Abstract
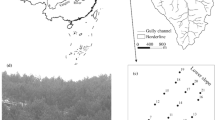
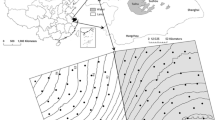
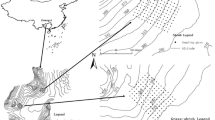
Soil water content (SWC) plays a crucial role in simulating hydrological process, guiding reforestation and controlling soil erosion in mountainous regions. Spatial-temporal variability of SWC increases the difficulty of quantifying SWC pattern in the prediction of soil moisture. Temporal stability analysis of SWC can reduce the labor consuming and simplify the costly field monitoring. This study aimed to evaluate the temporal stability of SWC at hourly, daily and monthly temporal periods and its controlling factors at a hillslope in the Three Gorges region. The SWC of five soil depths was monitored at 5 topographic locations (toe, lower, middle, upper and top slope positions) along a 170 m hillslope in the Three Gorges region (110°04′ ∼112°04′ E, 29°53′∼31°34′ N), Yichang City, Hubei Province, China from May 4th, 2018 to May 3rd, 2019. The results showed that the coefficient of variation of SWC ranged from 4% to 49%, which increased with rising soil depth within 40 cm but thereafter decreased. However, the high Spearman’s rank coefficients (P<0.05) indicated strong temporal stability at three temporal periods. The representative locations (RLs) varied in the different soil depths, which were toe, upper and middle slope positions at 0∼40, 40∼60 and 60∼80 cm depths of the investigated hillslope, respectively. Saturated hydraulic conductivity served as a dominant factor controlling the temporal stability of SWC. The result advances our thorough understanding of hydrology and soil water resource in the Three Gorges region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroni G, Ortuani B, Facchi A, Gandolfi C (2013) The role of vegetation and soil properties on the spatio-temporal variability of the surface soil moisture in a maize cropped field. J Hydrol 489: 148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.03.007
Biswas A (2014) Season and depth-dependent time stability for characterizing representative monitoring locations of soil water storage in a hummocky landscape. Catena 116: 38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.12.008
Boulet A, Prats SA, Malvar MC, González-Pelayo O (2015) Surface and subsurface flow in eucalyptus plantations in northcentral Portugal. J Hydrol Hydromech 63: 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1515/johh-2015-0015
Burns TT, Berg AA, Cockburn J, Tetlock E (2016) Regional scale spatial and temporal variability of soil moisture in a prairie region. Hydrol Process 30: 3639–3649. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10954
Chaney NW, Roundy JK, Herrera-Estrada JE, Wood EF (2015) High-resolution modeling of the spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture: Applications in network design. Water Resour Res 51: 619–638. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014964
Chen F, Song Nina, Chen G, Wang J (2015) Effects of exotic species Larix kaempferi on diversity and activity of soil microorganisms in Dalaoling National Forest Park. Ecological Processes 4(1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-015-0037-x
Cheng S, Li Z, Xu G, Li P, Zhang T, Cheng Y (2017) Temporal stability of soil water storage and its influencing factors on a forestland hillslope during the rainy season in China’s Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 76: 539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6850-z
Duan L, Huang M, Li Z, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2017) Estimation of spatial mean soil water storage using temporal stability at the hillslope scale in black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) stands. Catena 156: 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.03.023
Famiglietti JS, Ryu D, Berg AA, Rodell M, Jackson TJ (2008) Field observations of soil moisture variability across scales. Water Resour Res 44 (16): W01423. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005804
Gao L, Shao M (2012) Temporal stability of soil water storage in diverse soil layers. Catena 95: 24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.02.020
Gao L, Wang Y, Geris J (2019) The role of sampling strategy on apparent temporal stability of soil moisture under subtropical hydroclimatic conditions. J Hydrol 3: 260–270. https://doi.org/10.2478/johh-2019-0006
Gao L, Peng X, Biswas A (2020) Temporal instability of soil moisture at a hillslope scale under subtropical hydroclimatic conditions. Catena 187: 104362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104362
Guber A, Gish T, Pachepsky Y, et al. (2008) Temporal stability in soil water content patterns across agricultural fields. Catena 73: 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Catena.2007.09.010
He Z, Zhao M, Zhu X (2019) Temporal stability of soil water storage in multiple soil layers in high elevation forests. J Hydrol 569: 532–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.024
