Abstract
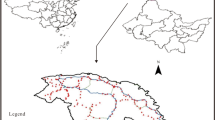
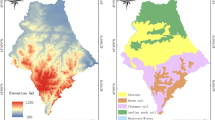
This study was conducted to analyze the variation of soil multifunctionality (SMF) along elevation and the driving factors in the Altun Shan. Soil samples (0–10 cm) were collected from 15 sites (H01 to H15) at every 200 m elevation interval, covering a total range from 900 m to 3500 m above mean sea level. We investigated climate factors (mean annual temperature, MAT; mean annual precipitation, MAP), soil environment (soil water content, electrical conductance, and pH), vegetation factors, and elevation to determine which of them are the main driving factors of the spatial variability of SMF in the Altun Shan. We explored the best-fit model of SMF along the changes in elevation using a structural equation model, performed variance partitioning analysis (VPA) on SMF with the “varpart” function to explain the relative contribution of various environmental factors to SMF changes, and used a random forest model for relative importance analysis. The results showed that SMF in the Altun Shan significantly increased with elevation in a linear trend. The main driver of changes in SMF was found to be MAP. Although the rise in elevation did not have a significant direct effect on changes in SMF, it could indirectly affect SMF by significantly influencing MAP, pH, MAT, and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). When considering climate, soil environment, and vegetation factors together, they explained 76% of the variation in SMF. The largest contribution to the variation in SMF was attributed to the independent effect of climate (0.31) and its interactive effect with soil (0.30). The relative importance of MAP on SMF changes was found to be the greatest. It is indicated that changes in SMF are caused by the combined effect of multiple environmental conditions. These findings are essential for understanding the spatial variability and drivers of SMF in dryland mountain ecosystems, especially concerning the function of mountain ecosystems in the context of global climatic changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data/Materials: Data is available on reasonable request from the first author.
References
Bian FH, Wu QT, Wu MD, et al. (2022) C: N: P stoichiometry in plants and soils of Phragmites australis wetland under different water-salt habitats. Chin J Appl Ecol 33(2): 385–396. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202202.040
Bui EN, Henderson BL (2013) C:N:P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 373(2): 553–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1823-9
Byrnes JEK, Gamfeldt L, Isbell F, et al. (2014) Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Challenges and solutions. Methods Ecol Evol 5(2): 111–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12143
Cleveland CC, Liptzin D (2007) C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass. Biogeochemistry 85(3): 235–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-007-9132-0
Condit R, Engelbrecht BMJ, Pino D, et al. (2013) Species distributions in response to individual soil nutrients and seasonal drought across a community of tropical trees. PNAS 110(13): 5064–5068. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218042110
Cui HW, Wagg C, Wang XT, et al. (2022) The loss of above- and belowground biodiversity in degraded grasslands drives the decline of ecosystem multifunctionality. Appl Soil Ecol 172: 104370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104370
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, et al. (2017) Soil microbial communities drive the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to global change in drylands across the globe. Ecol Lett 20(10): 1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12826
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Gallardo A, et al. (2013) Decoupling of nutrient cycles as a function of aridity in global dryland soils. Nature 502(7473): 672–676. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12670
Du BM, Kang H, Pumpane J, et al. (2014) Soil organic carbon stock and chemical composition along an elevation gradient in the Lushan Mountain, subtropical China. Ecol Res 29(3): 433–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-014-1135-4
Duan MJ, Gao QZ, Guo, YQ, et al. (2011) Species diversity distribution pattern of alpine grassland communities along an altitudinal gradient in the Northern Tibet. Pratacult Sci 28(10): 1845–1850. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11686/cyxb20120303
Eldridge DJ, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Quero JL, et al. (2020) Surface indicators are correlated with soil multifunctionality in global drylands. J Appl Ecol 57(2): 424–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13540
Ensslin A, Rutten G, Pommer U, et al. (2015). Effects of elevation and land use on the biomass of trees, shrubs and herbs at Mount Kilimanjaro. Ecosphere 6(3): 45. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES14-00492.1.
