poplar Longhorn Beetle management. J Beijing For Univ, 21(4): 6–12 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Luo Y Q, Liu R S, Xu Z C, Sun C C, Wen J B. 2002. Theories and technologies of ecologically regulating poplar longhorned beetle disaster in shelter forest. J Beijing For Univ, 24(5/6): 160–164 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Luo Y Q, Wen J B, Xu Z C. 2003. Current situation of research and control on poplar longhorned beetle, especially for Anoplophora glabripennis in China. Nachrichtenbl Deut Pflanzenschuzd, 55: 66–67
Morewood W D, Hoover K, Neiner P R, McNeil J C. 2004. Host tree resistance against the polyphagous wood-boring beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis. Entomol Exp Appl, 110: 79–86
Morewood W D, Neiner P R, McNeil J C, Hoover K. 2003. Oviposition preference and larval performance of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in four eastern North America hardwood tree species. Environ Entoml, 32: 1,028–1,034
Nowak D J, Pasek J E, Sequerira R A, Crane D E, Mastro V C. 2001. Potential effect of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) on urban trees in United Stated. J Econ Entomol, 94: 116–122
Papaj D R, Prokopy R J. 1989. Ecological and evolutionary aspects of learning in phytophagous insects. Ann Rev Entomol, 65: 65–89
Poland T M, Hack R A, Miller D L, Bauer L S. 2006a. Laboratory evaluation of the toxicity of systemic insecticides for control of Anoplophora glabripennis and Plectrodera scalator (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J Econ Entomol, 99(1): 85–93
Poland T M, Hack R A, Petrice T R, Millerand D L, Gao R T. 2006b. Field evaluations of systemic insecticides for control of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in China. J Econ Entomol, 99(1): 383–392
Singer M C, Thomas C D, Billinton H L, Parmesan C. 1989. Variation among conspecific insect population on the mechanistic basis of diet breadth. J Anim Behav, 37: 751–759
Smith M T, Bancroft J, Torpp J. 2002. Age-specific fecundity of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) on three tree species infested in the United States. J Environ Entomol, 31: 76–83
Smith M T, Tobin P C, Bancroft J, Li G, Gao R T. 2004. Dispersal and spatiotemporal daynamics of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in the China. Environ Entomol, 33: 435–442
Thompson J N, Pellmyr O. 1991. Evolutionof oviposition behaviour and host preference in Lepidoptera. Ann Rev Entomol, 65: 65–89
Thompson J N. 1998. The evolution of diet breadth: monophagy and polyphagy in swallowtail butterflies. J Evol Biol, 11: 563–578
Williams D W, Lee H P, Kim I K. 2004. Distribution and abundance of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in natural Acer stands in South Korea. J Environ Entomol, 33: 540–545
Xiao G R. 1992. Forest Insets of China. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House (in Chinese)
Zhang A J, Oliver J E, Aldrich J R, Wang B D, Mastro V C. 2002. Stimulatory beetle volatiles for the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky). Z Naturforsch, 57c: 553–558
Zhang A, Oliver J E, Chuhan K, Zhao B, Xia L, Xu Z. 2003. Evidence for contact sex recognition pheromone of the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Naturwissenschaften, 90: 410–413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Xf., Li, Xj., Luo, Yq. et al. Oviposition preference of Anoplophora glabripennis emerging from five host tree species under field conditions. For. Stud. China 10, 23–26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0013-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0013-y