Abstract
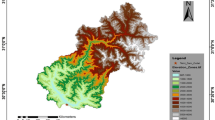
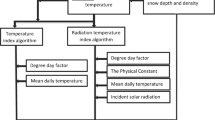
In this paper, the performance of the classic snowmelt runoff model (SRM) is evaluated in a daily discharge simulation with two different melt models, the empirical temperature-index melt model and the energy-based radiation melt model, through a case study from the data-sparse mountainous watershed of the Urumqi River basin in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China. Theclassic SRM, which uses the empirical temperature-index method, and a radiation-based SRM, incorporating shortwave solar radiation and snow albedo, were developed to simulate daily runoff for the spring and summer snowmelt seasons from 2005 to 2012, respectively. Dailymeteorological and hydrological data were collected from three stations located in the watershed. Snowcover area (SCA) was extracted from satellite images. Solarradiation inputs were estimated based on a digital elevation model (DEM). Theresults showed that the overall accuracy of the classic SRM and radiation-based SRM for simulating snowmelt discharge was relatively high. Theclassic SRM outperformed the radiation-based SRM due to the robust performance of the temperature-index model in the watershed snowmelt computation. Nosignificant improvement was achieved by employing solar radiation and snow albedo in the snowmelt runoff simulation due to the inclusion of solar radiation as a temperature-dependent energy source and the local pattern of snowmelt behavior throughout the melting season. Ourresults suggest that the classic SRM simulates daily runoff with favorable accuracy and that the performance of the radiation-based SRM needs to be further improved by more ground-measured data for snowmelt energy input.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudu S, Cui C, Saydi M, et al. (2012) Application of snowmelt runoff model (SRM) in mountainous watersheds: A review. WaterScience and Engineering 5(2): 123–136. https://doi.org/10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.02.001
Azmat M, Choi M, Kim TW, et al. (2016) Hydrological modeling to simulate streamflow under changing climate in a scarcely gauged cryosphere catchment. EnvironmentalEarth Sciences 75: 186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5059-2
Abudu S, Sheng Z, Cui C, et al. (2016) Integration of aspect and slope in snowmelt runoff modeling in a mountain watershed. WaterScience and Engineering 9(4): 265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2016.07.002
Brubaker KL, Rango A (1996) Response of snowmelt hydrology to climate change. WaterAir and Soil Pollution 90(1-2), 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619293
Boudhar A, Hanich L, Boulet G, et al. (2009) Evaluation of the snowmelt runoff model in the Moroccan High Atlas Mountains using two snow-cover estimates. HydrologicalScience Journal 54(6): 1094–1113. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.6.1094
Bilal H, Chamhuri S, Mazlin BM, et al. (2019). Recentsnow cover variation in the Upper Indus Basin of Gilgit Baltistan, Hindukush Karakoram Himalaya. Journalof Mountain Science 16(2): 296–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5201-3
Dou Y, Chen X, Bao A, et al. (2011) The simulation of snowmelt runoff in the ungauged Kaidu River Basin of TianShan Mountains, China. EnvironmentalEarth Sciences 62(5): 1039–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0592-5
Dey B, Sharma VK, Rango A (1989) A test of snowmelt-runoff model for a major river basin in Western Himalayas. HydrologyResearch 20(3): 167–178. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.1989.0013
Forbes KA, Kienzle SW, Coburn CA, et al. (2011) Simulating the hydrological response to predicted climate change on a watershed in southern Alberta, Canada. ClimaticChange 105(3-4), 555–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9890-x
Fu P, Rich PM (1999) Design and implementation of the Solar Analyst: an ArcView extension for modeling solar radiation at landscape scales. Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual ESRI User Conference, San Diego USA.
