Abstract
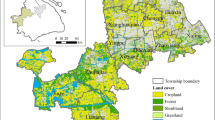
The Da-Xiao Liangshan mountains are critical ecological function areas and essential ecological barriers in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River in China. This study selected a total of six periods of land use land cover (LULC) data from 1995 to 2020, to estimate the ecosystem service value (ESV) and analyzed its spatiotemporal evolution and topographic gradient divergence. The results showed that: (1) The ESV increased by 1.1 billion yuan, with an increase rate of 1.47% from 1995 to 2020. Two time periods, 2005–2010 and 2015–2020, showed more significant increases than other periods. (2) The elevation and slope of mountainous areas determine the type of land use and further influence the spatial pattern of ESV. (3) Although woodland and grassland are the main land use types of the study area (more than 90%), the hydrological regulation function of the water area partially compensated for the impact of the encroachment of the built-up area on the ESV of grassland. (4) The spatial distribution of ESVs showed an inverted V-shaped characteristic as the topographic gradient increased, with the dominant position being the 5th topographic gradient zone. Finally, this study provided relevant recommendations for ecosystem protection and optimization. The findings of this study clarified the influence of topographical factors on the spatial differentiation of ESV and provided novel insights into ecosystem protection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao YB, Zhang HY, Yang LC, et al. (2021) Impacts of earthquake knowledge and risk perception on earthquake preparedness of rural residents. Nat Hazards 107: 1287–1310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04632-w
Amanibeni M, Chen Y, Vasileva M, et al. (2022) Quantitative-spatial relationships between air and surface temperature, a proxy for microclimate studies in fine-scale intra-urban areas? Sust Cities Soc 77: 103584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103584
Amanibeni M, Khalilnezhad M, Mahdizadeh S (2022) Hierarchical access to the edible landscape: the Akbarieh Garden in Iran. Landsc Res 47(3): 333–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/01426397.2021.2016667
Chen DS, Pan YQ, Jin XL, et al. (2021) The delineation of ecological redline area for catchment sustainable management from the perspective of ecosystem services and social needs: A case study of the Xiangjiang watershed, China. Ecol Indic 121: 107130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107130
Chen YZ, Xiao Y, Sun SQ, et al. (2019) Spatial-temporal changes of ESV in Xiangxi region based on terrain. Chin J Eco-Agric 27(4): 623–631. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.180751
Cheng Q, Zhou L, Wang T. (2022) Assessment of Ecosystem Services Value in Linghekou Wetland Based on Landscape Change. Environ Sustain Indic 15: 100195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2022.100195
Costanza R, d’Arge R, de Groot R, et al. (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387: 253–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/387253a0
Gong J, Xu C, Yan L, et al. (2021) Multi-scale analysis of ecosystem services trade-offs in an ecotone in the Eastern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Mt Sci 18(11): 2803–2819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6505-5
He R, Guo S, Deng X, et al. (2022a) Influence of social capital on the livelihood strategies of farmers under China’s rural revitalization strategy in poor mountain areas: a case study of the Liangshan Yi autonomous prefecture. J Mt Sci 19(4): 958–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6395-6
He Z, Shang X, Zhang T, et al. (2022b) Coupled regulatory mechanisms and synergy/trade-off strategies of human activity and climate change on ecosystem service value in the loess hilly fragile region of northern Shaanxi, China. Ecol Indic 143: 109325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109325
He N, Zhou Y, Wang L, et al. (2022c) Spatiotemporal differentiation and the coupling analysis of ecosystem service value with land use change in Hubei Province, China. Ecol Indic 145: 109693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109693
Jia G, Dong Y, Zhang S, et al. (2022) Spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem service trade-offs under the influence of forest conservation project in Northeast China. Front Ecol Evol 10: 978145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2022.978145
Li K, Zhang BY (2022) Spatial and temporal evolution of ecosystem service value in shaanxi province against the backdrop of Grain for Green. Forests 13(7): 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13071146
Li TH, Li WK, Qian ZH (2010) Variations in ecosystem service value in response to land use changes in Shenzhen. Ecol Econ 69(11): 1427–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.05.018
Long XR, Lin H, An XX, et al. (2022) Evaluation and analysis of ecosystem service value based on land use/cover change in Dongting Lake wetland. Ecol Indic 136: 108619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108619
Luo PY, Yu BJ, Li PF, et al. (2022) How 2D and 3D built environments impact urban surface temperature under extreme heat: A study in Chengdu, China. Build Environ 231: 110035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110035
Manley K, Nyelele C, Egoh BN (2022) A review of machine learning and big data applications in addressing ecosystem service research gaps. Ecosyst Serv 57: 101478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2022.101478
Ma S, Qiao YP, Wang LJ, et al. (2021) Terrain gradient variations in ecosystem services of different vegetation types in mountainous regions: Vegetation resource conservation and sustainable development. For Ecol Manage 482: 118856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118856
Pan NH, Guan QY, Wang QZ, et al. (2021) Spatial differentiation and driving mechanisms in ecosystem service value of arid region: a case study in the middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin, NW China. J Clean Prod 319: 128718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128718
Qin ZR, Zhao ZH, Xia LL, et al. (2023) Significant roles of core prokaryotic microbiota across soil profiles in an organic contaminated site: Insight into microbial assemblage, cooccurrence patterns, and potentially key ecological functions. Environ Res 231(2): 116195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116195
Sauter I, Kienast F, Bolliger J, et al. (2019) Changes in demand and supply of ecosystem services under scenarios of future land use in Vorarlberg, Austria. J Mt Sci 16(12): 2793–2809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5124-x