Fang JY, Yu GR, Liu LL, et al. (2018) Climate change, human impacts, and carbon sequestration in China. PNAS 115(16): 4015–4020. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700304115
Fay PA, Blair JM, Smith MD, et al. (2011) Relative effects of precipitation variability and warming on tallgrass prairie ecosystem function. Biogeosciences 8(10): 3053–3068. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-3053-2011
Fierer N, Mccain CM, Meir, P., et al. (2011). Microbes do not follow the elevational diversity patterns of plants and animals. Ecology 92(4): 797–804. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-1170.1
Gamfeldt L, Hillebrand H, Jonsson PR (2008) Multiple functions increase the importance of biodiversity for overall ecosystem functioning. Ecology 89(5): 1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1890/06-2091.1
Gao HN, Sun CX, Sun XM, et al. (2021) Stoichiometry characteristics of soil at different elevations in the Qilian Mountains. J Desert Res 41(1): 219–227. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00125
Gao M, Piao S, Chen A, et al. (2019) Divergent changes in the elevational gradient of vegetation activities over the last 30 years. Nat Commun 10: 2970. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11035-w
Gaston KJ (2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature 405(6783): 220–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012228
Guerra CA, Heintz-Buschart A, Sikorski J, et al. (2020) Blind spots in global soil biodiversity and ecosystem function research. Nat Commun 11(1): 3870. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17688-2
Guo Q, Hu ZM, Li SG, et al. (2012) Spatial variations in aboveground net primary productivity along a climate gradient in eurasian temperate grassland: effects of mean annual precipitation and its seasonal distribution. Glob Chang Biol 18(12): 3624–3631. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12010
Hector A, Bagchi R (2007) Biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature 448(7150):188–190. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05947
Hobbie SE, Nadelhoffer KJ, Hogberg P (2002) A synthesis: The role of nutrients as constraints on carbon balances in boreal and arctic regions. Plant Soil, 242(1): 163–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019670731128
Hooper DU, Vitousek PM (1998) Effects of plant composition and diversity on nutrient cycling. Ecol Monogr 68(1): 121–149. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9615(1998)068
Hou GL, Hu ZM (2022) Related theories of ecosystem risk under global change and their linkages. Chin J Appl Ecol 33(3): 629–637. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202203.022
Hu WG, Ran JZ, Dong LW, et al. (2021) Aridity-driven shift in biodiversity-soil multifunctionality relationships. Nat Commun 12(1): 5350. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25641-0
Huxman TE, Smith MD, Fay PA, et al. (2004) Convergence across biomes to a common rain-use efficiency. Nature 429(6992): 651–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02561.
Jing X, Sanders NJ, Shi Y, et al. (2015) The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and belowground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nat Commun 6: 8159. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9159.
Jing X, Wang YH, Chung HG, et al. (2014) No temperature acclimation of soil extracellular enzymes to experimental warming in an alpine grassland ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau. Biogeochemistry 117:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-013-9844-2
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol Appl 10(2): 423–436. https://doi.org/10.2307/2641104
Kemmitt SJ, Wright D, Goulding KWT, et al. (2006) pH regulation of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in two agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 38(5): 898–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.08.006
Li J, Li C, Kou Y, et al. (2020) Distinct mechanisms shape soil bacterial and fungal co-occurrence networks in a mountain ecosystem. Fems Microbiol Ecol 96(4): fiaa030. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiaa030
Li JP, Zheng ZR, Zhao NX, et al. (2016) Relationship between ecosystem multifuntionality and species diversity in grassland ecosystems under land-use types of clipping, enclosure and grazing. Chin J Plant Ecol 40(8): 735–747. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2015.0457
Li JR, Gilhooly WP, Okin GS, et al. (2017) Abiotic processes are insufficient for fertile island development: a 10-year artificial shrub experiment in a desert grassland. Geophys Res Lett 44(5): 2245–2253. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL072068.
