Abstract
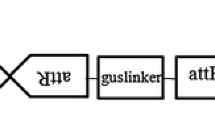
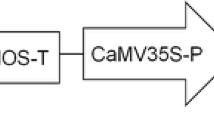
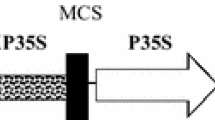
To develop a transformation protocol of Rosa hybrida ‘Samantha’ via Agrobacterium tumefaciens, the authors examined the effect of different factors on T-DNA transfer by measuring transient expression levels of an intron-containing β-glucuronidase gene. The results indicate that explant, light condition, salt concentration and acetosyringone (AS) concentration in co-culture medium are the most important factors, and factors like co-culture temperature, co-culture period and bacteria density have a strong effect on the growth of bacteria and then T-DNA transfer. Optimized co-cultivation was performed by inoculation of embryogenic callus with bacteria at a density of OD600=0.5–0.8 for 20 min and co-culture in darkness under 23°C on medium with 1/2 MS salts and 300 µmol·L−1 AS for 3 d.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Becker I, Vogel T, Iqhal J et al. 1994. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Phaseolus vulgaris. Adaption of some conditions. Ann Rep Bean Improv Coop. 37: 127–128
Chiton M D, Currier T C, Farrand S K et al. 1974. Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA and PS8 bacteriophase DNA not detected in crown gall tumors. Proceedings of National Academy Sciences USA. 19: 3 672–3 676
De Clercq J, Zambre M, Van Montagu M et al. 2002. An optimized Agrobacterium-mediated transformation procedure for Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray. Plant Cell Reports. 21: 333–340
Dohm A, Ludwig C, Schilling D et al. 2001. Transformation of roses with genes for antifungal proteins. Acta Horticulturae. 547: 27–34
Dubois L A M, de Vries D P, Koot A. 1997. Genetic variation of rose cultivars for direct shoot organogenesis. Acta Horticulturae. 447: 79–83
Firoozabady E, Moy Y, Courtney-Gutterson N et al. 1994. Regeneration of transgenic rose (Rosa hybrida) plants from embryogenic tissue. Bio/technology. 12: 609–613
Jefferson R A. 1987. Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Reptr. 5: 387–405
Kim C K, Chung J D, Park S H et al. 2004. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Rosa hybrida using the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. 78: 107–111
Kondo T, Hasegawa H, Suzuki M. 2000. Transformation and regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.) by Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer. Plant Cell Reports. 19: 989–993
Li X Q, Krasnyanski S F, Korban S S. 2002. Optimization of the uidA gene transfer into somatic embryos of rose via Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 40: 453–459
Merchant R, Davey M R, Lucas J A et al. 1998. Expression of a chitinase transgene in rose (Rosa hybrida L.) reduces development of black disease (Diplocarpon rosae Wolf). Molecular Breeding. 4: 187–194
Mondal T K, Bhattacharya A, Ahuja P S. 2001. Transgenic tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze cv. Kangra Jat] plants obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Reports. 20: 712–720
Montoro P, Teinseree N, Rattana W. 2000. Effect of exogenous calcium on Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer in Hevea brasiliensis (rubber tree) friable calli. Plant Cell Reports. 19: 851–855
Noriega C, Söndahl M R. 1991. Somatic embryogenesis in hybrida tea roses. Bio/technology. 9: 991–993
Rout G R, Samantaray S, Mottlely J et al. 1999. Biotechnology of the rose: a review of recent progress. Scientia Horticulturae. 81: 201–228
Suzuki S, Nakano M, 2002. Agrobaterium-mediated production of transgenic plants of Muscari armeniacum Leichtl. ex Bak. Plant Cell Reports. 20: 835–841
Tang W, Sederoff R, Whetten R. 2001. Regeneration of transgenic loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) from zygotic embryos transformed with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Planta. 213: 981–989
Turk S C H J, Melehers L S, den Dulk-Ras H et al. 1991. Environmental conditions differentially affect vir gene induction in different Agrobacterium strains. Role of the VirA sensor protein. Plant Molecular Biology. 16: 1 051–1 059
van der Salm T P M, van der Toorn C J G, Bouwer R et al. 1997. Production of Rol gene transformed plants of Rosa hybrida L. and characterization of their rooting ability. Molecular Breeding. 3: 39–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.30170666)]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Bao, M. Optimization of the uidA gene transfer of Rosa hybrida via Agrobacterium tumefaciens: an assessment of factors influencing the efficiency of gene transfer. For. Stud. China 6, 9–14 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-004-0034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-004-0034-0