Abstract
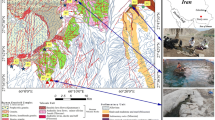
The Gulf of Suez region is one of the most interesting geothermal areas in Egypt because of the high temperatures of its springs. The eastern and western shores of the Gulf of Suez are characterized by superficial thermal manifestations including a cluster of hot springs with varied temperatures. Variations of deuterium and oxygen-18 concentrations in thermal waters have been used to aid in describing the source of recharge in the Gulf of Suez hot springs. Isotope and geochemical data for the Gulf of Suez thermal waters suggest that recharge to the hot springs may not be entirely from the Gulf of Suez water, but possibly from the meteoric water that comes from areas of higher altitude surrounding the hot springs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barragán R.M., Arellano V.M., Portugal E., Sandoval F., and Barrera V.M. (2001) Gas equilibrium for the Los Azufres (Michoacán) geothermal reservoir, México. In Proceedings of the 22 nd PNOC-EDC Geothermal Conference [M]. pp.81–87. Manila, Philippines.
Colletta B., Le Quellec P., Letouzey J., and Moretti I. (1988) Longitudinal evolution of the Suez rift structure (Egypt) [J]. Tectonophysics. 153, 221–233.
Davisson M.L., Presser T.S., and Criss R.E. (1994) Geochemistry of tectonically expelled fluids from the northern Coast Ranges, Rumsey Hills, California, USA [J]. Geochim. et Cosmochim Acta. 58, 1687–1699.
El Kiki F.E., Mabrook B., and Swailem F.M. (1978) Evaluation of trace elements and tritium content in some mineral springs in Egypt [J]. Isotope & Rad. Res. 10, 55–82.
Evans A.L. (1988) Neogene tectonic and stratigraphic events in the Gulf of Suez rift area, Egypt [J]. Tectonophysics. 153, 235–247.
Fournier R.O. and Potter R.W. (1979) Magnesium correction to Na-K-Ca chemical geothermometer [J]. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 43, 1543–1550.
Fournier R.O. and Truesdell A.H. (1973) An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters [J]. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 37, 1255–1275.
Garfunkel Z. and Bartov Y. (1977) The tectonics of the Suez Rift [J]. Geol. Surv. Isr. Bull. 71, 44.
Gesch D.B., Verdin K.L., and Greenlee S.K. (1999) New land surface digital elevation model covers the Earth [J]. Eos. Trans. AGU. 80, 69–70.
Giggenbach W.F. (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria: Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators [J]. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 52, 2749–2765.
Himida I.H., Bishay N.Z., and Diab M.S. (1972) Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies on Ayun Musa area [J]. Desert Institute Bulletin. 22, 17–32.
HydroGeoLogic, Inc., and Allison Geoscience Consutants, Inc. (1999) MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: User Manual Supplement for Version 4.0. [Z]. HydroGeoLogic, Inc., and Allison Geoscience Consutants, Inc.
Issar A., Rosenthal Y., and Eckstein R.B. (1971) Formation waters, hot springs and mineralization phenomena along the eastern shore of the Gulf of Suez [J]. International Association of Scientific Hydrology. 14, 25–44.
Jackson C.A.L., Gawthorpe R.L., and Sharp I.R. (2002) Growth and linkage of the East Tanka fault zone; structural style and syn-rift stratigraphic response [J]. Journal of the Geological Society of London. 159, 175–187.
McKenzie D.P., Davies D., and Molnar P. (1970) Plate Tectonics of the Red Sea and East Africa [J]. Nature. 226, 243–248.
Meneisy M.Y. and Kreuzer H. (1974) Potassium-argon ages of Egyptian basaltic rocks [J]. Geol. Jahrb. D9, 21–31.
Morgan P., Boulos K., and Swanberg C.A. (1983) Regional geothermal exploration in Egypt [J]. Geophysical Prospecting. 31, 361–376.
Nicholson, K. (1993) Geothermal Fluids: Chemistry and Exploration Techniques [M]. pp.253. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg.
Nieva and R. Nieva (1987) Developments in geothermal energy in Mexico. Part twelve: a cationic geothermometer for prospecting of geothermal resources [J]. Heat Recov. Syst. 7, 243–258.
Palmer M.R., Spivack A.J., and Edmond J.M. (1987) Temperature and pH controls over isotopic fractionation during adsorption of boron on marine clay [J]. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 51, 2319–2323.
Patton T.L., Moustafa A.R., Nelson R.A., and Abdine A.S. (1994) Tectonic evolution and structural setting of the Suez rift. In Interior Rift Basins. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Mem. (ed. Landon S.M.) [M]. 58, 9–55.
Said R. (1962) Geology of Egypt [M]. pp.377. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Sano Y., Nakamura Y., Notsu K., and Wakita H. (1988) Influence of volcanic eruptions on helium isotope ratios in hydrothermal systems induced by volcanic eruptions [J]. Geochim. et Gosmochim. Acta. 52, 1305–1308.
Schütz K.I. (1994) Structure and Stratigraphy of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. In Interior Rift Basins, AAPG Memoir 59 (ed. Landon S.M.) [M]. pp.57–96. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA.
Sellwood B.W. and Netherwood R.E. (1984) Facies evolution in the Gulf of Suez area: sedimentation history as an indicator of rift initiation and development [J]. Mod. Geol. 9, 43–69.
Shata A.A. (1990) Thermal Springs and Mineralized Water in the Gulf of Suez Taphrogenic Basin, Northeast Egypt [R]. pp.681–688. Memoires of the 22nd Congress of IAH, XXII, Lausanne.
Siedner G. (1973) K-Ar chronology of Cenozoic volcanic from northern Israel and Sinai [J]. Fortschr. Mineral. 50, 129–130.
Sturchio N.C. and Arehart G.B. (1996) Composition and origin of thermal waters in the Gulf of Suez area, Egypt [J]. Applied Geochemistry. 2, 471–479.
United States Geological Survey, USGS (1998) The Red Sea Basin Province [Z]. Open File No.99-50-A. United States Geological Survey, Washington.
Verma M.P. (2000) Revised Quartz Solubility Temperature Dependence Equation Along the Water-vapor Sauration Curve [R]. pp.1927–1932. World Geothermal Congress, Kyushu-Tohoku, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaher, M.A., Saibi, H. & Ehara, S. Geochemical and stable isotopic studies of Gulf of Suez’s hot springs, Egypt. Chin. J. Geochem. 31, 120–127 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-012-0558-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-012-0558-2