Abstract
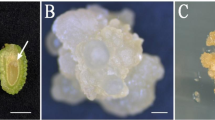
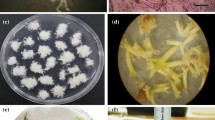
An efficient protocol for secondary somatic embryogenesis in camphor tree is reported. Secondary somatic embryos (SSEs), initially obtained from the primary embryos of a nascent embryogenic culture in 2002, were proliferated and maintained for more than 4 yr via cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis. Throughout this period, the embryo populations retained a high level of competence for plant regeneration. SSEs were produced on the surfaces of the cotyledons and radicular ends of maternal somatic embryos (MSEs). Histological observations of the various stages of secondary embryo development revealed four typical stages, namely, globular, heart-shaped, torpedo, and cotyledonary. The process of secondary embryogenesis continued in a cyclic way, with each newly formed embryo producing a subsequent generation of secondary embryos. In order to progress developmentally beyond proliferation cycles, cotyledonary embryos from one of embryogenic lines (L14) were cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 0.1–3.0 mg l−1 abscisic acid (ABA) or 0.05–1.0 mg l−1 thidiazuron (TDZ) in darkness for 2 mo to achieve maturation. Matured embryos were then transferred to MS-based germination medium containing either 0.1 mg l−1 TDZ, 0.2 mg l−1 indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), and 0.5 mg l−1 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) or 0.1 mg l−1 TDZ and 0.2 mg l−1 IBA and were cultured in light for germination. Over 50% of embryos matured in the presence of 0.5 mg l−1 ABA were able to germinate with shoots and poor root system. Frequencies of embryos germinating normal shoots among different genotypes did not change significantly. A total of 93% of the shoots from the germinated embryos converted to plantlets on half strength MS medium with 0.5 mg l−1 IBA by 3 wk. Plantlets acclimatized successfully to ex vitro conditions and developed as field-grown plants with normal appearance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberlenc-Bertossi F.; Noirot M.; Duval Y. BA enhances the germination of oil palm somatic embryos derived from embryogenic suspension cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 56: 53–57; 1999.
Agarwal S.; Kanwar K. Comparison of genetic transformation in Morus alba L. via different regeneration systems. Plant Cell Rep. 26: 177–185; 2007.
Al-Ramamneh E. A.; Sriskandarajah S.; Serek M. Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in Schlumbergera truncata. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 84: 333–342; 2006.
Andrade G. M.; Merkle S. A. Enhancement of American chestnut somatic seedling production. Plant Cell Rep. 24: 326–334; 2005.
Babu K. N.; Sajina A.; Minoo D.; John C. Z.; Mini P. M.; Tushar K. V.; Rema J.; Ravindran P. N. Micropropagation of camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 74: 179–183; 2003.
Canhoto J. M.; Lopes M. L.; Cruz G. S. Somatic embryogenesis induction in Bay Laurel (Laurus nobilis). In: Jain S.; Gupta P.; Newton R. (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 4. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 341–367; 1999.
Canhoto J. M.; Rama S. C.; Cruz G. S. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in carob (Ceratonia Siliqua L.). In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant. 42: 514–519; 2006.
Capuana M.; Debergh P. C. Improvement of the maturation and germination of horse chestnut somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 48: 23–29; 1997.
Catarina C. S.; Moser J. R.; Bouzon Z.; Floh E.; Maraschin M.; Viana A. M. Protocol of somatic embryogenesis: Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae). In: Jain S.; Gupta P. (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 427–443; 2005.
Catarina C. S.; Olmedo A. D.; Meyer G. D.; Macedo J.; Amorim W. D.; Viana A. M. Repetitive somatic embryogenesis of Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae): effect of somatic embryo developmental stage and dehydration. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 78: 55–62; 2004.
Cerda F.; Aquea F.; Gebauer M.; Medina C.; Arce-Johnson P. Stable transformation of Pinus radiata embryogenic tissue by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 70: 251–257; 2002.
Chalupa V. Protocol of somatic embryogenesis: penunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) and sessile oak (Quercus petraea /Matt./ Liebl.). In: Gupta P.; Jain S. (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 369–378; 2005.
Chandler S. F.; Lu C. Y. Biotechnology in ornamental horticulture. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant. 41: 591–601; 2005.
Charity J. A.; Holland L.; Grace L. J.; Walter C. Consistent and stable expression of the nptII, uidA and bar genes in transgenic Pinus radiata after Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation using nurse cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 23: 606–616; 2005.
Cruz-Hernández A.; Witjaksono Litz R. E.; Gomez Lim M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of embryogenic avocado cultures and regeneration of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 497–503; 1998.
Du L.; Bao M. Z. Plant regeneration from protoplasts isolated from embryogenic suspension cultured cells of Cinnamomum camphora L. Plant Cell Rep. 24: 462–467; 2005.
Escobar M. A.; Park J. I.; Polito V. S.; Leslie C. A.; Uratsu S. L.; McGranahan G. H.; Dandekar A. M. Using GFP as a scorable marker in walnut somatic embryo transformation. Ann. Bot. 85: 831–835; 2000.
FLEPPC (Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council). List of invasive species. Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council, Florida EPPC Newsletter, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 3–4. Available: http://www.fleppc.org (Accessed: January 3, 2003); 2001.
