Abstract
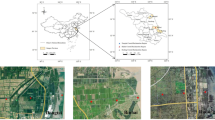
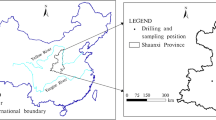
Inundation of the Three Gorges Reservoir has created a 30-m water-level fluctuation zone with seasonal hydrological alternations of submergence and exposure, which may greatly affect soil properties and bank stability. The aim of this study was to investigate the response of soil pore structure to seasonal water-level fluctuation in the reservoir, and particularly, the hydrological change of wetting and drying cycles. Soil pore structure was visualized with industrial X-ray computed tomography and digital image analysis techniques. The results showed that soil total porosity (> 100 μm), total pore number, total throat number, and mean throat surface area increased significantly under wetting and drying cycles. Soil porosity, pore number and throat number within each size class increased in the course of wetting and drying cycles. The coordination number, degree of anisotropy and fractal dimension were indicating an increase. In contrast, the mean shape factor, pore-throat ratio, and Euler-Poincaré number decreased due to wetting and drying cycles. These illustrated that the wetting and drying cycles made soil pore structure become more porous, continuous, heterogeneous and complex. It can thus be deduced that the water-level fluctuation would modify soil porosity, pore size distribution, and pore morphology in the Three Gorges Reservoir, which may have profound implications for soil processes, soil functions, and bank stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao YH, Gao P, He XB (2015) The water–level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir–A unique geomorphological unit. Earth–Science Reviews 150: 14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.07.005
Bao YH, He XB, Wen AB, et al. (2018) Dynamic changes of soil erosion in a typical disturbance zone of China's Three Gorges Reservoir. Catena 169: 128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.032
Baveye P, Boast CW, Ogawa S, et al. (1998) Influence of image resolution and thresholding on the apparent mass fractal characteristics of preferential flow patterns in field soils. Water Resources Research 34(11): 2783–2796. https://doi.org/10.1029/98WR01209
Blake GR, Hartge KH (1986) Bulk density. In: Klute A (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1–Physical and Mineralogical Methods., 2nd edition. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison. pp 363–375.
Chang C, Xie ZQ, Xiong GM, et al. (2011) The effect of flooding on soil physical and chemical properties of riparian zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Natural Resources 26(7): 1236–1244. (In Chinese)
Dal Ferro ND, Charrier P, Morari F (2013) Dual–scale micro–CT assessment of soil structure in a long–term fertilization experiment. Geoderma 204: 84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.04.012
Danielson RE, Sutherland PL (1986) Porosity. In: Klute A (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1–Physical and Mineralogical Methods., 2nd edition. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison. pp 443–462.
Doube M, Klosowski MM, Arganda–Carreras I, et al. (2010) BoneJ: free and extensible bone image analysis in ImageJ. Bone 47: 1076–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2010.08.023
Ersoy O, Aydar E, Gourgaud A, et al. (2008) Quantitative analysis on volcanic ash surfaces: application of extended depth–of–field (focus) algorithm for light and scanning electron microscopy and 3D reconstruction. Micron 39: 128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2006.11.010
Fierer N, Schimel JP (2002) Effects of drying–rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 34: 777–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00007-X
Gong XM, Teng QZ, Wang ZY, et al. (2016) Throat segmentation of 3D rock image based on skeleton. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition) 48: 100–106. (In Chinese)
Harrigan TP, Mann RW (1984) Characterization of microstructural anisotropy in orthotropic materials using a second rank tensor. Journal of Materials Science 19: 761–767.
He XB, Bao YH, Nan, HW, et al. (2009) Tillage pedogenesis of purple soils in Southwestern China. Journal of Mountain Science 6: 205–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-009-1038-y
He XB, Feng H, Feng ZD (2005) 3D image of soil microstructure using synchrotron X–ray computed microtomography. Acta Pedologica Sinica 42: 328–330. (In Chinese)
Hussein J, Adey MA (1998) Changes in microstructure voids and b–fabric of surface samples of a Vertisol caused by wet/dry cycles. Geoderma 85: 63–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(98)00014-7
Katuwal S, Norgaard T, Moldrup P, et al. (2015) Linking air and water transport in intact soils to macropore characteristics inferred from X–ray computed tomography. Geoderma 237–238: 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.08.006
Kravchenko A, Wang A, Smucker A, et al. (2011) Long–term differences in tillage and land use affect intra–aggregate pore heterogeneity. Soil Science Society of America Journal 75: 1658–1666. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2011.0096
Li CL (2007) Effect of pore–throat ratio on reservoir permeability. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency 14(5): 78–79. (In Chinese)
Luo LF, Lin H, Li SC (2010) Quantification of 3–D soil macropore networks in different soil types and land uses using computed tomography. Journal of Hydrology 393: 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.03.031
Mermut AR (2009) Historical development in soil micromorphological imaging. Journal of Mountain Science 6: 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-009-1026-2
Müller K, Katuwal S, Young I, et al. (2018) Characterising and linking X–ray CT derived macroporosity parameters to infiltration in soils with contrasting structures. Geoderma 313: 82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.020
Ma RM, Cai CF, Li ZX, et al. (2015) Evaluation of soil aggregate microstructure and stability under wetting and drying cycles in two Ultisols using synchrotron–based X–ray microcomputed tomography. Soil and Tillage Research 149: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.12.016
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray–level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 9: 62–66.
