Abstract
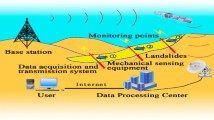
Panzhihua city (26°05′–27°21′N, 101°08′–102°15′E), located in a mountainous area, is one of the large cities in Sichuan province, China. A landslide occurred in the filling body of the eastern part of the Panzhihua airport on October 3, 2009 (hereafter called the 10.3 landslide). We conducted field survey on the landslide and adopted emergency monitoring and warning models based on the Internet of Things (IoT) to estimate the losses from the disaster and to prevent a secondary disaster from occurring. The results showed that four major features of the airport site had contributed to the landslide, i.e, high altitude, huge amount of filling rocks, deep backfilling and great difficulty of backfilling. The deformation process of the landslide had six stages and the unstable geological structure of high fillings and an earthquake were the main causes of the landslide. We adopted relative displacement sensing technology and Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) technology to achieve remote, real-time and unattended monitoring of ground cracks in the landslide. The monitoring system, including five extensometers with measuring ranges of 200, 450 and 700 mm, was continuously working for 17 months and released 7 warning signals with an average warning time of about 26 hours. At 10 am on 6 December 2009, the system issued a warning and on-site workers were evacuated and equipment protected immediately. At 2:20 pm on 7 December, a medium-scale collapse occurred at the No. 5 monitoring site, which justified the alarm and proved the reliability and efficiency of the monitoring system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton K (2009) That ‘Internet of Things’ Thing. RFID Journal.: (www.rfidjournal.com/article/view/4986/1/0/, accessed on 22 June 2009)
Atzori L, Iera A, Morabito G (2010) The Internet of Things: A survey. Computer Networks 15:2787–2805. DOI: 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010
Deng JH, Wang JL, Cai JH (2011) Deformation monitoring and analysis of landslides in Panzhihua city. Geotechnical Investigation and Surveying 4:79–83. (In Chinese)
Domingo MC (2012) An overview of the Internet of Things for people with disabilities. Journal of Network and Computer Applications (2): 584–596. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnca.2011.10.015
Gong ZH, Li TB, Gong XW, et al. (2007) Remediation measures on the landslide in fill slopes in the north-east part of Panzhihua airport. Journal of Engineering Geology 15(2):237–244. (In Chinese)
Huang RQ and Xu Q (2008) Catastrophic Landslides in China. Beijing: Science Press (In Chinese)
Kortuem G, Kawsar F, Fitton D, et al. (2010) Smart objects as building blocks for the Internet of Things. Internet Computing, IEEE (1):44–51. DOI: 10.1109/MIC.2009.143
Lagmay AMA, Tengonciang AMP, Rodolfo RS, et al. (2008) Science guides search and rescue after the 2006 Philippine landslide. Disasters 3:416–433. DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-7717.2008.01047.x
Li B, Lai YS, Huang Q, et al. (2009) Design of landslide monitoring system based on a wireless sensor network. Modern Electronics Techniques (12):169–173. (In Chinese)
Liao MS, Zhang L, Balz T (2009) Post-earthquake landslide detection and early detection of landslide prone areas using SAR. Urban Remote Sensing Event, 2009 Joint, 1–5. DOI: 10.1109/URS.2009.5137742
Liu YF, Song JX (2011) Using the Internet of Things technology to construct digital mines. Procedia Environmental Sciences, (10):1104–1108. DOI: 10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.176
Prokop A, Panholzer H (2009) Assessing the capability of terrestrial laser scanning for monitoring slow moving landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. (9): 1921–1928. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-9-1921-2009.
Sassa Kyoji (2005) Landslide disasters triggered by the 2004 Mid-Niigata Prefecture earthquake in Japan. Landslides (2):135–142. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-005-0054-4
Strozzi T, Farina P, Corsini A, et al. (2005) Survey and monitoring of landslide displacements by means of L-band satellite SAR interferometry. Landslides (3): 193–201. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-005-0003-2
Sun EJ, Zhang XK, Li ZX (2012) The Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing (CC) based tailings dam monitoring and pre-alarm system in mines. Safety Science (4):811–815. DOI: 10.1016/j.ssci.2011.08.028.
Tarchi D, Casagli N, Fanti R, et al. (2003) Landslide monitoring by using ground-based SAR interferometry: an example of application to the Tessina landslide in Italy. Engineering Geology (1–2):15–30. DOI: 10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00196-5
Tezaa G, Galgaro A, Zaltron N, et al. (2007) Terrestrial laser scanner to detect landslide displacement fields: A new approach. International Journal of Remote Sensing (16):3425–3446. DOI: 10.1080/01431160601024234
Tezaa G, Atzenib C, Balzanic M, et al. (2008) Ground-based monitoring of high-risk landslides through joint use of laser scanner and interferometric radar. International Journal of Remote Sensing (16):4735–4756. DOI: 10.1080/01431160801 942227
Tuo XG, Wang HH, Yang JB, et al. (2012) A remote mountain crack monitoring devices. China Invention Patent, 200910216547.4. (In Chinese)
Wang HH, Tuo XG, Xu Q, et al. (2010) Remote monitoring system for mountain cracks. Automation and Instrumentation (1):42–45. (In Chinese)
Wang ZJ, Chong JJ, Ni SD, et al. (2011) Determination of focal depth by two waveform-based methods: A case study of the 2008 Panzhihua earthquake. Earthquake Science (4):321–328. DOI: 10.1007/s11589-011-0794-2
Weber RH (2010) Internet of Things — New security and privacy challenges. Computer Law and Security Review (1):23–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.clsr.2009.11.008
Xi DS, Wang HH, Tuo XG (2010) Low-power design of the Mountain Cracks Remote Monitoring System. Measurement and Control Technology 29(8):43–46. (In Chinese)
Xi DS, Wang HH, Tuo XG, et al. (2011) A kind of landslide monitoring device. China’ Practical Patents, 201020655552.3. (In Chinese)
Xiao RC (2010) The IoT: The third tide in world information industries revolution? New Media (7):49–51.
Yan B, Huang GW (2009) Supply chain information transmission based on RFID and the Internet of Things. International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control, and Management, 8—9 Aug. 2009: 166–169. DOI: 10.1109/CCCM.2009.5267755
Yuan YF, Liu WL, Zhang YB (2008) Stability analysis of the Panzhihua Airport landslide block. Subgrade Engineering (2):5–7. (In Chinese)
Zacharewicz G, Deschamps JC, Francois J (2011) Distributed simulation platform to design advanced RFID based freight transportation systems. Computers in Industry (6): 597–612. DOI:10.1016/j.compind.2011.04.009
Zhou MF, Robinson PT, Lesher CM, et al. (2005) Geochemistry, petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Panzhihua gabbroic layered intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits, Sichuan Province, SW China. Journal of Petrology (11):2253–2280. DOI: 10.1093/petrology/egi054
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hh., Tuo, Xg., Zhang, Gy. et al. Panzhihua airport landslide (Oct. 3rd 2009) and an emergency monitoring and warning system based on the internet of things. J. Mt. Sci. 10, 873–884 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2368-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2368-3