Abstract
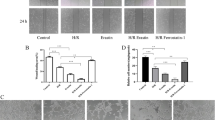
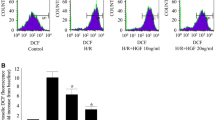
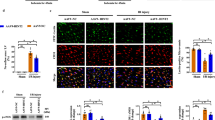
We aimed to explore the effects of myeloid-derived growth factor (Mydgf) on the regulation of hypoxia/reoxygenation (HR)–induced apoptosis of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs). CMECs were exposed to hypoxia for 24 h and reoxygenation for 6 h to establish an HR cell model. Subsequently, an adenovirus was used to overexpress Mydgf in CMECs. Flow cytometry and TUNEL staining were used to detect the extent of apoptosis, whereas qPCR was used to detect the relative expression of Mydgf mRNA. Western blotting was also performed to detect the expression of apoptosis-related proteins and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)–related proteins, including C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP), glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP 78), and cleaved Caspase-12. The endoplasmic reticulum stress agonist tunicamycin (TM) was used to stimulate CMECs for 24 h as a rescue experiment for Mydgf. Flow cytometry revealed that the HR model effectively induced endothelial cell apoptosis, whereas qPCR and western blotting showed that Mydgf mRNA and protein levels decreased significantly after HR treatment (P < 0.05). Overexpression of Mydgf in cells effectively reduced apoptosis after HR. Furthermore, western blotting showed that HR induced a significant upregulation of CHOP, GRP78, and cleaved-Caspase-12 expression in CMECs, whereas HR-treated cells downregulated the expression of CHOP, GRP78, and cleaved-Caspase-12 after Mydgf overexpression. Under HR conditions, TM significantly reversed the protective effect of Mydgf on CMECs. Mydgf may reduce CMEC apoptosis induced by HR by regulating oxidative stress in ERS.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Berndt R, Albrecht M, Rusch R (2021) Strategies to overcome the barrier of ischemic microenvironment in cell therapy of cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(5):2312
Bulluck H, Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2016) Reducing myocardial infarct size: challenges and future opportunities. Heart 102(5):341–348
Chen Q, Thompson J, Hu Y, Lesnefsky EJ (2021) Chronic metformin treatment decreases cardiac injury during ischemia-reperfusion by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress with improved mitochondrial function. Aging 13(6):7828–7845
Deng T, Wang Y, Wang C, Yan H (2019) FABP4 silencing ameliorates hypoxia reoxygenation injury through the attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Life Sci 224:149–156
Gandhi S, Garratt KN, Li S, Wang TY, Bhatt DL, Davis LL, Zeitouni M, Kontos MC (2022) Ten-year trends in patient characteristics, treatments, and outcomes in myocardial infarction from National Cardiovascular Data Registry Chest Pain-MI Registry. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 15(1):e008112
Garcia NA, Moncayo-Arlandi J, Sepulveda P, Diez-Juan A (2016) Cardiomyocyte exosomes regulate glycolytic flux in endothelium by direct transfer of GLUT transporters and glycolytic enzymes. Cardiovasc Res 109(3):397–408
Houseright RA, Miskolci V, Mulvaney O, Bortnov V, Mosher DF, Rindy J, Bennin DA, Huttenlocher A (2021) Myeloid-derived growth factor regulates neutrophil motility in interstitial tissue damage. J Cell Biol 220(8):e202103054
Hsieh PC, Davis ME, Lisowski LK, Lee RT (2006) Endothelial-cardiomyocyte interactions in cardiac development and repair. Annu Rev Physiol 68:51–66
Haas MJ, Warda F, Bikkina P, Landicho MA, Kapadia P, Parekh S, Mooradian AD (2022) Differential effects of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Vascul Pharmacol 02(142):e106948
Korf-Klingebiel M, Reboll MR, Klede S, Brod T, Pich A, Polten F, Napp LC, Bauersachs J, Ganser A, Brinkmann E, Reimann I, Kempf T, Niessen HW, Mizrahi J, Schönfeld HJ, Iglesias A, Bobadilla M, Wang Y, Wollert KC (2015) Myeloid-derived growth factor (C19orf10) mediates cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Nat Med 21(2):140–149
Simon JN, Vrellaku B, Monterisi S, Chu SM, Rawlings N, Lomas O, Marchal GA, Waithe D, Syeda F, Gajendragadkar PR, Jayaram R, Sayeed R, Channon KM, Fabritz L, Swietach P, Zaccolo M, Eaton P, Casadei B (2021) Oxidation of protein kinase A regulatory subunit PKARIα protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting lysosomal-triggered calcium release. Circulation 143(5):449–465
Tan Y, Mui D, Toan S, Zhu P, Li R, Zhou H (2020) SERCA overexpression improves mitochondrial quality control and attenuates cardiac microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:696–707
Tang V, Fu S, Rayner BS, Hawkins CL (2019) 8-Chloroadenosine induces apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells through the activation of the unfolded protein response. Redox Biol 26:101274
Wang S, Binder P, Fang Q, Wang Z, Xiao W, Liu W, Wang X (2018a) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the heart: insights into mechanisms and drug targets. Br J Pharmacol 175(8):1293–1304
Wang Y, Li Y, Feng J, Liu W, Li Y, Liu J, Yin Q, Lian H, Liu L, Nie Y (2020) Mydgf promotes Cardiomyocyte proliferation and Neonatal Heart regeneration. Theranostics 10(20):9100–9112
Wang Y, Zhao RZ, Liu WW, Wang ZL, Rong JD, Long XP, Liu ZJ,Ge JB, Shi B (2019) Exosomal circHIPK3 released from hypoxia-pretreated cardiomyocytes regulates oxidative damage in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via the miR-29a/IGF-1 Pathway. Oxidative Med Cellu Longev 7954657
Wang YY, Han XT, Fu MQ, Wang JF, Song Y, Liu Y, Zhang JJ, Zhou JM, Ge JB (2018b) Qiliqiangxin attenuates hypoxia-induced injury in primary rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via promoting HIF-1 alpha-dependent glycolysis. J Cell Mol Med 22(5):2791–2803
Zhao L, Feng S, Wang S, Fan M, Jin W, Li X, Wang C, Yang Y (2020) Production of bioactive recombinant human myeloid-derived growth factor in Escherichia coli and its mechanism on vascular endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Mol Med 24(2):1189–1199
Funding
This study was supported by a scientific research project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81860061 and 82160057). This work was also supported by the Guizhou Science and Technology Foundation (ZK[2021]353).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan Wang and Bei Shi conceived and designed the experiments;
Yu Zhang and Jiao Li performed the experiments;
Ranzhun Zhao and Xianping Long analyzed the data;
Chaofu Li, Weiwei Liu, and Wenming Chen prepared figures;
Yan Wang drafted the paper;
Bei Shi revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, J. et al. Role of Mydgf in the regulation of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 58, 669–678 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-022-00709-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-022-00709-3