Heathman G, Cosh M, Merwade V, Han E (2012) Multi-scale temporal stability analysis of surface and subsurface soil moisture within the upper cedar creek watershed, Indian. Catena 95: 91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.03.008
Hu W, Shao M, Han F, Reichardt K, Tan J (2010) Watershed scale temporal stability of soil water content. Geoderma 158: 181–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.04.030
Hu W, Tallon L, Si B (2012) Evaluation of time stability indices for soil water storage upscaling. J Hydrol 475: 229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.09.050
Hu W, Si B (2016) Estimating spatially distributed soil water content at small watershed scales based on decomposition of temporal anomaly and time stability analysis. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20: 571–587. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-12-6467-2015
Hupet F, Vanclooster M (2002) Intraseasonal dynamics of soil moisture variability within a small agricultural maize cropped field. J Hydrol 261: 86–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00016-1
Jacobs J, Hsu E, Choi M (2010) Time stability and variability of electronically scanned thinned array radiometer soil moisture during Southern Great Plains hydrology experiments. Hydrol Process 24: 2807–2819. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7703
Jacobs J, Mohanty B, En-Ching H, Miller D (2004) SMEX02: field scale variability, time stability and similarity of soil moisture. Remote Sens Environ 92: 436–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.02.017
Jacopo D, Renato M (2019) Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture: Addressing the monitoring at the catchment scale. J Hydrol 570: 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.014
Jarasiunas G, Kinderiene L (2016) Impact of agro-environmental systems on soil erosion processes and soil properties on hilly landscape in Western Lithuania. J Environ Eng Landsc 24: 60–69. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2015.1054289
Jia Y, Shao M (2013) Temporal stability of soil water storage under four types of revegetation on the northern Loess Plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 117: 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.10.013
Joshi Champa, Binayak P. Mohanty, Jennifer M. Jacobs (2011) Spatiotemporal analyses of soil moisture from point to footprint scale in two different hydroclimatic regions. Water Resour Res 47(1): 105–118. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR009002
Koch J, Cornelissen T, Fang Z, Bogena H, Diekkrüger B, Kollet S, Stisen S (2016) Inter-comparison of three distributed hydrological models with respect to seasonal variability of soil moisture patterns at a small forested catchment. J Hydrol 533: 234–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.002
Lai X, Zhu Q, Zhou Z, Liao K (2017) Influences of sampling size and pattern on the uncertainty of correlation estimation between soil water content and its influencing factors. J Hydrol 555: 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.10.010
Lai X, Zhou Z, Zhu Q, Liao K (2018) Identifying representative sites to simultaneously predict hillslope surface and subsurface mean soil water contents. Catena 167: 363–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.016
Lee E, Kim S (2019) Seasonal and spatial characterization of soil moisture and soil water tension in a steep hillslope. J Hydrol 568: 676–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.11.027
Li X, Shao M, Jia X, Wei X (2016) Profile distribution of soil water content and its temporal stability along a 1340-m long transect on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 137: 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.09.005
Liu Z, Wang Y, Tian A, Yu P, Xiong W, Xu L, Wang Y (2017) Intra-annual variation of stem radius of Larix principis-rupprechtii and its response to environmental factors in Liupan Mountains of Northwest China. Forests 8: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100382
Liu Z, Wang Y, Yu P, Tian A, Wang Y, Xiong W, Xu L (2018) Spatial pattern and temporal stability of root-zone soil moisture during rowing season on a larch plantation hillslope in northwest China. Forests 9: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9020068
Lv L, Liao K, Lai X, Zhu Q, Zhou S (2016) Hillslope soil moisture temporal stability under two contrasting land use types during different time periods. Environ Earth Sci 75: 560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5238-1
Manfreda S, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (2006) On the spatial and temporal sampling of soil moisture fields. Water Resour Res 42: W05409. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004548
Martinez G, Pachepsky Y, Vereecken H, Hardelauf H, Herbst M, Vanderlinden K (2013) Modeling local control effects on the temporal stability of soil water content. J Hydrol 481: 106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.024