Song, G., Wang, P., 2017. Spatial pattern of land use along the terrain gradient of county in Songnen High Plain: A case study of Bayan county. Sci Geogr Sin 37: 1218–1225. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.08.012
Su SL, Xiao R, Jiang ZL, et al. (2012) Characterizing landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes for urbanization impacts at an eco-regional scale. Appl Geogr 34: 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.12.001
Tian J, Peng Y, Huang Y, et al. (2022) Identifying the priority areas for enhancing the ecosystem services in hilly and mountainous areas of southern China. J Mt Sci 19(2): 338–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6672-z
Wang Q, Li YB, Luo GJ (2020) Spatiotemporal change characteristics and driving mechanism of slope cultivated land transition in karst trough valley area of Guizhou Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 79: 284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09035-x
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chen X (2022) Spatiotemporal change in ecosystem service value in response to land use change in Guizhou Province, southwest China. Ecol Indic 144: 109514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109514
Wei D, Yang LC, Bao ZK, et al. (2022a). Variations in outdoor thermal comfort in an urban park in the hot-summer and cold-winter region of China. Sust Cities Soc 77: 103535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103535
Wei D, Zhao G, Liu S, et al. (2022b). Indoor thermal comfort in a rural dwelling in southwest China. Front Public Health 10: 1029390. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1029390
Wei JH, Wen YL, Gong ZJ, et al. (2022c). Land use changes and ecosystem service value in the buffer zone of Poyang Lake in recent 30 Years. Acta Geogr Sin 42(22): 9261–9273. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202108202321
Wu J, Wang G, Chen W, et al. (2022) Terrain gradient variations in the ecosystem services value of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Glob Ecol Conserv 34: e02008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2022.e02008
Xie GD, Zhang CX, Zhang LM, et al. (2015) Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. J Nat Resour 30(8): 1243–1254. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001
Xiao PN, Zhou Y, Li MY, et al. (2023) Spatiotemporal patterns of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effects of Hubei Province based on the InVEST model. Environ Dev Sustain 25: 6419–6448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02310-w
Xiong SG, Wan J, Long HL, et al. (2016) Spatiotemporal dynamics and implications of ecosystem service value in the key ecological function area: Case of Yichang City, Hubei Province. Soil Water Conserv Res 23(1): 296–302. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2016.01.046
Xu C, Li C, Zhang TZ, et al. (2017) Distribution and variation analysis of mountain ecosystem based on topographic gradient in Huailai County of Hebei Province. Soil Water Conserv Bull 37(5): 198–204. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13961/jxnki.stbctb.2017.05.033
Xu NY, Sun SQ, Xue DY, et al. (2019) Ecosystem service value and its spatial response to human interference on the basis of terrain gradient in Gannan region, China. Acta Geogr Sin 39(1): 97–107. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201809121965
Yang HJ, Gou XH, Xue B, et al. (2023) Research on the change of alpine ecosystem service value and its sustainable development path. Ecol Indic 146:108983. https://doi.org/10.1016/jxcolind.2023.109893
Yang SH, Hu SG, Qu SJ (2018) Terrain gradient effect of ecosystem service value in middle reach of Yangtze River, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 29(3): 976–986. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201803.016
Yang W, Chang J, Xu B, et al. (2008). Ecosystem service value assessment for constructed wetlands: A case study in Hangzhou, China. Ecol Econ 68(1–2): 116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.02.008
Zhou P, Zhang HJ, Huang B, et al. (2022) Are productivity and biodiversity adequate predictors for rapid assessment of forest ecosystem services values? Ecosyst Serv 57: 101466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2022.101466
Zhang XB, Luo J, Shi PJ, et al. (2020) Spatial-temporal evolution pattern and terrain gradient differentiation of ecosystem service value in Zhangye, Northwest China at the grid scale. Chin J Appl Ecol 31(2): 543–553. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202002.007
Zhang XY, Lu L, Yu H, et al. (2021) Multi-scenario simulation of the impacts of land-use change on ecosystem service value on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin J Ecol 40(3): 887–898. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202103.025
Zhao R, Zhang LP, Yao MX, et al. (2020) A geographically weighted regression model augmented by Geodetector analysis and principal component analysis for the spatial distribution of PM2.5. Sust Cities Soc 56: 102106.
Acknowledgments
The paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52078423), the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (Grant No. 2020YFS0309 and 2020YFS0054), the China Engineering Science and Technology Strategic Consulting Project (Grant No. 2022JDR0356), and the Key Research Institution of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Sichuan Province: Research Center of National Parks (Grant No. GJGY2023-YB001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JIN Tao: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. CHEN Yang: conceptualization, methodology, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. SHU Bo: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology. GAO Min: data curation, formal analysis, visualization. QIU Jian: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, writing-review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Data Availability: Due to the sensitive nature of the data, it is not made openly accessible. Researchers interested in accessing the data can contact the corresponding author.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, T., Chen, Y., Shu, B. et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value and topographic gradient effect in the Da-Xiao Liangshan Mountains in Sichuan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 2344–2357 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-7986-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-7986-9