Abstract
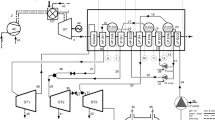
The steam ejector is a crucial component in the waste heat recovery system. Its performance determines the amount of recovered heat and system efficiency. However, poor ejector performance has always been the main bottleneck for system applications. Therefore, this study proposes an optimization methodology to improve the steam ejector’s performance by utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques, response surface methodology (RSM), and genetic algorithm (GA). Firstly, a homogeneous equilibrium model (HEM) was established to simulate the two-phase flow in the steam ejector. Then, the orthogonal test was presented to the screening of the key decision variables that have a significant impact on the entrainment ratio (ER). Next, the RSM was used to fit a response surface regression model (RSRM). Meanwhile, the effect of the interaction of geometric parameters on the performance of the steam ejector was revealed. Finally, GA was employed to solve the RSRM’s global optimal ER value. The results show that the RSRM exhibits a good fit for ER (R2=0.997). After RSM and GA optimization, the maximum ejector efficiency is 27.94%, which is 48.38% higher than the initial ejector of 18.83%. Furthermore, the optimized ejector efficiency is increased by 46.4% on average under off-design conditions. Overall, the results reveal that the combination of CFD, RSM, and GA presents excellent reliability and feasibility in the optimization design of a two-phase steam ejector.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area/mm2
- c :
-
Speed of sound/m·s−1
- c p :
-
Specific heat/J·kg−1·K−1
- D :
-
Diameter/mm
- h :
-
Enthalpy/kJ·kg−1
- K :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy/m2·s−2
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity/W·m−1 ·K−1
- L :
-
Length/mm
- P :
-
Pressure/MPa
- q :
-
Mass flow rate/g·s−1
- \({{\dot S}_\phi}\) :
-
Source term
- T :
-
Temperature/K
- \({\vec u}\) :
-
Velocity vector components/m·s−1
- α :
-
Angle/(°)
- ρ :
-
Density/kg·m−3
- τ :
-
Viscous stress/N·m−2
- η :
-
Coefficient
- Γ :
-
Diffusion coefficient/m2·s−1
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity/kg·m−1·s−1
- μ T :
-
Turbulent viscosity/kg·m−1·s−1
- b:
-
Back flow
- diff:
-
Diffuser
- eff:
-
Effective
- mix:
-
Mixing chamber
- ne:
-
Nozzle exist
- p:
-
Primary flow
- s:
-
Secondary flow
- th:
-
Throat
- φ :
-
Arbitrary scalar
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AR:
-
Area ratio
- CCD:
-
Central composite design
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamics
- DOF:
-
Degree of freedom
- ER:
-
Entrainment ratio
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- HEM:
-
Homogeneous equilibrium model
- MS:
-
Mean squared error
- NXP:
-
Nozzle exit position
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- RSRM:
-
Response surface regression model
- UDF:
-
User-defined functions
- UDS:
-
User-defined scalars
References
Han Y., Sun Y.Y., Wu J.J., An efficient solar-aided waste heat recovery system based on steam ejector and WTA pre-drying in solar/lignite hybrid power plants. Energy, 2020, 208: 118372.
Li D., Zhao H., Kong F., et al., Application of ejector in solid oxide fuel cell anode circulation system. Journal of Thermal Science, 2022, 31: 634–649.
Bai T., Liu Y., Yan G., et al., Theoretical performance analysis of an ejector enhanced high-temperature heat pump with dual-pressure condensation and evaporation. Journal of Thermal Science, 2022, 31: 1367–1379.
Yang X., Long X., Yao X., Numerical investigation on the mixing process in a steam ejector with different nozzle structures. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2012, 56: 95–106.
Zhu Y.H., Cai W.J., Wen C., Li Y., Numerical investigation of geometry parameters for design of high performance ejectors. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2009, 29: 898–905.
Varga S., Oliveira A.C., Diaconu B., Influence of geometrical factors on steam ejector performance — A numerical assessment. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2009, 32: 1694–1701.
Chen W.X., Chong D.T., Yan J.J., Liu J.P., The numerical analysis of the effect of geometrical factors on natural gas ejector performance. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 59: 21–29.
Banasiak K., Hafner A., Andresen T., Experimental and numerical investigation of the influence of the two-phase ejector geometry on the performance of the R744 heat pump. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2012, 35: 1617–1625.
Chen Z., Zhao H.X., Kong F.C., Liu G.D., Wang L., Lai Y.H., Synergistic effect of adjustable ejector structure and operating parameters in solar-driven ejector refrigeration system. Solar Energy, 2023, 250: 295–311.
Wu Y.F., Zhao H.X., Zhang C.Q., Wang L., Han J.T., Optimization analysis of structure parameters of steam ejector based on CFD and orthogonal test. Energy, 2018, 151: 79–93.
He Y., Deng J.Q., Li Y.F., Zhang X.P., Synergistic effect of geometric parameters on CO2 ejector based on local exergy destruction analysis. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 184: 116256.