Hock R (1999) A distributed temperature-index ice-and snowmelt model including potential direct solar radiation. Journalof Glaciology 45(149): 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022143000003087
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV (1995) Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer data. RemoteSensing of Environment 54(2): 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(95)00137-P
Hock R (2003) Temperature index melt modelling in mountain areas. Journalof Hydrology 282(1-4), 104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00257-9
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV, et al. (2002) MODIS snow-cover products. RemoteSensing of Environment 83(1-2), 181–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00095-0
Hu R (2004) Physical Geography of the Tianshan Mountains in China. ChinaEnvironmental Science Press. 140–233. (In Chinese)
Huang W, Huang Z, Cui C. (2007) Temporal and spatial distribution of snow density and its characteristics in Xinjiang. Journalof Glaciology and Geocryology 29(1): 66–71. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2007.01.011
Han P, Long D, Han Z, et al. (2019) Improved understanding of snowmelt runoff from the headwaters of China’s Yangtze River using remotely sensed snow products and hydrological modeling. RemoteSensing of Environment 224: 44–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.01.041
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2010) Assessment of snowmelt runoff using remote sensing and effect of climate change on runoff. WaterResources Management 24(9): 1763–1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9523-1
Hofierka J, Šúri M (2002) The solar radiation model for Open source GIS: implementation and applications. Proceedings of the Open source GIS — GRASS users’ conference, Trento Italy, September 2002.
Karimi H, Zeinivand H, Tahmasebipour N, et al. (2016) Comparison of SRM and WetSpa models efficiency for snowmelt runoff simulation. EnvironmentalEarth Sciences 75: 664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5490-z
Kondo J, Yamazaki T (1990) A Prediction model for snowmelt, snow surface temperature and freezing depth using a heat balance method. Journalof Applied Meteorology 29: 375–384. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1990)0290375:APMFSS2.0.CO;2
Kumar L, Skidmore AK, Knowles E (1997) Modeling topographic variation in solar radiation in a GIS environment. InternationalJournal of Geographic Information Science 11(5): 475–497. https://doi.org/10.1080/136588197242266
Li X, Williams MW (2008) Snowmelt runoff modeling in an arid mountain watershed, Tarim Basin, China. HydrologicalProcesses 22(19): 3931–3940. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7098
Liu B, Jordan RC (1960) The interrelationship and characteristic distribution of direct, diffuse and total solar radiation. SolarEnergy 4(3): 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(60)90062-1
Li H, Wang J. (2008) The snowmelt runoff model applied in the Upper Heihe River Basin. Journalof Glaciology and Geocryology 30(5): 769–775. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/ir.casnw.net/handle/362004/11922
Ma H, Cheng G (2003) A test of snowmelt runoff model (SRM) for the Gongnaisi River basin in the western Tianshan Mountainous, China. ChineseScience Bulletin 48(20): 2253–2259. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182862
Martinec J (1975) Snowmelt runoff model for stream flow forecasts. HydrologyResearch 6(3): 145–154. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.1975.0010
Martinec J, Rango A, Roberts RT (2008) Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) User’s Manual. NewMexico State University Press. 19–39.