Lin XB, Sun YM, Jiang XF, et al. (2020) Soil fertility characteristics and their influencing factors in tea plantations of Jiangxi Province, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 31(4): 1163–1174. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202004.022
Liu M, Zhang G, Yin F, et al. (2022) Relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality along the elevation gradient in alpine meadows on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Ecol Indicat 141: 109097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109097
Luo M, Zhou YC, Tang FH, et al. (2023) Soil properties of carbonate rocks under different vegetation. Carsol Sin 42(02):277–289. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11932/karst2022y17
Lv YH, Zan T, Ma WJ, et al. (2004) Influence of lime and serpentine-fused phosphate on tobacco production and soil acidity regulation. Ecol Environ 13(3): 379–381. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2004.03.032
Maestre FT, Quero JL, Gotelli NJ, et al. (2012) Plant species richness and ecosystem multifunctionality in global drylands. Science 335(6065): 214–218. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215442.
Manning P, Van der Plas F, Soliveres S, et al. (2018) Redefining ecosystem multifunctionality. Nat Ecol Evol 2(3): 427–436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-017-0461-7
Miller AJ, Amundson R, Burke IC, et al. (2004) The effect of climate and cultivation on soil organic C and N. Biogeochemistry 67(1): 57–72. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOG.0000015302.16640.a5
Moyano FE, Manzoni S, Chenu C (2013) Responses of soil heterotrophic respiration to moisture availability: an exploration of process and models. Soil Biol Biochem 59: 72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.002
Mukai M, Aiba S, Kitayama K (2016) Soil-nutrient availability and the nutrient-use efficiencies of forests along an altitudinal gradient on Yakushima Island, Japan. Ecol Res 31(5): 719–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-016-1381-8
Muller M, Oelmann Y, Schickhoff U, et al. (2017) Himalayan treeline soil and foliar C:N:P stoichiometry indicate nutrient shortage with elevation. Geoderma 291: 21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.12.015
Pang JF, Zhang B, Wang B, et al. (2020) Characteristics of soil ecological stoichiometry under different elevation on the north slope of Kunlun Mountains. J Arid Land Res Environ 34(1): 178–185. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2020.024
Peng SJ, Luo Y, Cai HY, et al. (2022) A new list of threatened woody species in China under future global change scenarios. Biodiversity Sci 30(5): 21459. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.17520/biods.2021459
Post WM, Emanuel WR, Zinke PJ, et al. (1982) Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature 298(5870): 156–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/298156a0
Qin HL, Fu XX, Lu Y, et al. (2019) Soil C:N:P stoichiometry at different elevations in Mao’er Mountain, Guangxi, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 30(3): 711–717. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201903.027
Rodell M, Houser PR, Jambor U, et al. (2004) The global land data assimilation system. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 85(3): 381–394. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-85-3-381
Sanderson MA, Skinner RH, Barker DJ, et al. (2004) Plant species diversity and management of temperate forage and grazing land ecosystems. Crop Sci 44(4): 1132–1144. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.1132
Schimel J, Balser TC, Wallenstein M (2007) Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology 88(6):1386–1394. https://doi.org/10.1890/06-0219
Soliveres S, Maestre FT, Eldridge DJ, et al. (2014) Plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality peak at intermediate levels of woody cover in global drylands. Global Ecol Biogeogr 23(12): 1408–1416. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12215
Sun J, Zhou T, Liu M, et al. (2020) Water and heat availability are drivers of the aboveground plant carbon accumulation rate in alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecol Biogeogr 29(1): 50–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.13006
Tan B, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, et al. (2011) Effects of snow pack removal on the dynamics of winter-time soil temperature, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in alpine forests of west Sichuan. Chin J Appl Ecol 22(10): 2553–2559. (in Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.2011.0362
Tashi S, Singh B, Keitel C, et al. (2016) Soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in forests along an altitudinal gradient in the eastern Himalayas and a meta-analysis of global data. Global Change Biol 22(6): 2255–2268. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13234
Tian HZ, Xiao Y, Yang TB, et al. (2021) Glacier area changes and their responses to air temperature changes in the Altun Mountainsfrom 1973 to 2020. J Glaciol Geocryol 43(5): 424–1434. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2021.0093