Song W.L., Shen X.S., Huang Y.L., Jiang P.X., Zhu Y.H., Fuel ejector design and optimization for solid oxide fuel cells using response surface methodology and multi-objective genetic algorithm. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 232: 121067.
Li Y.F., Deng J.Q., He Y., Numerical study on the interaction of geometric parameters of a transcritical CO2 two-phase ejector using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 214: 118799.
Palacz M., Smolka J., Nowak A.J., Banasiak K., Hafner A., Shape optimisation of a two-phase ejector for CO2 refrigeration systems. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2017, 74: 212–223.
Gupta P., Kumar P., Rao S.M.V., Artificial neural network based shape optimization of supersonic ejectors in the critical flow regime. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 216: 119046.
Ariafar K., Buttsworth D., Sharifi N., Malpress R., Ejector primary nozzle steam condensation: Area ratio effects and mixing layer development. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 71: 519–527.
Li Z.M., Wang J.L., Zheng H.T., CFD simulation of the supersonic steam ejector. ASME 2010 4th International Conference on Energy Sustainability, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/ES2010-90123
Wang X.D., Dong J.L., Wang T., Tu J.Y., Numerical analysis of spontaneously condensing phenomena in nozzle of steam-jet vacuum pump. Vacuum, 2012, 86: 861–866.
Varga S., Lebre P.M.S., Oliveira A.C., CFD study of a variable area ratio ejector using R600a and R152a refrigerants. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2013, 36: 157–165.
Giacomelli F., Biferi G., Mazzelli F., Milazzo A., CFD modeling of the supersonic condensation inside a steam ejector. Energy Procedia, 2016, 101: 1224–1231.
Yu M.H., Zhao H.X., Wang X., Han J.T., Lai Y.H, Investigation on the performance of the pump-free double heat source ejector refrigeration system with R1234yf. Journal of Thermal Science, 2020, 31: 1452–1464.
Ameur K., Aidoun Z., Ouzzane M., Modeling and numerical approach for the design and operation of two-phase ejectors. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 109: 809–818.
Lucas C., Rusche H., Schroeder A., Koehler J., Numerical investigation of a two-phase CO2 ejector. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2014, 43: 154–166.
Smolka J., Bulinski Z., Fic A., Nowak A.J., Banasiak K., Hafner A., A computational model of a transcritical R744 ejector based on a homogeneous real fluid approach. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2013, 37: 1208–1224.
Bell I.H., Wronski J., Quoilin S., Lemort V., Pure and pseudo-pure fluid thermophysical property evaluation and the open-source thermophysical property library CoolProp. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53: 2498–2508.
Yu M.H., Wang C., Wang L., Zhao H.X., Optimization design and performance evaluation of R1234yf ejectors for ejector-based refrigeration systems. Entropy (Basel), 2022, 24(11): 1632.
Bartosiewicz Y., Aidoun Z., Desevaux P., Mercadier Y., Numerical and experimental investigations on supersonic ejectors. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2005, 26: 56–70.
Colarossi M., Trask N., Schmidt D.P., Bergander M.J., Multidimensional modeling of condensing two-phase ejector flow. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2012, 35: 290–299.
Pianthong K., Seehanam W., Behnia M., Sriveerakul T., Aphornratana S., Investigation and improvement of ejector refrigeration system using computational fluid dynamics technique. Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48: 2556–2564.
Elbel S., Historical and present developments of ejector refrigeration systems with emphasis on transcritical carbon dioxide air-conditioning applications. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2011, 34: 1545–1561.
Chen Y.M., Sun C.Y., Experimental study of the performance characteristics of a steam-ejector refrigeration system. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 1997, 15(4): 384–394.
Arjmandi H., Amiri P., Saffari Pour M., Geometric optimization of a double pipe heat exchanger with combined vortex generator and twisted tape: A CFD and response surface methodology (RSM) study. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2020, 18: 100514.
Sun X., Kim S., Yang S.D., Kim H.S., Yoon J.Y., Multi-objective optimization of a Stairmand cyclone separator using response surface methodology and computational fluid dynamics. Powder Technology, 2017, 320: 51–65.
Elsayed K., Lacor C., Modeling, analysis and optimization of aircyclones using artificial neural network, response surface methodology and CFD simulation approaches. Powder Technology, 2011, 212: 115–133.
Liu G., Zhao H., Wang Z., et al., Performance study and multi-objective optimization of a two-temperature co2 refrigeration system with economizer based on energetic, exergetic and economic analysis. Journal of Thermal Science, 2022, 31: 1416–1433.
Li F.L., Li R.G., Li X.C., Tian Q., Experimental investigation on a R134a ejector refrigeration system under overall modes. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 137: 784–791.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhao, H., Zhang, X. et al. Performance Improvement of Two-Phase Steam Ejector based on CFD Techniques, Response Surface Methodology and Genetic Algorithm. J. Therm. Sci. 33, 675–695 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-024-1923-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-024-1923-2