Abstract
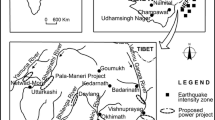
Mountain ecosystem, on the earth, has plenty of natural resources. In Himachal Pradesh all the rivers are snowfed and therefore rich in water resources. These resources have been supporting enough for the generation of electricity through introducing hydropower projects since the last decade. However, every developmental activity has its own negative impacts on the surrounding environment. Due to the fragile nature of topography and delicacy of ecology of the Himalaya, it results in lot of disturbances because of high degree of human interferences like construction of major hydropower projects. The increased extent of geological hazards, such as landslides, rock fall and soil erosion, have mainly due to alike developmental interventions in the natural ecosystem. So understanding and analysing such impacts of the hydropower projects have mainly been on the environment in various forms but natural hazards have been frequent ones. The present study, therefore, focuses mainly on the Parbati Stage II (800 MW) and the Parbati Stage III (520 MW) hydropower projects; both of which fall within the Kullu district of Himachal Pradesh. Based on the perception survey of the local communities, the existing land use pattern, status of total acquired land of the residents by hydropower projects, frequent natural hazards and resultant loss to the local communities due to upcoming construction of hydropower projects surrounding to the Parbati Stage II and III have been analysed in the paper. Also, the preventive measures to mitigate these adverse impacts have been suggested to strengthen these projects in eco-friendly manner in the mountain context.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandrasekharan M.E. 1995. Case study of reservoir sedimentation in the Western Ghat region of Kerala, in Central Board of Irrigation and Power (eds.), Environmental Impact Assessment Studies (Case Studies), Pub. No. 248, pp. 192–197, New Delhi.
Financial Times. 1999. Consortium chosen for Chamera, Power in Asia, No. 283–284 (August), p.12.
GOI. 1985. Guidelines for Environmental Impact Assessment of River valley projects. Ministry of Environment and Forest, Govt. of India, New Delhi.
Gupta G.P. 1975. Sediment production-status report on data collection and utilization. Soil Conservation Digest 3(2):10–21.
Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board (HPSEB). 1998. Environmental Impact Assessment and Management Plan, Parbati Hydroelectric Project, Stage II.
Hindustan Times. 2006. Villagers stall project work, 30 January 2006, Chandigarh. pp. 6.
Kulkarni A.V., Rathore. B.P. Mahazan S. and Mathur P. 2005. Alarming retreat of Parbati glacier, Beas basin, Himachal Pradesh. Current Science 88(11):1844–1850.
Kuniyal J.C., Vishvakarma S.C.R., Badola H.K. and Jain A.P. 1999. Tourism in Kullu valley: An environmental assessment-A report. G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development, Almora, pp. 1–189.
Kuniyal J.C. 2002. Mountain expeditions: minimising the impact. Environmental Impact Assessment Review 22(6):561–81.
Kuniyal J.C. and Sharma R. 2002. Public involvement in environmental assessment of hydropower projects-A case study of the Himalayan Beas valley of Himachal state, India. Presented in an International Conference on “Challenges and Options for Sustainable Development of the Himalayas-Beyond 2002”, 1st–4th October 2002, Palampur. pp. 1–29.
Kuniyal J.C., Vishvakarma S.C.R., Badola H.K. and Jain A.P. 2004. Tourism in Kullu valley: An Environmental Assessment. G. B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development, Himavikas Pub. No.15, Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh, Dehra Dun. pp.1–210.
Mazari R.K. and Sah M.P. 2005. Pulia nala cloudburst of July 16, district Kullu, Himachal Pradesh: Lesson for policy implementation. Himalayan Geology 25(2):153–161.
Panigrahy N. 2003. Importance of environmental impact studies in hydropower projects. In: Mathur G.N., Goyal D.P., Chawala A.S. and Singh R.B. (eds.), Proc. of International Conference Accelerated Construction of hydropower projects. Vol.-I, 15–17 Oct. 2003, Gedu Bhutan. pp: X2–X9.
Prasad V.H. and Roy P.S. 2005. Estimation of snowmelt runoff in the Beas basin, India. Geocarto (20):2.
Li Zhenhai, Zhao Rong. 2004. Study on significance of environmental impact assessment of water conservancy and hydropower engineering construction—An example of Zhangfeng reservoir project (China). pp. 1–14.
South Asia Network for Dams, River and People (SANDRP). 2005. Dams River and People. 3(2–3):16, New Delhi.
Singh R.B. and Roy S.S. 2003. Impacts of climate change on mountain ecosystem. in: Dash & Roy (eds.), Assessment of Climate Change in India and Mitigation Policies, WWF-India, New Delhi. pp.220–230.
Singh S., Kothari A. and Kulan A. 1991. Evaluating major irrigation projects in India, International Journal of Sustainable Development 1(1): 78–84.S
Singh V. and Sharma M.L. 1998. Mountain Ecosystem: A Scenario of Unsustainability, Indus Publishing Co., New Delhi.
Varshney R.S. 1995. Hydroelectric development in Ganga valley and its impacts on the environment. In: Central Board of Irrigation and Power (eds.), Environmental Impact Assessment Studies (Case Studies), New Delhi. Pub. No. 248:65–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S., Kuniyal, J.C. & Sharma, J.C. Assessment of man-made and natural hazards in the surroundings of hydropower projects under construction in the beas valley of northwestern Himalaya. J. Mt. Sci. 4, 221–236 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-007-0221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-007-0221-2