Martínez G, Pachepsky Y, Vereecken H (2014) Temporal stability of soil water content as affected by climate and soil hydraulic properties: a simulation study. Hydrol Process 28: 1899–1915. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9737
Metzger J, Wutzler T, Dalla Valle, et al. (2017) Vegetation impacts soil water content patterns by shaping canopy water fluxes and soil properties. Hydrol Process 31: 3783–3795. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11274
Nasta P, Penna D, Brocca L, Zuecco G, Romano N (2018) Downscaling near-surface soil moisture from field to plot scale: A comparative analysis under different environmental conditions. J Hydrol 557: 97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.017
Patrick J, Starks Gary (2005) Heat temporal stability of soil moisture profile J Hydrol 324: 400–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.09.024
Penna D, Brocca L, Borga M, Dalla Fontana G (2013) Soil moisture temporal stability at different depths on two alpine hillslopes during wet and dry periods. J Hydrol 477: 55–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.052
Qiu Y, Fu B, Wang J, Chen L (2001) Spatial variability of soil moisture content and its relation to environmental indices in a semi-arid gully catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J Arid Environ 49: 723–750. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2001.0828
Rosenbaum U, Bogena H, Herbst M, et al. (2012) Seasonal and event dynamics of spatial soil moisture patterns at the small catchment scale. Water Resour Res 51 (1): 619–638. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2001.0828
Trancoso R, Larsen J, McAlpine C, McVicar T, Phinn S (2016) Linking the Budyko framework and the Dunne diagram. J Hydrol 535:581–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.017
Vachaud G, Passerat de Silans A, Balabanis P, Vauclin M (1985) Temporal stability of spatial measured soil water probability density function. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49: 822–828. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900040006x
Vivoni E, Gebremichael M, Watts C, Bindlish R, Jackson T (2006) Comparison of ground-based and remotely-sensed surface soil moisture estimates over complex terrain during SMEX04. Remote Sens Environ 112: 314–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.10.028
Wang X, Pan Y, Zhang Y, et al. (2013) Temporal stability analysis of surface and subsurface soil moisture for a transect in artificial revegetation desert area, China. J Hydrol. 507: 100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.021
Wang W, Zhang F, Yuan L, et al. (2016) Environmental factors effect on stem radial variations of Picea crassifolia in Qilian Mountains, Northwestern China. Forests 7: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7100210
Xu G, Li Z, Li P (2017) The spatial pattern and temporal stability of the soil water content of sloped forestland on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Sci Soc Am J 81: 902–914. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2016.10.0331
Zhang P, Shao M (2013) Temporal stability of surface soil moisture in a desert area of northwestern China. J Hydrol 505: 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.08.045
Zhao W, Cui Z, Zhang J (2017) Temporal stability and variability of soil water content in a gravel-mulched field in northwestern China. J Hydrol 552: 249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.031
Zhou J, Fu B, Lv N, et al. (2013) Temporal stability of soil moisture under different land uses/cover in the Loess Plateau based on a finer spatio-temporal period. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 10: 10083–10125. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-10-10083-2013
Zhu Q, Lin H (2009) Simulation and validation of concentrated subsurface lateral flow paths in an agricultural landscape. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13: 1503–1518. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-13-1503-2009
Zhu Q, Zhou Z, Duncan E (2017) Integrating real-time and manual monitored data to predict hillslope soil moisture dynamics with high spatio-temporal resolution using linear and non-linear models. J Hydrol 545: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.014
Acknowledgement
Financial support for this research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41771261 and 41601215), Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2015CFA141 and 2016CFA027), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. CCNU18QN002 and CCNU17ZDJC06). We appreciate the assistance from the Governors of the Dalaoling Forest Park during the field experiment. Special thanks go to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Ys., Liu, Mx., Yi, J. et al. Temporal stability analysis of soil moisture along a coniferous forest hillslope with subtropical monsoon climate in southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 18, 2900–2914 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6679-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6679-5