Abstract
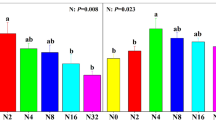
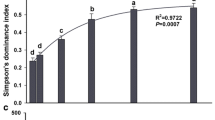
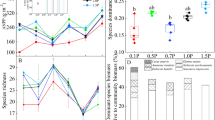
The mechanism that sustains the temporal stability of aboveground net primary production (ANPP) respond to nitrogen deposition is still controversial. Consequently, we investigated the mechanism of temporal stability of ANPP through the effect of N addition on diversity, species asynchrony and portfolio effects in northern Tibet alpine steppe over a period of three years. Our results showed that the community temporal stability did not significantly correlate with the species richness and Shannon-Wiener diversity. Species asynchrony and stability was also not significantly affected by N addition (p > 0.05). Furthermore, there was no significant relationship between species asynchrony and temporal stability. Although the value of portfolio effects (z) (z = 1.304, 95% confidence intervals: 1.029–1.597) was more than 1, the portfolio effects was not a primary driver of temporal stability due to the biodiversity being unaffected. The above results suggested that the richness, species asynchrony and portfolio effect could not support for mechanism of stability at the alpine steppe. From the results of path analysis, species temporal stability positively supports the community temporal stability in the alpine steppe ecosystem. According to the character of environment and vegetation of alpine steppe at North Tibet, we inferred that dominance species stability is more important than species richness for the community temporal stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezemer TM, Putten WHVD (2007) Ecology: diversity and stability in plant communities. Nature 446 (7135): 7–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05749
Clark CM, Cleland EE, Collins SL, et al. (2007) Environmental and plant community determinants of species loss following nitrogen enrichment. Ecology Letter 10(7): 596. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01053.x
Cottingham KL, Brown BL, Lennon JT (2001) Biodiversity may regulate the temporal variability of ecological systems. Ecology Letter 4(1): 72–85. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00189.x
Gonzalez A, Loreau M (2009) The causes and consequences of compensatory dynamics in ecological communities. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics System. 40(1): 393–414. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.39.110707.173349
Grman E, Lau JA, Schoolmaster DR, et al. (2010) Mechanisms contributing to stability in ecosystem function depend on the environmental context. Ecology Letter 13(11): 1400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01533.x
Hautier Y, Niklaus PA, Hector A (2009) Competition for light causes plant biodiversity loss after eutrophication. Science 324: 636–638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1169640
Hautier Y, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, et al. (2014) Eutrophication weakens stabilizing effects of diversity in natural grasslands. Nature 508(7497): 521. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13014
Hautier Y, Tilman D, Isbell F, et al. (2015) Anthropogenic environmental changes affect ecosystem stability via biodiversity. Science 348(6232): 336–40. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa1788
Hector A, Hautier Y, Saner P, et al. (2010) General stabilizing effects of plant diversity on grassland productivity through population asynchrony and overyielding. Ecology 91(8): 2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1162.1
Hillebrand H, Bennett DM, Cadotte MW (2008) Consequences of dominance: a review of evenness effects on local and regional ecosystem processes. Ecology 89(6): 1510–1520. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-1053.1
Houlahan JE, Currie DJ, Cottenie K, et al. (2007) From the cover: compensatory dynamics are rare in natural ecological communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104(9): 3273–3277. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603798104
Isbell F, Reich PB, Tilman D, et al. (2013) Nutrient enrichment, biodiversity loss, and consequent declines in ecosystem productivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110(29): 11911. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1310880110
Isbell FI, Polley HW, Wilsey BJ (2009) Species interaction mechanisms maintain grassland plant species diversity. Ecology 90(7): 1821. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0514.1
Ives AR, Carpenter SR (2007) Stability and diversity of ecosystems. Science 317(5834): 58–62. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133258
Jia JY (2008) Study of atmospheric wet deposition of Nitrogen in Tibetan Plateau Dissertation, Tibet University. China
Ladwig LM, Collins SL, Swann AL, et al. (2012) Above- and belowground responses to nitrogen addition in a chihuahuan desert grassland. Oecologia 169(1): 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-2173-z
Leps J (2004) Variability in population and community biomass in a grassland community affected by environmental productivity and diversity. Oikos 107: 64–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.13023.x
Loreau M, de Mazamcourt C (2013) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability: a synthesis of underlying mechanisms. Ecology Letters 16: 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12073
Loreau M, de Mazancourt C (2008) Species synchrony and its drivers: neutral and nonneutral community dynamics in fluctuating environments. The American Naturalist 172: E48–E66. https://doi.org/10.1086/589746
Murdoch WW, Stewart-Oaten A (1989) Aggregation by parasitoids and predators: effects on equilibrium and stability. American Naturalist 134: 288–310.