Martinec J, Rango A (1986) Parameter Values for Snowmelt Runoff Modelling. Journalof Hydrology 84(3-4), 197–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(86)90123-X
Marcil GK, Trudel M, Leconte R (2016) Using Remotely Sensed MODIS Snow Product for the Management of Reservoirs in a Mountainous Canadian Watershed. WaterResources Management 30(8): 2735–2747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1319-5
Meng X, Yu D, Liu Z (2015) Energy Balance-Based SWAT Model to Simulate the Mountain Snowmelt and Runoff — Taking the Application in Juntanghu Watershed (China) as an Example. Journalof Mountain Science 12(2): 368–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3081-6
Nagler T, Rtto H, Malcher P, et al. (2008) Assimilation of meteorological and remote sensing data for snowmelt runoff forecasting. RemoteSensing of Environment 112(4): 1408–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.07.006
Pellicciotti F, Brock B, Strasser U, et al. (2005) An enhanced temperature-index glacier melt model including the shortwave radiation balance: Development and testing for Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. Journalof Glaciology 51(175): 573–587. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756505781829124
Rango A, Martinec J (1995) Revisiting the degree-day method for snowmelt computations. Journalof the American Water Resources Association 31(4): 657–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1995.tb03392.x
Roesch A, Gilgen A, Wild M, et al. (1999) Assessment of GCM simulated snow albedo using direct observations. ClimateDynamics, 15(6): 405–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820050290
Rango A, Martinec J (1981) Accuracy of snowmelt runoff simulation. NordicHydrology 12(4-5), 265–274. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.1981.0021
Saydi M, Abudu S, Cui C, et al. (2013) Hydrological characteristics of typical watersheds in North Tianshan. Journalof China Hydrology 33(2): 87–92. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2013.02.018
Saydi M, Ding J, Abudu S, et al. (2016) Simulation of snowmelt runoff in the northern slope of Tianshan mountains. AridZone Research 33(3): 636–642. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13866/j.azr.2016.03.25
Tekeli AE, Akyürek Z, Şorman A (2005) Using MODIS snow cover maps in modeling snowmelt runoff process in the eastern part of Turkey. RemoteSensing of Environment 97(2): 216–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2005.03.013
Vicuña S, Garreaud RD, Mcphee J (2011) Climate change impacts on the hydrology of a snowmelt driven basin in semiarid Chile. ClimaticChange 105(3-4), 469–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9888-4
Verdhen A, Chahar BR, Sharma OP (2014) Snowmelt modelling approaches in watershed models: computation and comparison of efficiencies under varying climatic conditions. WaterResources Management 28(11): 3439–3453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0662-7
Vafakhah M, Nouri A, Alavipanah SK (2015) Snowmelt-runoff estimation using radiation SRM model in Taleghan watershed. EnvironmentalEarth Sciences 73(3): 993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3449-5
Wu L, Li H, Wang L (2011) Application of a degree -day model for determination of mass balance of Urumqi Glacier No.1, Eastern Tianshan, China Journal of Earth Science 22(4): 470–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-011-0201-x
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (1986) Intercomparison of models of snowmelt runoff. GenevaSwitzerland, World Meteorological Organization.
Xie S, Du J, Zhou X, et al. (2018) A progressive segmented optimization algorithm for calibrating time-variant parameters of the snowmelt runoff model (SRM). Journalof Hydrology 566: 470–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.030
Yang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z (1992) A Study on the Snow Density in the Head Area of Urumqi River Basin. ActaGeographica Sinica 3: 260–266. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.11821/xb199203007
Zeinivand H, de Smedt FD (2010) Prediction of snowmelt floods with a distributed hydrological model using a physical snow mass and energy balance approach. NaturalHazards 54(2): 451–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-009-9478-9
Zhang Y, Liu S, Ding Y (2007) Glacier meltwater and runoff modelling, Keqicar Baqi glacier, southwestern Tien Shan, China. Journalof Glaciology 53(180): 91–98. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3189/172756507781833956
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771470, 51069017 and 41261090). Wethank Professor A-xing ZHU at the Department of Geography University of Wisconsin-Madison for his advice on the introduction and structure of this paper. Wealso thank the additional support from Maryam Basit at the Xinjang Bureau of Water Resources and Hydrology, Urumqi, and Anwar Kadir from the Xinjiang Water Resources Center, Urumqi, for their assistance in the basin characteristics analysis. Thehydrological and meteorological data used in this paper were provided by the Xinjiang Water Resources Research Institute, the Xinjang Water Resources and Hydrology Bureau and the National Meteorological Information Center of China. TheDEM and MODIS data were obtained from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saydi, M., Ding, Jl., Sagan, V. et al. Snowmelt modeling using two melt-rate models in the Urumqi River watershed, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. J. Mt. Sci. 16, 2271–2284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5365-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5365-8