Pagliai M, Vignozzi N, Pellegrini S, (2004) Soil structure and the effect of management practices. Soil and Tillage Research 79: 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.07.002
Pan XJ, Wan CY, Zhang ZY, et al. (2017) Protection and ecological restoration of water level fluctuation zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Landscape Research 9(1): 44–50. https://doi.org/10.16785/j.issn1943-989x.2017.1.011
Peng XH, Horn R, Smucker A (2007) Pore shrinkage dependency of inorganic and organic soils on wetting and drying cycles. Soil Science Society of America 71: 1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2006.0156
Perret JS, Prasher SO, Kacimov AR (2003) Mass fractal dimension of soil macropores using computed tomography: from the box–counting to the cube–counting algorithm. European Journal of Soil Science 54: 569–579. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00546.x
Peth S, Horn R, Beckmann F, et al. (2008) Three–dimensional quantification of intra–aggregate pore–space features using synchrotron–radiation–based microtomography. Soil Science Society of America Journal 72(4): 897–907. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0130
Pires LF, Borges JAR, Rosa JA, et al. (2017) Soil structure changes induced by tillage systems. Soil and Tillage Research 165: 66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.07.010
Pires LF, Cooper M, Cássaro FAM, et al. (2008) Micromorphological analysis to characterize structure modifications of soil samples submitted to wetting and drying cycles. Catena 72: 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2007.06.003
Rajaram G, Erbach DC (1999) Effect of wetting and drying on soil physical properties. Journal of Terramechanics 36: 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-4898(98)00030-5
Rasband WS (1997–2014) ImageJ. U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA. https://doi.org/imagej.nih.gov/ij/Smith
Jr TG, Lange GD, Marks WB (1996) Fractal methods and results in cellular morphology–dimensions, lacunarity and multifractals. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 69: 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0270(96)00080-5
Starkloff T, Larsbob M, Stoltea J, et al. (2017) Quantifying the impact of a succession of freezing–thawing cycles on the pore network of a silty clay loam and a loamy sand topsoil using Xray tomography. Catena 156: 365–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.04.026
Tang CS, Wang DY, Shi B, et al. (2016) Effect of wetting–drying cycles on profile mechanical behavior of soils with different initial conditions. Catena 139: 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.12.015
Tang CS, Cui YJ, Shi B, et al. (2011) Desiccation and cracking behavior of clay layer from slurry state under wetting–drying cycles. Geoderma 166: 111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.07.018
Tang Q, Bao YH, He XB, et al. (2016) Flow regulation manipulates contemporary seasonal sedimentary dynamics in the reservoir fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Science of the Total Environment 548–549: 410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.158
Tarquis AM, Torre IG, Martín–Sotoca JJ, et al. (2018) Scaling characteristics of soil structure. In: Mcbratney AB, Minasny B, Stockmann U (eds.), Pedometrics. Springer International Publishing AG part of Springer Nature, Switzerland. pp 155–193.
Vogel HJ (2000) A numerical experiment on pore size, pore connectivity, water retention, permeability, and solute transport using network models. European Journal of Soil Science 51: 99–105. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00275.x
Wadell H (1932) Volume, shape, and roundness of rock particles. The Journal of Geology 40: 443–451.
Wang K, Ning L (2008) Numerical simulation of rock porethroat structure effects on NMR T2 distribution. Applied Geophysics 5(2): 86–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-008-0013-7
Zhang JR, Wang JM, Zhu YC, et al. (2017) Application of fractal theory on pedology: a review. Chinese Journal of Soil Science 48(1): 221–228. (In Chinese)
Zhao D, Xu MX, Liu GB, et al. (2017) Quantification of soil aggregate microstructure on abandoned cropland during vegetative succession using synchrotron radiation–based micro–computed tomography. Soil and Tillage Research 165: 239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.08.007
Zhou H, Peng XH, Perfect E, et al. (2013) Effects of organic and inorganic fertilization on soil aggregation in an Ultisol as characterized by synchrotron based X–ray micro–computed tomography. Geoderma 195–196: 23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.11.003
Zhou H, Peng XH, Peth E, et al. (2012) Effects of vegetation restoration on soil aggregate microstructure quantified with synchrotron–based micro–computed tomography. Soil and Tillage Research 124: 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2012.04.006
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41771321, 41771320 and 41571278) and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2018SZ0132). We appreciate Professor Xinhua Peng and Associate Professor Hu Zhou of the Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Science for guiding on the image analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Sj., Tang, Q., Bao, Yh. et al. Effects of seasonal water-level fluctuation on soil pore structure in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 15, 2192–2206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5013-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5013-3