Abstract
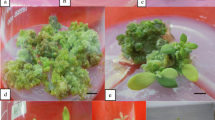
The capacity for indirect shoot organogenesis of leaf and root explants of four Dieffenbachia cultivars were examined on a modified Murashige and Skoog (MS; Physiol Plant 15:473–495, 1962) medium supplemented with different plant growth regulators in 112 combinations. Callus formation was only observed from leaf explants on MS supplemented with 1–10 μM thidiazuron (TDZ) and 0.5–1.0 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) regardless of cultivars. The combination of 5 μM TDZ and 1 μM 2,4-D resulted in the greatest callus formation frequency among the four cultivars tested. Significant differences in callus and shoot formation from leaf explants were also observed among cultivars. Cultivars Camouflage, Camille, Octopus, and Star Bright produced green nodular, brown nodular, yellow friable, and green compact calli with corresponding maximum callus formation frequencies of 96%, 62%, 54%, and 52%, respectively. A maximum of 6.7 shoots/callus was observed in cv. Camouflage, followed by cvs. Camille and Star Bright at 3.7 and 3.5, respectively. Calli of cv. Octopus displayed no capacity for shoot organogenesis. Regardless of cultivar, callus formation was not observed on root explants. Regenerated shoots were successfully acclimatized in a shaded greenhouse condition with 100% survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal P.; Ranu R. Regeneration of plantlets from leaf and petiole explants of Pelargonium Hortorum. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 36: 392–397; 2000.
Bacchetta L.; Remotti P. C.; Bernardini C.; Saccardo F. Adventitious shoot regeneration from leaf explants and stem nodes of Lilium. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 74: 37–44; 2003.
Berrios E. F.; Gentzbittel L.; Serieys H.; Alibert G.; Sarrafi A. Influence of genotype and gelling agents on in vitro regeneration by organogenesis in sunflower. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 59: 65–69; 1999.
Chen J.; Devanand P. S.; Norman D. J.; Henny R. J.; Chao C. T. Analysis of genetic relatedness of Dieffenbachia cultivars using AFLP markers. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 129: 81–87; 2004.
Chen J.; Henny R. J.; Chao C. T. Somaclonal variation as a source for cultivar development of ornamental aroids. Recent Res. Devel. Plant Sci. 1: 31–43; 2003.
Haensch K. T. Thidiazuron-induced morphogenetic response in petiole cultures of Pelargonium hortorum and Pelargonium domesticum and its histological analysis. Cell Biol. Morphogenesis 23: 211–217; 2004.
Henny R. J. Ornamental aroids: culture and breeding. Hort. Rev. 10: 1–33; 1988.
Henny R. J.; Chen J. Cultivar development of ornamental foliage plants. Plant Breed. Rev. 23: 245–289; 2003.
Hutchinson M. J.; Krishnaraj S.; Saxena P. K. Morphological and physiological changes during thidiazuron-induced somatic embryogenesis in geranium (Pelargonium hortorum Bailey) hypocotyl cultures. Int. J. Plant Sci. 157: 440–446; 1996.
Kallak H.; Reidla M.; Hilpus I.; Virumae K. Effects of genotyps, explant source, growth regulators on organogenesis in carnation callus. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 51: 127–135; 1997.
Khanam N.; Khoo C.; Khan A. G. Effects of cytokinin/auxin combination on organogenesis, shoot regeneration and tropane alkaloid production in Duboisia myoporoides. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 62: 125–133; 2000.
Knauss J. F. A tissue culture method for producing Dieffenbachia picta cv. ‘Perfection’ free of fungi and bacteria. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 89: 293–296; 1976.
Kuehnle A. R.; Sugii N. Callus induction and plantlet regeneration in tissue cultures of Hawaiian anthuriums. HortScience. 26: 919–921; 1991.
Landi L.; Mezzetti B. TDZ, anxin and genotype effects on leaf organogenesis in Fragaria. Plant Cell Rep. 25: 281–288; 2005.
Ma G.; Xu W. Induction of somatic embryogenesis and adventitious shoots from immature leaves of cassava. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 70: 281–288; 2002.
Mithila J.; Hall J. C.; Victor J. M. R.; Saxena P. K. Thidiazuron induces shoot organogenesis at low concentrations and somatic embryogenesis at high concentrations on leaf and petiole explants of African violet (Saintpaulia ionantha Wendl.). Plant Cell Rep. 21: 408–414; 2003.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–495; 1962.
Nontaswatsri C.; Fukai S.; Touma T.; Goi M. Comparison of adventitious shoot formation of various carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) cultivars. J. Hort. Sci. Biotech. 77: 520–525; 2002.
Orlikowska T.; Sabala I.; Nowak E. Adventitious shoot regeneration on explants of Anthurium, Codiaeum, Dieffenbachia, Gerbera, Rosa and Spathiphyllum for breeding purpose. Acta Hort. 420: 115–117; 1995.
Phillips G. C. In vitro morphogenesis in plants—recent advances. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 40: 342–345; 2004.
Robichon M. P.; Renou J. P.; Jalouzot R. Plant regeneration of ivy leaved geranium through shoot organogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 49: 209–212; 1997.
SAS Institute Inc Version 8.02. SAS Institute, Cary, NC1999.
Shen X.; Chen J.; Kane M. E. Indirect shoot organogenesis from leaves of Dieffenbachia cv. Camouflage. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 89: 83–90; 2007.
Thao N. T. P.; Ozaki Y.; Okubo H. Callus induction and plantlet regeneration in ornamental Alocasia. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 73: 285–289; 2003.
Vardja R.; Vardja T. The effect of cytokinin type and concentration and the number of subculture on the multiplication rate of some decorative plants. Proc. Estonian. Acad. Sci. Biol. Ecol. 50: 22–32; 2001.
Voyiatzi C.; Voyiatzis D. G. In vitro shoot proliferation rate of Dieffenbachia exotica cultivar ‘Marianna’ as affected by cytokinins, the number of recultures and the temperature. Sci. Hortic. 40: 163–169; 1989.
Zhang C. L.; Chen D. F.; Elliott M. C.; Slater A. Thidiazuron-induced organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 37: 305–310; 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Gregory C. Philips
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X., Kane, M.E. & Chen, J. Effects of genotype, explant source, and plant growth regulators on indirect shoot organogenesis in Dieffenbachia cultivars. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 44, 282–288 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9112-7