Abstract
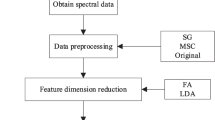
The problem of mine water source has always been an important hidden danger in mine safety production. The water source under the mine working face may lead to geological disasters, such as mine collapse and water disaster. The research background of mine water source identification involves many fields such as mining production, environmental protection, resource utilization and technological progress. It is a comprehensive and interdisciplinary subject, which helps to improve the safety and sustainability of mine production. Therefore, timely and accurate identification and control of mine water source is very important to ensure mine production safety. Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) technology, characterized by high sensitivity, specificity, and spatial resolution, overcomes the time-consuming nature of traditional chemical methods. In this experiment, sandstone water and old air water were collected from the Huainan mining area as original samples. Five types of mixed water samples were prepared by varying their proportions, in addition to the two original water samples, resulting in a total of seven different water samples for testing. Four preprocessing methods, namely, MinMaxScaler, StandardScaler, Standard Normal Variate (SNV) transformation, and Centering Transformation (CT), were applied to preprocess the original spectral data to reduce noise and interference. CT was determined as the optimal preprocessing method based on class discrimination, data distribution, and data range. To maintain the original data features while reducing the data dimension, including the original spectral data, five sets of data were subjected to Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) dimensionality reduction. Through comparing the clustering effect and Fisher’s ratio of the first three dimensions, PCA was identified as the optimal dimensionality reduction method. Finally, two neural network models, CT+PCA+CNN and CT+PCA+ResNet, were constructed by combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Residual Neural Networks (ResNet), respectively. When selecting the neural network models, the training time, number of iterative parameters, accuracy, and cross-entropy loss function in the classification problem were compared to determine the model best suited for water source data. The results indicated that CT+PCA+ResNet was the optimal approach for water source identification in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data/Materials: The datasets generated during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abedin KM (2022) Laser-induced fluorescence studies on some edible oils and aromatic frankincense oil excited by blue and violet diode lasers at 447 nm and 405 nm. J Spectrosc 2417545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2417545
Chen CW, Zhou XF (2022) Collaborative representation-based fuzzy discriminant analysis for face recognition. Vis Comput 38: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00371-021-02325-W
Chen H, Guo MM, Tian Y, et al. (2022) Advances in convolutional neural networks for flow field reconstruction. J Mech 54(09): 2343–2360. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.6052/0459-1879-22-130
Chen SY, Jia YW, Jiang YR, et al. (2022) Classification and identification of manuka honey adulterated with spectral graph of multi-wavelength laser-induced fluorescence. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis. Spectrosc Spectral Anal 42(09): 2807–2812. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2022)09-2807-06
Cheng FF, Xia JA, Qiao KC, et al. (2022) Cadmium detection in water by laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chelating resin. J Appl Laser 42(10): 156–161. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.14128/j.cnki.al.20224210.156
He JC, Xu JC, Zhang L, et al. (2023) An interpretive constrained linear model for ResNet and MgNet. Neural Netw 162: 384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUNET.2023.03.011
He T, Liu NH, Wu BY, et al. (2023) 3D fault recognition method based on ResU-Net and its application. J Eng Math 40(01): 1–19. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-3085.2023.01.001
Hou SX, Lian A, Chu YD (2023) Bearing fault diagnosis method using the joint feature extraction of Transformer and ResNet. Meas Sci Technol 34(7). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/ACC885
Li GZ, Zhao HN, Lin M (2022) Research on computer-generated image Recognition based on null space Analysis. J Comput Simul 39(01): 162–165+185. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2022.01.035
Liang ZZ, Zhang L (2022) Regularized linear discriminant analysis for Kullback Leibler divergence uncertainty set. J Acta Autom. Sin 48(04): 1033–1047. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c210434
Liu JQ, Yan H, Wang XT, et al. (2023) Improved YOLOv5 object detection network based on improved pyramid and skip connection. Control Decis 38(06): 1730–1736. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.1414
Oliva Danson J, Cheung Cynthia, Perrault Katelynn A (2022) Fisher ratio feature selection by manual peak area calculations on comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography data using standard mixtures with variable composition, storage, and interferences. J Anal Bioanal Chem 415(13). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00216-022-04484-8
Qi QJ, Sun Z, Liu WG, et al. (2023) Research on risk assessment model of coal mine water hazard accidents induced by flood disasters. J Coal Sci Technol 51(01): 395–402. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2022-0051
Qiu CX, Bendickson Aaron, Kalyanapu Joshua, et al. (2023) Accuracy and architecture studies of residual neural network method for ordinary differential equations. J Sci Comput 95(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10915-023-02173-X
Sun CX, Li HY, Song MX, et al. (2023) A ranking-based cross- entropy loss for early classification of time series. J IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3250203
Xiao LL, Hu SY, Niu C, et al. (2022) Chemical characteristics of groundwater and discrimination of sudden (surging) water sources in the Binchang Mining area. J Xi’an Univ Sci Technol 42(04): 724–732. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2022.0412
Xie KP, Yi DZ, Liu YQ, et al. (2023) SAF-CNN: Sparse acceleration framework of convolutional neural networks for embedded FPGA. J Comput Res Dev 60(05): 1053–1072. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.7544/issn1000-1239.202220735
Xie X, Liu XL, Wang JX, et al. (2023) Wireless RFID tag quantity estimation method based on multilayer perception. Chin J Comput 46(03): 499–511. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.00499
Xie ZM, Wang J, Mo CM. (2023) IFWA-Optimized BLSTM and transformer fusion for 3D prediction model of seawater quality. Trans. Chin. Soc Agric Eng 39(04): 162–170. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202210188
Yan PC, Zhang XF, Kan XY, et al. (2023) Fast identification method of mine water source based on laser-induced fluorescence technology and optimized LSTM. Water 15(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040701
Yang F, Lei T, Yang RJ (2021) Progress in laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy for detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Chin J Anal Lab 41(10): 1214–1220. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2021.081606
Zhao X, Zhang JY, Long QQ (2023) Indoor visible light positioning method based on circle Chaotic Mapping and ISSA-ELM neural network. Acta Opt Sin 43(02): 33–42. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3788/AOS0206004
Zhu SJ, Jiang CL, Bi B, et al. (2023) Identification of mine water inrush source based on combination weight-improved grey correlation degree theory. J Coal Sci Technol 50(04): 165–172. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2584094
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Collaborative Innovation Center of Mine Intelligent Equipment and Technology, Anhui University of Science & Technology (CICJMITE202203), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0604503), Anhui Province Postdoctoral Research Fund Funding Project (2019B350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YAN Peng-cheng: Methodology, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing - review & editing. ZHAO Yu-ting: Investigation, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing - original draft. LI Guo-dong: Data curation, Software. WANG Jing-bao: Resources, Visualization. WANG Wen-chang: Project administration, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Pc., Zhao, Yt., Li, Gd. et al. Water source identification in mines combining LIF technology and ResNet. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 3392–3401 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8189-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8189-0