Abstract
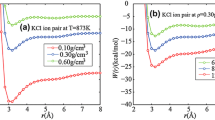
Magmatic-hydrothermal processes play an important role in the transport, enrichment, and mineralization of cesium. In this study, classical molecular dynamics simulations were performed to investigate the properties of Cs-Cl and Cs-F ion pairs in hydrothermal fluids. The association constants (log10KA(m)) under a wide range of temperature (i.e. 298–1273 K) and fluid density (i.e. 0.1–1.0 g/cm3) were derived from the potential of mean force (PMF) curves. The results indicate that Cs-Cl and Cs-F ion pairs have similar stabilities. This is different from other alkali metal cations (e.g., Li+, Na+, and K+), which prefer binding with F over Cl. The stabilities of Cs-Cl and Cs-F ion pairs increase with increasing temperature (except for the fluid density ≤ 0.1 g/cm3) or decreasing fluid density, which is similar to other alkali halide ion pairs. Comparisons among the stabilities of Cs-Cl/F and other alkali halide ion pairs indicate that the Li–F ion pair has the highest stability in hydrothermal fluids.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MP, Tildesley D (2017) Computer simulation of liquids (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press
Andersen HC (1983) Rattle: a “velocity” version of the shake algorithm for molecular dynamics calculations. J Comput Phys 52(1):24–34
Berendsen HJC, Grigera JR, Straatsma TP (1987) The missing term in effective pair potentials. J Phys Chem 91(24):6269–6271
Bradley DC, McCauley AD, Stillings LM (2017) Mineral-deposit model for lithium-cesium-tantalum pegmatites. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5070-O
Brandes E, Stage C, Motschmann H, Rieder J, Buchner R (2014) Is surface layering of aqueous alkali halides determined by ion pairing in the bulk solution? J Chem Phys 141(18):10
Brugger J, Liu W, Etschmann B, Mei Y, Sherman DM, Testemale D (2016) A review of the coordination chemistry of hydrothermal systems, or do coordination changes make ore deposits? Chem Geol 447:219–253
Černý P (2005) The Tanco rare-element pegmatite deposit, Manitoba: regional context, internal anatomy, and global comparisons. In: Linnen RL, Samson IM (eds), Rare-element geochemistry and mineral deposits. GAC Short Course Notes, vol. 17. Geological Association of Canada, pp 127–158
Černý P, Ercit TS (2005) The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited. Can Mineral 43:2005–2026
Chen AA, Pappu RV (2007) Quantitative characterization of ion pairing and cluster formation in strong 1:1 electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 111(23):6469–6478
Chen T, Hefter G, Buchner R (2003) Dielectric spectroscopy of aqueous solutions of KCl and CsCl. J Phys Chem A 107(20):4025–4031
Chialvo AA, Simonson JM (2003) Aqueous Na+Cl− pair association from liquidlike to steamlike densities along near-critical isotherms. J Chem Phys 118(17):7921–7929
Cui ST, Harris JG (1994) Ion association and liquid structure in supercritical water solutions of sodium chloride: a microscopic view from molecular dynamics simulations. Chem Eng Sci 49(17):2749–2763
Dang LX (1992) Development of nonadditive intermolecular potentials using molecular dynamics: solvation of Li+ and F− ions in polarizable water. J Chem Phys 96(9):6970–6977
Dang LX (1995) Mechanism and thermodynamics of ion selectivity in aqueous solutions of 18-crown-6 ether: a molecular dynamics study. J Am Chem Soc 117(26):6954–6960
European Union (2018) Report on critical raw materials and the circular economy
Fennell CJ, Bizjak A, Vlachy V, Dill KA (2009) Ion pairing in molecular simulations of aqueous alkali halide solutions. J Phys Chem B 113(19):6782–6791
Foustoukos DI, Seyfried WE Jr (2007) Trace element partitioning between vapor, brine and halite under extreme phase separation conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71(8):2056–2071
Franck EU (1961) Uberkritisches wasser als elektrolytisches losungsmittel. Angew Chem 73(10):309–322
Fuoss RM (1980) Conductimetric determination of thermodynamic pairing constants for symmetrical electrolytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77(1):34–38
Gao J (1994) Simulation of the Na+Cl− ion-pair in supercritical water. J Phys Chem 98(24):6049–6053
Gujt J, Bester-Rogac M, Hribar-Lee B (2014) An investigation of ion-pairing of alkali metal halides in aqueous solutions using the electrical conductivity and the Monte Carlo computer simulation methods. J Mol Liq 190:34–41
He M, Liu X, Lu X, Wang R (2017) Molecular simulation study on K+-Cl− ion pair in geological fluids. Acta Geochim 36(1):1–8
Hefter GT, Salomon M (1996) Conductivities of KF and CsF in methanol at 25°C. J Solut Chem 25(6):541–553
Hoover WG (1985) Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys Rev A 31(3):1695–1697
Joung IS, Cheatham TE III (2008) Determination of alkali and halide monovalent ion parameters for use in explicitly solvated biomolecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 112(30):9020–9041
Justice MC, Justice JC (1976) Ionic interactions in solutions. I. The association concepts and McMillan-Mayer theory. J Solut Chem 5(8): 543–561
Kumar N, Leray I, Depauw A (2016) Chemically derived optical sensors for the detection of cesium ions. Coord Chem Rev 310:1–15
