Abstract
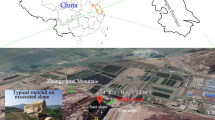
Zhangmu Town in Tibet of China, which lies in the southern piedmont of the median Himalayas, is a small but strategically important port of trade exchange between China and Nepal. Many rockfall events have occurred in Zhangmu since 1970, resulting in huge economic losses and serious influence on the bilateral trade. We conducted a detailed field investigation on the high and steep slope in Zhangmu Town, and analyzed the distribution features, stability, failure modes and evolution of dangerous rocks of potential rockfalls. Then we numerically simulated the movement path, velocity and accumulation forms of the rockfall with PFC3D program. The results indicated that the dangerous rock belt could be divided into three sections, namely, unstable section, slightly stable section and basically stable section. It was estimated that the rock debris and single dangerous rock would be unstable in the case of earthquakes or rainstorms. Due to the terrain constraints, the fallen rocks would scatter near the mouth of the Zhangmu ditch and in the Buqu River through multiple times of rolling, collision-induced diversion and bouncing. Without reinforcement, the rockfall could cause serious damage to the car parks, gas stations and National Highway 318 along the line from Zhangmu Town to Zhangmu ditch. Based on the field survey and numerical simulation, we recommended rockfall removal and interception as the major prevention measures, and protective sheds as auxiliary measure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abellán A, Vilaplana JM, Martínez J (2006) Application of a long-range Terrestrial Laser Scanner to a detailed rockfall study at Vall de Núria (Eastern Pyrenees, Spain). Eng Geol 88(3–4):136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.09.012
Agliardi F, Crosta GB (2003) High resolution three-dimensional numerical modelling of rockfalls. International Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(4):455–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00021-2
Binal A, Ercanoglu M (2010) Assessment of rockfall potential in the Kula (Manisa, Turkey) Geopark Region. Environ Earth Sci 61(7):1361–1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0454-1
Chen G, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Wu J (2013) Numerical Simulation in Rockfall Analysis: A Close Comparison of 2-D and 3-D DDA. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46(3):527–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0360-9
Collins BD, Stock GM (2016) Rockfall triggering by cyclic thermal stressing of exfoliation fractures. Nat Geosci 9(5):395–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2686
Corona C, Lopez-Saez J, Favillier A, et al. (2017) Modeling rockfall frequency and bounce height from three-dimensional simulation process models and growth disturbances in submontane broadleaved trees. Geomorphology 281:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.12.019
Dhakal S, Bhandary NP, Yatabe R, Kinoshita N (2011) Experimental, numerical and analytical modelling of a newly developed rockfall protective cable-net structure. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 11(12):3197–3212. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-3197-2011
Dussauge C, Grasso JR, Helmstetter A (2003) Statistical analysis of rockfall volume distributions: Implications for rockfall dynamics. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 108 (B6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000650
Gischig VS, Hungr O, Mitchell A, Bourrier F (2015) Pierre3D: a 3D stochastic rockfall simulator based on random ground roughness and hyperbolic restitution factors. Can Geotech J 52(9):1360–1373. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0312
Hu J, Li SC, Li LP, et al. (2018) Field, experimental, and numerical investigation of a rockfall above a tunnel portal in southwestern China. B Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1365–1382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1152-y
Johari A, Javadi AA (2012) Reliability assessment of infinite slope stability using the jointly distributed random variables method. Scientia Iranica 19(3):423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scient.2012.04.006
Klimes J (2011) Rockfall Hazard And Risk Assessment on Forested Slopes, Examples From Czechia. Geografie-Prague 116(2):144–155. https://doi.org/10.37040/geografie2011116020144
Koo RCH, Kwan JSH, Lam C, et al. (2016) Dynamic response of flexible rockfall barriers under different loading geometries. Landslides 14(3):905–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0772-9
Lambert S, Bourrier F, Toe D (2013) Improving three-dimensional rockfall trajectory simulation codes for assessing the efficiency of protective embankments. Int J Rock Mech Min 60:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.12.029