Gutièrrez P.; Rugini E. Influence of plant growth regulators, carbon sources and iron on the cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of transgenic cherry rootstock ‘Colt’ (Prunus avium × P. pseudocerasus). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 79: 223–232; 2004.
Jayashree R.; Rekha K.; Venkatachalam P.; Uratsu S. L.; Dandekar A. M.; Jayasree P. K.; Kala R. G.; Priya P.; Kumari S. S.; Sobha S.; Ashokan M. P.; Sethuraj M. R.; Thulaseedharan A. Genetic transformation and regeneration of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg) transgenic plants with a constitutive version of an anti-oxidative stress superoxide dismutase gene. Plant Cell Rep. 22: 201–209; 2003.
Karami O.; Deljou A.; Kordestani G. K. Secondary somatic embryogenesis of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 92: 273–280; 2008.
Kaur N.; Pati P. K.; Sharma M.; Ahuja P. S. Somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of Rosa bourboniana desp. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 42: 124–127; 2006.
Khan H.; Siddique I.; Anis M. Thidiazuron induced somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Capsicum annuum. Biol. Plant. 50: 789–792; 2006.
Land Protection. NRM facts pest series. Department of Natural Resources and Mines, State of Queensland, Australia. Available: http://www.nrm.qld.gov.au (Accessed: January 9, 2003); 2001.
Langhansová L.; Konrádová H.; Vaněk T. Polyethylene glycol and abscisic acid improve maturation and regeneration of Panax ginseng somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 22: 725–730; 2004.
Linossier L.; Veisseire P.; Cailloux F.; Coudret A. Effects of abscisic acid and high concentrations of PEG on Hevea brasiliensis somatic embryos development. Plant Sci. 124: 183–191; 1997.
Maximova S.; Miller C.; de Mayolo G. A.; Pishak S.; Young A.; Guiltinan M. J. Stable transformation of Theobroma cacao L. and influence of matrix attachment regions on GFP expression. Plant Cell Rep. 21: 872–883; 2003.
Merkle, S. A. Somatic embryogenesis in Magnoliaceae. In: Bajaj, Y. P. S. (ed) Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed I. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, vol. 30. Springer, New York, pp 388–403; 1995.
Mooney P. A.; Van Staden J. Induction of embryogenesis in callus from immature embryos of Persea americana. Can. J. Bot. 65: 622–626; 1987.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–479; 1962.
Nair R. R.; Gupta S. D. High-frequency plant regeneration through cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis in black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Plant Cell Rep. 24: 699–707; 2006.
Pliego-Alfaro F.; Murashige T. Somatic embryogenesis in avocado (Persea americana Mill.) in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 12: 61–66; 1988.
Poupin M. J.; Arce-Johnson P. Transgenic trees for a new era. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant. 41: 91–101; 2005.
Quiroz-Figueroa F. R.; Fuentes-Cerda C. F. J.; Rojas-Herrera R.; Loyola-Vargas V. M. Histological studies on the developmental stages and differentiation of two different somatic embryogenesis systems of Coffea arabica. Plant Cell Rep. 20: 1141–1149; 2002.
Raemakers C. J. J. M.; Jacobsen E.; Visser R. G. F. Secondary somatic embryogenesis and applications in plant breeding. Euphytica. 81: 93–107; 1995.
Rout G. R.; Nanda R. M. Protocol of somatic embryogenesis in Acacia arabica (Lamk.) Willd. In: Jain S.; Gupta P. (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 401–412; 2005.
Rugini E.; Mencuccini M.; Biasi R.; Altamura M. M. Olive (Olea europaea L.). In: Jain S.; Gupta P. (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 345–360; 2005.
Sánchez-Romero, C.; Márquez-Martín, B.; Pliego-Alfaro, F. Somatic and zygotic embryogenesis in Avocado. In: Plant cell monographs, somatic embryogenesis, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 271–284; 2005.
Sharma S. K.; Millam S. Somatic embryogenesis in Solanum tuberosum L.: a histological examination of key developmental stages. Plant Cell Rep. 23: 115–119; 2004.
Tereso S.; Miguel C.; Zoglauer K.; Valle-Piquera C.; Oliveira M. M. Stable Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissues from Pinus pinaster Portuguese genotypes. Plant Growth Regul. 50: 57–68; 2006.
Trigiano R. N.; Buckley L. G.; Merkle S. A. Somatic embryogenesis in woody legumes. In: Jain S.; Gupta P.; Newton R. (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 4. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 189–208; 1999.
Xiao W.; Huang X. L.; Huang X.; Chen Y. P.; Dai X. M.; Zhao J. T. Plant regeneration from protoplasts of Musa acuminata cv. Mas (AA) via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 90: 191–200; 2007.
Zhang C. L.; Chen D. F.; Kubalakova M.; Zhang J.; Scott N. W.; Elliott M. C.; Slater A. Efficient somatic embryogenesis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) breeding lines. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 93: 209–221; 2008.
Zimmerman J. L. Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell. 5: 1411–1423; 1993.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by research project from Ministry of Education Foundation of China (NCET-04-0733). We thank all the colleagues in our lab for constructive discussion and technical support. We are also grateful to Dr. Alex C. McCormac for critical editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: D. T. Tomes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Dai, X., Liu, G. et al. Cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis and efficient plant regeneration in camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora L.). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 46, 117–125 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-009-9272-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-009-9272-0