Abstract
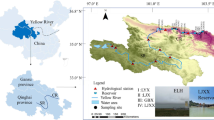
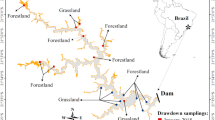
In order to understand the effect of river impoundment on carbon dynamics, a large reservoir in a subtropical area, the Xinanjiang Reservoir, was investigated in detail. CO2 emissions from the water–air interface was studied, as was organic carbon burial in sediment. The results show a significant seasonal difference in CO2 emissions. River impoundment led to the enhancement of aquatic photosynthesis, generating large amounts of authigenic organic carbon that was then buried in sediment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros N et al (2011) Carbon emission from hydroelectric reservoirs linked to reservoir age and latitude. Nat Geosci 4:593–596
Giles J (2006) Methane quashes green credentials of hydropower. Nature 444(30):524–525
McCully P (2004) Tropical hydropower is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. International Rivers Network reports
Steinhurst W et al (2012) Hydropower greenhouse gas emissions. State of the research. www.synapse-energy.com
Wang F et al (2015) Seasonal variation of CO2 diffusion flux from a large subtropical reservoir in East China. Atmos Environ 103:129–137
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41573064), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFA0601003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
11th International Symposium on Geochemistry of the Earth’s Surface.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Wang, B., Zhou, T. et al. CO2 emission and organic carbon burial in the Xinanjiang Reservoir. Acta Geochim 36, 465–468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0197-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0197-8