Tian YH, Lv GH, Yang XD, et al. (2012) Influence of water and saline stress on rhizosphere soil enzymes activities for arid region plants. J Arid Land Res Environ 26(3): 156–163. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2012.03.020
Valencia E, Maestre FT, le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, et al. (2015) Functional diversity enhances the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to aridity in Mediterranean drylands. New Phytol 206(2): 660–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13268
Wang C, Wang XB, Liu DW, et al. (2014) Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nat Commun 5: 4799. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5799
Whitaker J, Ostle N, Nottingham, AT (2014) Microbial community composition explains soil respiration responses to changing carbon inputs along an Andes-to-Amazon elevation gradient. J Ecol 102(4): 1058–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12247
Wu Y, Zhang XF, Dong SK, et al. (2013) Species composition, diversity, and biomass of representative plant communities in eastern Arjin Mountain Nature Reserve, Northwest China. Chin J Ecol 32(9): 2250–2256. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.2013.0348
Xian XX, Kong FL, Zhu FL, et al. (2019) Effects of Water and Salt Gradients on Soil Nutrient Indices and Enzyme Activities in Coastal Wetlands. Bull Soil Water Conserv 39(1): 65–71. https://doi.org/10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.01.011
Xu YJ, Dong K, Jiang M, et al. (2022) Soil moisture and species richness interactively affect multiple ecosystem functions in a microcosm experiment of simulated shrub encroached grasslands. Sci Total Environ 803: 149950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149950
Yang H, Li Y, Wu M, et al. (2011) Plant community responses to nitrogen addition and increased precipitation: the importance of water availability and species traits. Global Change Biol 17(9): 2936–2944 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02423.x
Yin S, Wang CK, Jin Y, et al. (2019) Changes in soil-microbe-exoenzyme C:N:P stoichiometry along an altitudinal gradient in Mt. Datudingzi, Northeast China. Chin J Plant Ecol 43(11): 999–1009. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2019.0141
Yu JL, Bing HJ, Chang RY, et al. (2022) Microbial metabolic limitation response to experimental warming along an altitudinal gradient in alpine grasslands, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena 214: 106243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106243
Yuan GY (1991) The vertical natural zone of the alking moutains and east Kunlun mountains. J arid land Res Environ 5(1): 78–85. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.1991.01.009
Zhang M, Zhang XK, Liang WJ, et al. (2011) Distribution of soil organic carbon fractions along the altitudinal gradient in Changbai Mountain, China. Pedosphere 21(5): 615–620.
Zhang AL, Li XY, Wu SX, et al. (2021) Spatial pattern of C:N:P stoichiometry characteristics of alpine grassland in the Altun Shan Nature Reserve at North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 207: 105691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105691
Zhang JF, Zhang XD, Zhou JX, et al. (2005) Effects of salinity stress on poplars seedling growth and soil enzyme activity. Chin J Appl Ecol 16(3): 426–430. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-93322005.0462
Zhao DH, Shen CC, Zhang ZM, et al. (2022) Coupling relationship between soil functions and environmental factors along an altitudinal gradient: a case study of the Meili mountain. Environ Sci 44(2): 924–931. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202204207
Zheng MH, Zhou ZH, Luo YQ, et al. (2019) Global pattern and controls of biological nitrogen fixation under nutrient enrichment: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biol 25(9): 3018–3030. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14705
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tianshan Talent Plan (2022TSYCCX0001), Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang (2022D01D083) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U2003214 and 41977099). We thank the Ecological Processes and Biological Adaptation team for financial and experimental instrumentation help. Thanks got to LU Yong-xing GUO Hao and GUO Xing for their assistance in field sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This specific study was designed by ZHANG Shi-hang, with help from CHEN Yu-sen. Data extraction and statistical analyses were performed by ZHANG Shi-hang and CHEN Yu-sen. ZHANG Shi-hang wrote the first draft of the manuscript; LU Yong-xing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, ZHOU Xiao-bing and ZHANG Yuanming contributed substantially to revisions.
ZHOU Xiao-bing: Funding acquisition; Investigation; all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Sh., Chen, Ys., Lu, Yx. et al. Trends and drivers of soil multifunctionality along elevation gradients in the Altun Shan drylands of China. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 3203–3214 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8032-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8032-7