Polley H W, Wilsey B J, Derner JD (2007) Dominant species constrain effects of species diversity on temporal variability in biomass production of tallgrass prairie. Oikos 116(12): 2044–2052. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2007.0030-1299.16080.x
Sasaki T, Lauenroth W (2011) Dominant species, rather than diversity, regulates temporal stability of plant communities. Oecologia 166: 761–768.
Song MH, Yu FH (2015) Reduced compensatory effects explain the nitrogen-mediated reduction in stability of an alpine meadow on the tibetan plateau. New Phytologist 207(1): 70. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13329
Steiner CF, Long ZT, Krumins JA, et al. (2005) Temporal stability of aquatic food webs: partitioning the effects of species diversity, species composition and enrichment. Ecology Letter 8(8): 819–828. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00785.x
Stevens CJ, Dise NB, Mountford JO, et al. (2004) Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science 303(5665): 1876. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094678
Stevens CJ, Lind EM, Hautier Y, et al. (2016) Anthropogenic nitrogen deposition predicts local grassland primary production worldwide. Ecology 96(6): 1459–1465. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-1902.1
Sun J, Qin X, Yang J (2016) The response of vegetation dynamics of the different alpine grassland types to temperature and precipitation on the tibetan plateau. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 188(1): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5014-4
Tilman D (1999) The ecological consequences of changes in biodiversity: a search for general principles. Ecology 80(5): 1455–1474. https://doi.org/10.2307/176540
Tilman D, Lehman CL, Bristow CE (1998) Diversity-stability relationships: statistical inevitability or ecological consequence? American Naturalist 151(3): 277–282. https://doi.org/10.2307/2463349
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JM (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 441(7093): 629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04742
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, et al. (1997) Technical report: human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecological Applications 7(3): 737–750. https://doi.org/10.2307/2269431
Wang S, Duan J, Xu G, et al. (2012) Effects of warming and grazing on soil n availability, species composition, and ANPP in an alpine meadow. Ecology 93(11): 2365. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-1408.1
Xu Z, Ren H, Li M, et al. (2015) Environmental changes drive the temporal stability of semiarid natural grasslands through altering species asynchrony. Journal of Ecology 103(5): 1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.28dj1
Yang H, Jiang L, Li L, et al. (2012) Diversity-dependent stability under mowing and nutrient addition: evidence from a 7-year grassland experiment. Ecology Letter 15(6): 619–626. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01778.x
Yang Z, Ruijven JV, Du G (2011) The effects of long-term fertilization on the temporal stability of alpine meadow communities. Plant and Soil 345(1–2): 315–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0784-0
Zhang Y, Loreau M, Lü X, et al. (2016) Nitrogen enrichment weakens ecosystem stability through decreased species asynchrony and population stability in a temperate grassland. Global Change Biology 22(4): 1445–1455. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13140
Zhang YH, Loreau M, He NP, et al. (2017) Mowing exacerbates the loss of ecosystem stability under nitrogen enrichment in a temperate grassland. Functional Ecology 31: 1637–1646. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12850
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0502002), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41401072), the Science Foundation for Young Scientists of IMDE, CAS, and the Open Fund of the Key Laboratory of Mountain Surface Processes and Ecological Regulation, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Jb., Wang, Xd. Temporal stability of aboveground net primary production in northern Tibet alpine steppe in response to nitrogen addition. J. Mt. Sci. 16, 2679–2686 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5135-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5135-7