Abstract
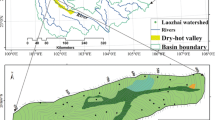
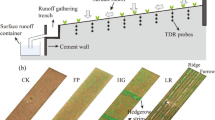
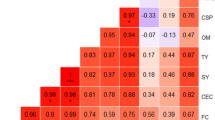
Research on the effects of soil erosion on soil productivity has attracted increasing attention. Purple soil is one of the main soil types in China and plays an important role in the national economy. However, the relationship between erosion and the productivity of purple soils has not been well studied. The purpose of this research was to determine if soil depth, which is dependent on the rate of erosion, has an influence on crop yield and growth. Plot and pot experiments at different soil depths were performed. Results indicate that soils from different parental materials had different growth features and crop yields due to the differential fertility of the derived soils. The yield reduction rate increases exponentially with the depth of eroded soil (level of erosion). The yield reduction rate per unit eroded soil horizon (10 cm) is approximately 10.5% for maize and wheat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker MM, Govers G, Rounsevell MDA (2004) The crop productivity-erosion relationship: an analysis based on experimental work. Catena 57(1): 55–76.
Bakker MM, Govers G, Jones R, et al. (2005) The Effect of Soil Erosion on Agricultural Productivity. Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol.7, 00695.
Bakker MM, Govers G, Jones RA, et al. (2007) The effect of soil erosion on Europe’s crop yields. Ecosystems 10: 1209–1219.
de la Rosa D, Moreno JA, Mayol F, et al. (2000) Assessment of soil erosion vulnerability in western Europe and potential impact on crop productivity due to loss of soil depth using the ImpelERO model. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 81: 179–190.
den Biggelaar C, Lal R, Wiebe K, et al. (2003) The Global Impact of Soil Erosion on Productivity II: Effects On Crop Yields And Production Over Time. Advances in Agronomy 81: 49–95.
Fenton TE, Kazemi M, Lauterbach-Barrett MA (2005) Erosional impact on organic matter content and productivity of selected Iowa soils. Soil & Tillage Research 81: 163–171.
Gantzer CJ. Anderson SH. Thompson AL, et al.(1990) Estimating soil erosion after 100years of cropping on Sanborn field. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 45(6): 641–644
Grewal MS, Kuhad MS (2002) The influence and management research of removing surface soil to productivity. Soil and Water Conservation in China (7): 20–20.
Heckrath G (2005) Tillage erosion and its effect on soil properties and crop yield in Denmark. Journal of Environmental Quality 34: 312–324.
Jones CA, Dyke PT, Williams JR, et al. (1991) EPIC: An operational model for evaluation of agricultural sustainability. Agricultural System 37(4): 341–350.
Lal R (1998) Soil erosion impact on agronomic productivity and environment quality. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 17(4): 319–464.
Li ZM, Tang SJ, Zhang XW, et al. (1991) Purple soil in China (1), Beijing, Science Press. P 340. (In Chinese)
Liu GC, Li L, Wu LS, Wang GX, Zhou ZH, Du SH (2009) Determination of Soil Loss Tolerance of a Regosols in Hilly Area of Southwest China. Soil Science Society of America Journal 73(2): 412–417.
Lobo D, Lozano Z, Delgado F (2005) Water erosion risk assessment and impact on productivity of a Venezuelan soil. Catena 64: 297–306.
Mokma DL, Sietz MA (1992) Effects of soil erosion on corn yields on Marlette soils in South-central Michigan. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 47(4): 325–327.
Olson KR, Carmer SG (1990) Corn yield and plant population differences between eroded phases of Illinois soils. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 45(5): 562–566.
Olson KR, Lal R. Norton LD (1994) Evaluation of methods to study soil erosion-productivity relationships. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 49(6): 586–590
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1978) Soil physical and chemical analysis. Shanghai Science Technology Press, Shanghai. (In Chinese)
Pierce FJ, Larson WE, Dowdy RH (1984) Soil productivity in the Corn Belt: An assessment of erosion’s long-term effects. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 39(2): 131–136.
Schumacher TE, Lindstrom MJ, Mokma DL, et al. (1994) Corn yield: erosion relationships of representative loess and till soils in the North central United States. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 49(1): 77–81.
Su ZA, Zhang JH, Nie XJ (2010) Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil Properties and Crop Yields on Slopes in the Sichuan Basin, China. Pedosphere 20: 736–746.
The National Soil Erosion-Soil Productivity Research Planning Committee, Science and Education Administration-Agricultural Research (1981) Soil erosion effect on soil productivity: A research perspective. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 36(2): 82–90.
Weesies GA, Livingston SJ, Hosteter WD, et al. (1994) Effect of soil erosion on crop yield in Indiana: Results of a 10 year study. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 49(6): 597–600.
Wang ZQ, Liu BY, Wang XY, et al (2009) Erosion effect on the productivity of black soil in Northeast China. Science in China, Series D-Earth Science 52(7): 1005–1021.
Williams JR., Renard KG, Dyke PT (1983) EPIC, a new method for assessing erosion’s effect on soil productivity. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 38: 381–383.
Zhu B, Kuang FH, Gao MR, et al. (2009) Effects of Soil Thickness on Productivity of Sloping Cropland of Purple Soil. Journal of Mountain Science (in Chinese) 27(6): 735–739.
Zhou ZH, Du SH, Liu GC (2009) Research on Effect of soil erosion on cultivated land soil productivity. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science 37(16): 7601–7603. (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Jin, J., Du, S. et al. A quantification of the effects of erosion on the productivity of purple soils. J. Mt. Sci. 9, 96–104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2241-9