Abstract
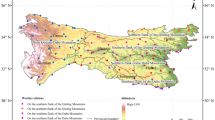
Gongga Mountain, locates on the eastern edge of Tibetan Plateau of China, is the highest mountain in China except summits in Tibet. Only limited meteorological data on Gongga Mountain have been published so far. Here we present the meteorological records from two stations, Moxi Station (at 1,621.7 m above sea level (a.s.l.), 1992–2010) and Hailuogou Station (at 2,947.8 m a.s.l., 1988–2010), on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain. In the past two decades, the annual precipitation decreased while the annual mean temperature increased at Hailuogou Station. Both precipitation and temperature increased at Moxi Station. The precipitation variation on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain is influenced by both East Asian Monsoon and Indian Monsoon, so that the precipitation concentrated between May and October. The temperature variation on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain in the past two decades showed similar trends as that of the northern hemispheric and global. In the past two decades, the temperature increased 0.35°C and 0.3°C/decade at Hailuogou Station and Moxi Station respectively, which was higher than the increase extents of northern hemispheric and global temperature. The most intense warming occurred at the first decade of 21st century. The winter temperature increased more at Hailuogou Station than at Moxi Station. A remarkable increase of temperature in March was observed with only a little precipitation at both high and low altitude stations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller C, Begert M, Zenklusen E, et al. (2008) Monitoring climate at Jungfraujoch in the high Swiss Alpine region. Science of the Total Environment 391(2–3): 262–268. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.10.005
Barry RG (1994) Past and potential future changes in mountain environments: A review. In: Beniston M (ed.), Mountain Environments in Changing Climate, Routledge Publishing Company, London and New York. pp 3–33.
Becker A, Bugmann H (1997) Predicting global change impacts on mountain hydrology and ecology: Integrated catchment hydrology/Altitudinal gradient studies. IGBP Report 43, Stockholm.
Beniston M (2000) Environmental change in mountains and uplands. Arnold/Holder Publishers, London, UK and Oxford University Press, New York, USA.
Beniston M (2003) Climate change in mountain regions: A review of possible impacts. Journal of Climate 59: 5–31.
Beniston M (2005) Mountain climates and climate change: An overview of processes focusing on the European Alps. Pure and Applied Geophysics 162: 1587–1606.
Cheng G (1993) Hydrologic features of maritime-type glaciers in the region of Gongga Mountain. In: Chen F, and Gao S (eds), Research on Alpine Ecosystem in Gongga Mountain, Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press. pp 69–79. (In Chinese with English abstract.)
Duan C, Zhang X, Hu S (1982) Basic characteristics of the climate of Gongga mountainous region. In: Chengdu Institute of Geography, CAS (ed), Geographic expedition in the Gongga Mountain, Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press. pp35–46. (In Chinese with English abstract.)
Gao S, Peng J (1993) Research of climate in the Gongga Mountain. In: Chen F, and Gao S (eds), Research on Alpine Ecosystem in Gongga Mountain, Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press. pp 59–68. (In Chinese with English abstract.)
Gao YX (1984) Chinese Physical Geography: Climate. In: Editor committee of Chinese Physical Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ed), Chinese Physical Geography, Science Press, Beijing, China. pp26. (In Chinese)
Grassl H (1994) The Alps under local, regional and global pressures. In: Beniston M (ed), Mountain Environments in Changing Climat, Routledge publishing Company, London and New York. pp 34–41.
Guo J, Wang G (2011) Climate change on the Mt. Gongga and its impact on tourism. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 33(1): 214–218.
Heim A (1933) Minya Gongkar. Verlag Hans Huber, Bern, Switzerland.
Jones PD, Moberg B (2003) Hemispheric and large-scale surface air temperature variations: An extensive revision and an update to 2001. Journal of Climate 16: 206–223.
Kang S, Xu Y, You Q, et al. (2010) Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environment Research Letters 5: 015101 (8pp). Doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/5/1/015101
Kapos V, Rhind J, Edwards M, et al. (2000) Developing a map of the world’s mountain forests. In: Price MF and Butt N (eds), Forest in a sustainable mountain environment, CAB International, Wallingford.
Klötzli F (1994) Vegetation als Spielball naturgegebener Bauherren. Phytocoenologia 24: 667–675.
Liu X, Chen B (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. International Journal of Climatology 20: 1729–1742.
Lv Y, Wang G (2008) Response of runoff variation to climate change in Hailuogou drainage basin in Gongga Mount in 1990–2007. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 30(6): 960–966. (In Chinese)
Messerli B, Ives J (1984) Gongga Shan (7,556 m) and Yulongxue Shan (5596 m). Geoecological observations in the Hengduan Mountains of Southwest China. In: Lauer W(ed), Natural Environment and Man in Tropical Mountain Systems, Proceedings of the Symposium of IGU Commision on Mountain Geoecology, 24.2–26.2, 1983, Mainz, Germany. pp 55–78.
Meybeck M, Green P, Vörösmarty C (2001) A new typology for mountains and other relief classes: An application to global continental water resources and population distribution. Mountain Research Development 21: 34–45.
Tang M, Cheng G, Lin Z (1998) Contemporary climatic variations over Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and their influences on environments, Guangdong Science & Technology Press, Guangzhou, China. pp 161–183. (In Chinese)
Thomas A (1997) The climate of the Gongga Shan range, Sichuan Province, PR China. Arctic and Alpine Research 29(2): 226–232.
Wen C (1989) Influence of the relief on condition of a water and heat in the Hengduan Mountainous region. Mountain Research 7(1): 65–72.
Ye D, Gao Y (1979) Meteorology on Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Science Press, Beijing, China. pp1–35. (In Chinese)
Zhang J, Lin Z (1985) Climate of China. Science and Technology Press of Shanghai, Shanghai, China. p527.
Zhong X, Zheng Y (1992) A preliminary study on the natural vertical zonation of Gongga mountainous regions. In: Chengdu Institute of Geography, CAS (ed), Geographic expedition in the Gongga Mountain, Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, Chengdu, China. pp 78–95. (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Yh., Li, W., Zhou, J. et al. Temperature and precipitation variations at two meteorological stations on eastern slope of Gongga Mountain, SW China in the past two decades. J. Mt. Sci. 10, 370–377 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2328-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2328-y