Leine RI, Schweizer A, Christen M, et al. (2013) Simulation of rockfall trajectories with consideration of rock shape. Multibody Sys Dyn 32(2):241–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-013-9393-4
Li HB, Li XW, Li WZ, et al. (2019) Quantitative assessment for the rockfall hazard in a post-earthquake high rock slope using terrestrial laser scanning. Eng Geol 248:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.11.003
Li K, Meng LH, Xu S, An L (2016) Method to determine microscopic parameters pf pfc2d numerical model. J Northeastern Univ 37(4):563–567. https://doi.org/10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.04.023
Lu N, Godt J (2008) Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions. Water Resour Res 44 (11). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006976
Mavrouli O, Corominas J (2010) Rockfall vulnerability assessment for reinforced concrete buildings. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 10(10):2055–2066. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-10-2055-2010
Pappalardo G, Mineo S, Rapisarda F (2014) Rockfall hazard assessment along a road on the Peloritani Mountains (northeastern Sicily, Italy). Nat Hazard Earth Sys 14(10):2735–2748. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-2735-2014
Piacentini D, Ercolessi G, Pizziolo M, Troiani F (2015) Rockfall runout, Mount Cimone area, Emilia-Romagna Region, Italy. J Maps 11(4):598–605. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2014.956154
Plassiard JP, Donze FV (2010) Optimizing the design of rockfall embankments with a discrete element method. Eng Struct 32(11):3817–3826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.08.025
Rammer W, Brauner M, Dorren LKA, et al. (2010) Evaluation of a 3-D rockfall module within a forest patch model. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 10(4):699–711. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-10-699-2010
Sarro R, Mateos RM, García-Moreno I, et al. (2014) The Son Poc rockfall (Mallorca, Spain) on the 6th of March 2013: 3D simulation. Landslides 11(3):493–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0487-8
Shen WG, Zhao T, Dai F, et al. (2019) DEM analyses of rock block shape effect on the response of rockfall impact against a soil buffering layer. Eng Geol 249:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.011
Singh PK, Kainthola A, Panthee S, Singh TN (2016) Rockfall analysis along transportation corridors in high hill slopes. Environ Earth Sci 75 (5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5489-5
Sturzenegger M, Sartori M, Jaboyedoff M, Stead D (2007) Regional deterministic characterization of fracture networks and its application to GIS-based rock fall risk assessment. Eng Geol 94(3–4):201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.08.002
Tan DY, Yin JH, Qin JQ, et al. (2018) Large-scale physical modeling study on the interaction between rockfall and flexible barrier. Landslides 15(12):2487–2497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1058-1
Thoeni K, Giacomini A, Lambert C, et al. (2014) A 3D discrete element modelling approach for rockfall analysis with drapery systems. Int J Rock Mech Min 68:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.008
Viero A, Furlanis S, Squarzoni C, et al. (2012) Dynamics and mass balance of the 2007 Cima Una rockfall (Eastern Alps, Italy). Landslides 10(4):393–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0338-4
Volkwein A, Schellenberg K, Labiouse V, et al. (2011) Rockfall characterisation and structural protection — a review. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 11(9):2617–2651. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-2617-2011
Wei LW, Chen H, Lee CF, et al. (2014) The mechanism of rockfall disaster: A case study from Badouzih, Keelung, in northern Taiwan. Eng Geol 183:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.10.008
Xia M, Zhao C (2014) Dimensional analysis of effects of microscopic parameters on macroscopic parameters for clump parallel-bond model. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(2):327–338. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.02.008
Yu ZX, Zhao L, Liu YP, et al. (2019) Studies on flexible rockfall barriers for failure modes, mechanisms and design strategies: a case study of Western China. Landslides 16(2):347–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1093-y
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2019YFC1509704) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1704243).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zf., Liu, Hd., He, Sm. et al. Field investigation and numerical simulation on rockfalls in Zhangmu Town, Tibet, China. J. Mt. Sci. 19, 740–755 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-7095-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-7095-6