London D, Morgan GB, Icenhower J (1998) Stability and solubility of pollucite in granitic systems at 200 MPa H2O. Can Mineral 36(2):497–510
London D (2018) Ore-forming processes within granitic pegmatites. Ore Geol Rev 101:349–383
Manohar S, Atkinson G (1993) The effect of high pressure on the ion pair equilibrium constant of alkali metal fluorides: a spectrophotometric study. J Solut Chem 22(10):859–872
Marcus Y, Hefter G (2006) Ion pairing. Chem Rev 106(11):4585–4621
Mohorič T, Bren U (2017) Microwave irradiation affects ion pairing in aqueous solutions of alkali halide salts. J Chem Phys 146(4):9
Nosé S (1984a) A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol Phys 52(2):255–268
Nosé S (1984b) A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J Chem Phys 81(1):511–519
Paterson R, Jalota SK, Dunsmore HS (1971) Ion association of caesium chloride solutions and its effect upon the interionic frictional coefficients of an irreversible thermodynamic analysis. J Chem Soc A (0): 2116–2121
Pethybridge AD, Spiers DJ (1974) Association constants of 1:1 electrolytes in water from conductivity measurements. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 11:423–424
Pethybridge AD, Spiers DJ (1977) Conductance of some alkali metal halides in dilute aqueous solution at 25°C. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 73:768–775
Plugatyr A, Svishchev IM (2009) Accurate thermodynamic and dielectric equations of state for high-temperature simulated water. Fluid Phase Equil 277(2):145–151
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23(3):327–341
Smith DE, Dang LX (1994) Computer-simulations of NaCl association in polarizable water. J Chem Phys 100(5):3757–3766
Stubbs JM (2016) Molecular simulations of supercritical fluid systems. J Supercrit Fluids 108:104–122
Takamoto M, Hong FL, Higashi R, Katori H (2005) An optical lattice clock. Nature 435:321–324
Todorov IT, Smith W, Trachenko K, Dove MT (2006) DL_POLY_3: New dimensions in molecular dynamics simulations via massive parallelism. J Mater Chem 16(20):1911–1918
U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (2017) Critical mineral resources of the United States - economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply. USGS Professional Paper.
U.S. Geological Survey (2011) Mineral commodity summaries 2011. U.S. Geological Survey
Varala R, Rao KS (2015) Cesium salts in organic synthesis: a review. Curr Org Chem 19(13):1242–1274
Wagner W, Cooper JR, Dittmann A, Kijima J, Kretzschmar HJ, Kruse A, Mareš R, Oguchi K, Sato H, Stöcker I, Šifner O, Takaishi Y, Tanishita I, Trübenbach J, Willkommen T (2000) The IAPWS industrial formulation 1997 for the thermodynamic properties of water and steam. J Eng Gas Turbines Power 122(1):150–184
Wang RC, Hu H, Zhang AC, Huang XL, Ni P (2004) Pollucite and the cesium-dominant analogue of polylithionite as expressions of extreme Cs enrichment in the Yichun topaz-lepidolite granite, southern China. Can Mineral 42(3):883–896
Wang RC, Hu H, Zhang AC, Fontan F, Zhang H, De Parseval P (2006) Occurrence and late re-equilibration of pollucite from the Koktokay no. 3 pegmatite, Altai, northwestern China. Am Miner 91(5–6): 729–739
Wang RC, Hu H, Zhang AC, Fontan F, de Parseval P, Jiang SY (2007) Cs-dominant polylithionite in the Koktokay#3 pegmatite, Altai, NW China: in situ micro-characterization and implication for the storage of radioactive cesium. Contrib Mineral Petrol 153:355–367
Wang RC, Che XD, Zhang WL, Zhang AC, Zhang H (2009) Geochemical evolution and late re-equilibration of Na-Cs-rich beryl from the Koktokay #3 pegmatite (Altai, NW China). Eur J Mineral 21(4):795–809
Wang T, Zhang X, Liu X, Lu X, Wang R (2021) A molecular dynamics study of Li speciation in hydrothermal fluids and silicate melts. Chem Geol 584: 120528
Yui K, Sakuma M, Funazukuri T (2010) Molecular dynamics simulation on ion-pair association of NaCl from ambient to supercritical water. Fluid Phase Equil 297(2):227–235
Zhang X, Liu X, He M, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Lu X (2020) A molecular dynamics simulation study of KF and NaF ion pairs in hydrothermal fluids. Fluid Phase Equil 518: 112625
Zhang ZG, Duan ZH (2004) Lithium chloride ionic association in dilute aqueous solution: a constrained molecular dynamics study. Chem Phys 297(1–3):221–233
Zhang Z, Duan Z (2005) Prediction of the PVT properties of water over wide range of temperatures and pressures from molecular dynamics simulation. Phys Earth Planet Inter 149(3–4):335–354
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos 92062213, 91855209, 42125202 and 41872041). We acknowledge the financial support from the State Key Laboratory for Mineral Deposits Research at Nanjing University. We are grateful to the High Performance Computing Center (HPCC) of Nanjing University for doing the numerical calculations in this paper on its blade cluster system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, X., Wang, T. et al. A molecular simulation study of Cs-Cl and Cs-F ion pairs in hydrothermal fluids. Acta Geochim 41, 325–334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-022-00527-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-022-00527-0