Abstract
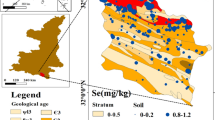
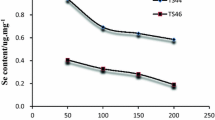
Selenium is one of the life-related elements. Survey reveals that selenium enrichment in the studied strata from Kaiyang County is considered to be closely related to the following factors: regional black shale series in Niutitang Formation of Early Cambrian, strong adsorption of organic matter (OM), magmatic hydrothermal migrate along the deep fault, mixing and migration of hydrothermal brine, regional uranium mineralization and presence of a great deal sulfides. For selenium enrichment in its weathered soil and crops, the reason responsible is selenium-enriched bedrock, which provides material sources for weathering profile and is considered as the main controlling factor of selenium content in the soil profile. After leaching and migrates downwards, organic carbon (OC) adsorption, iron-manganese layer adsorption, geochemical barrier role, selenium content in different profiles, there are mainly three types of distribution features: bottom enrichment type, top enrichment type and no significant enrichment type. Comprehensive analyses find that selenium enrichment area is mainly distributed in the Machang, Gaoyun-Fengsan-Guanpo, Baimadong, Chuandong-Hefeng-Shaoshang and Longgang-Gaozhai region, etc. Besides, around the east part of the county, in Huali and Yongxing selenium are relatively scarce.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Lan, Zhong Hong, Hu Ruizhong, Xiao Jiafei, and Zou Yanrong (2006) Early Cambrian oceanic anoxic event in northern Guizhou: Biomarkers and organic carbon isotope [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica. 9, 2413–2423 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Luming (1990) Discussion on the origin of uranium deposit No. 504 [J]. Uranium Geology. 3, 135–145 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Luming and Zhang Qifa (1993) The distribution features of Ni-Se-Re-Tl in Uranium-Mercury-Molybdenum deposit No. 504 [J]. Guizhou Science. 4, 57–62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng Caixia, Liu Shen, Hu Ruizhong, Liu Jiajun, Luo Taiyi, Chi Guoxiang, and Qi Youqiang (2010) Geochemistry of Lower Cambrian Se-Rich black rock series in Zunyi, Guizhou Province, Southwest China: The petrogenesis and enrichment mechanism of selenium [J]. Earth Science—Journal China University of Geosciences. 6, 947–958 (in Chinese with English abstract).
He Shaolin (2011) Committed livelihood projects—Guiyang multi-target regional geochemical survey results Introduction [J]. Guizhou Geology. 4, 318–314 (in Chinese)..
Li Chaoyang, Liu Yuping, Ye Lin, and Pi Daohui (2003) Discussion on Some Problems in the Study of Mineralization in Guizhou [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry. 4, 350–355 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Juan, Long Jian, and Wang Jingren (2004) Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils of Kaiyang region, Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science. 5, 579–582 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Juan, Long Jian, and Wang Jingren (2005) Se content of paddy soil in the middle region of Guizhou Province and its effect on Se content of rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science. 4, 571–574 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Shengrong and Gao Zhenmin (1995) REE characteristics of black rock series of the lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Hunan-Guizhou provinces, China, with a discussion on the REE patterns in marine hydrothermal sediments [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica. 2, 221–229 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Tung (1976) Chemical element abundances in the earth and it’s major shells [J]. Geochimica. 3, 167–174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Haili, Gao Junbo, Long Jie, Yang Ruidong, and Bi Kun (2012a) Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich strata and weathered soil from Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province [J]. Earth and Environment. 2, 161–170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Haili, Long Jie, Han Xiaotong, Kong Fancui, and Yang Ruidong (2012b) The geochemical characteristics of trace element of the red clay profiles weathered from Neoproterozoic Dengying Fm. Dolomite in Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science. 5, 1086–1093 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tu Guangchi, Gao Zhenmin, Hu Ruizhong, Zhang Qiang, Li Chaoyang, Zhao Zhenhua, and Zhang Baogui (2004) Dispersing Element Geochemistry and Metallogenic Mechanism [M]. China Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Wang Ganlu and Zhu Xiaoqing (2003) A study on the selenium background level in the soils in Guizhou [J]. Research of Environmental Science. 1, 23–26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Shijie, Ji Hongbing, Ouyang Ziyuan, Zhou Dequan, Zheng Leping, and Li Tingyu (1999) Preliminary studies on weathered soil from carbonate [J]. Science in China (Series D). 5, 441–449 (in Chinese).
Wang Min, Sun Xiaoming, and Ma Mingyang (2004) Rare-earth elements geochemistry and genesis of Xinhua large-size phosphorite deposit in western Guizhou [J]. Mineral Deposits. 4, 484–493 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jingren and Li Tinghui (2001) Development and Utilization of Selenium Resources in Kaiyang County [M]. Guizhou Science and Technology Press, Guiyang (in Chinses).
Xing Guangxi and Zhu Jianguo (2003) Chemistry of Trace Element and Rare-Earth Element in Soil [M]. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Yang Ruidong (2008) The distribution of rare-earth elements and trace elements in latecritic profile: Implication for karst environment [J]. Geological Review. 3, 409–418 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Ruidong, Zhang Chuanlin, Luo Xingrong, Tian Jingquan, Bao Yafan, and Song Guoqi (2006) Geochemical characteristics of Early Cambrian cherts in Quruqtagh, Xinjiang, West China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica. 4, 598–605 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Ruidong, Zhu Lijun, Gao Hui, Zhang Weihua, Jiang Lijun, Wang Qiang, and Bao Miao (2005) A study on characteristics of the hydrothermal vent and relating biota at the cambrian bottom in Songlin, Zunyi County, Guizhou Province [J]. Geological Review. 5, 481–492 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, H., Yang, R. Distribution and controlling factors of selenium in weathered soil in Kaiyang County, Southwest China. Chin. J. Geochem. 33, 300–309 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0691-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0691-1