Abstract
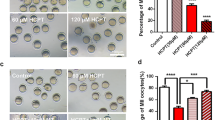
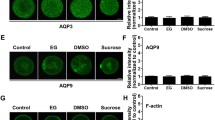
Hormesis describes a biphasic dose-response relationship generally characterized by a low-dose excitement and a high-dose inhibition. This phenomenon has been observed in the regulation of cell, organ, and organismic level. However, hormesis has not reported in oocytes. In this study, we observed, for the first time, hormetic responses of PIPP levels in oocytes by inhibitor of Akt1 or PKCδ. The expression of PIPP was detected by qPCR, immunofluorescent (IF), and Western Blot (WB). To observe the changes of PIPP levels, we used the inhibitors against pAkt1 (Ser473) or PKCδ, SH-6 or sotrastaurin with low and/or high-dose, treated GV oocytes and cultured for 4 h, respectively. The results showed that PIPP expression was significantly enhanced when oocytes were treated with SH-6 or sotrastaurin 10 μM, but decreased with SH-6 or sotrastaurin 100 μM. We also examined the changes of PIPP levels when GV oocytes were treated with exogenous PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 or LY294002 for 4 h. Our results showed that PIPP level was enhanced much higher under the treatment of 0.1 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 than that of 1 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, which is consistent with the changes of PIPP when oocytes were treated with inhibitors of pAkt1 (Ser473) or PKCδ. In addition, with PIPP siRNA, we detected that down-regulated PIPP may affect distributions of Akt, Cdc25, and pCdc2 (Tyr15). Taken together, these results show that the relationships between PIPP and Akt may follow the principle of hormesis and play a key role during release of diplotene arrest in mouse oocytes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari D, Busayavalasa K, Zhang JJ, Hu MW, Risal S, Bayazit MB, Singh M, Diril MK, Kaldis P, Liu K (2016) Inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdk1 mediates prolonged prophase I arrest in female germ cells and is essential for female reproductive lifespan. Cell Res 26:1212–1225
Agamas C, Ghanam RH, Xu F, Sun Y, Chen Y, Saad JS (2017) The interplay between calmodulin and membrane interactions with the pleckstrin homology domain of Akt. J Biol Chem 292:251–263
Akera T, Chmátal L, Trimm E, Yang K, Aonbanghen C, Chenoweth DM, Janke C, Schultz RM, Lampson MA (2017) Spindle asymmetry drives non-Mendelian chromosome segregation. Science 358:668–672
Balla T (2013) Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation. Physiol Rev 93:1019–1137
Bischof J, Brand CA, Somogy K, Majer I, Thome S, Mori M, Schwarz US, Lenart P (2017) A Cdk1 gradient guides surface contraction waves in oocytes. Nat Commun 8:849. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00979-6
Calabrese EJ, Iavicoli I, Calabrese V (2013) Hormesis: its impact on medicine and health. Hum Exp Toxicol 32:120–152
Deng X, Feng C, Wang EH, Zhu YQ, Cui C, Zong ZH, Li GS, Liu C, Meng J (2011) Yu BZ. Influence of proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, on early development of fertilized mouse eggs, via inhibition of phosphorylation of AKT. Cell Prolif 44(2):156–165
Di Paolo G, De Camilli P (2006) Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443:651–657
Dongil K, Kruse M, Kim D-I, Hille B, Suh B-C (2016) Phosphoinositide 5-and 3-phosphatase activities of a voltage-sensing phosphatase in living cells show identical voltage dependence. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:E3686–E3695
Edward JMM, Collins BJ, Ashby PR, Prescott AR, Murray-Tait V, Armit LJ, Arthur JSC, Alessi DR (2004) The in vivo role of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 binding to PDK1 PH domain defined by knockin mutation. EMBO 23:2071–2082
Feng C, Yu A, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zong Z, Su W, Zhang Z, Yu B (2007) Involvement of protein kinase B/AKT in early development of mouse fertilized eggs. Biol Reprod 77:560–568
Heo WD, Inoue T, Park WS, Kim ML, Park BQ, Wandless TJ, Meyer T (2006) PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(4,5)P2 lipids target proteins with polybasic clusters to the plasma membrane. Science 314:1458–1461
Hiraoka D, Aono R, Hanada S, Okumura E, Kishimoto T (2016) Two new competing pathways establish the threshold for cyclin-B-Cdk1 activation at the meiotic G2/M transition. J Cell Sci 129:3153–3166
Janetopoulos C, Ma L, Devreotes PN, Iglesias PA (2004) Chemoattractant-induced phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate accumulation is spatially amplified and adapts, independent of the actin cytoskeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:8951–8956
Jethwa NJ, Chung GHC, Lete MG, Alonso A, Byme RD, Calleja LB (2015) Endomembrane PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 acticates the PI3K-Akt pathway. J Cell Sci 128:3456–3465
Ji LL, Kang CH, Zhang Y (2016) Exercise-induced hormesis and skeletal muscle health. Free Radic Biol Med 98:113–122
Kim J, Singh AK, Takata Y, Lin K, Shen J, Lu Y, Kerenyi MA, Orkin SH, Chen T (2015) LSD1 is essential for oocyte meiotic progression by regulating CDC25B expression in mice. Nat Commun 6:10116. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10116
Kölsch V, Charest PG, Firtel RA (2008) The regulation of cell motility and chemotaxis by phospholipid signaling. J Cell Sci 121:551–559
Kurokawaa T, Takasugab S, Sakataa S, Yamaguchic S, Horied S, Hommac KJ, Sasakib T, Okamuraa Y (2012) 3’ Phosphatase activity toward phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate [PI(3,4)P2] by voltage-sensing phosphatase (VSP). Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:10089–10094
Lete MG, Byrne RD, Alonso A, Poccia D, Larijani B (2017) Vesicular PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and Rab7 are key effectors of sea urchin zygote nuclear membrane fusion. J Cell Sci 130:444–452
Lees JA, Zhang Y, Oh MS, Schauder CM, Yu X, Baskin JM, Dobbs K, Notarangelo LD, De Camilli P, Walz T, Reinisch KM (2017) Architecture of the human PI4KIIIα lipid kinase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:13720–13725
Liu L, Li S, Li H, Yu D, Li C, Li G, Cao Y, Feng C, Deng X (2018) Protein kinase Cδ involved in the regulation of pAkt1 (Ser473) on the release of mouse oocytes from diplotene arrest. Cell Biochem Funct 36:221–227
Peake JM, Markworth JF, Nosaka K, Raastad T, Wadley GD, Coffey VG (2015) Modulating exercise-induced hormesis: does less equal more? J Appl Physiol 119:172–189
Ma JY, Li M, Luo YB, Song SH, Tian DM, Yang J, Zhang B, Hou Y, Schatten H, Liu ZH, Sun QY (2013) Maternal factors required for oocyte developmental competence in mice: transcriptome analysis of non-surrounded nucleolus (NSN) and surrounded nucleolus (SN) oocytes. Cell Cycle 12:1928–1938
Manning BD, Toker (2017) AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 169:381–405
Meng J, Cui C, Liu Y, Jin M, Wu D, Liu C, Wang E, Yu B (2013) The role of 14-3-3ε interaction with phosphorylated Cdc25B at its Ser321 in the release of the mouse oocyte from prophase I arrest. PLoS One 8(1):e53633. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053633
Okamura Y, Doxon JE (2011) Voltage-sensing phosphatase: its molecular relationship with PTEN. Physiology 26:6–13
Ooms LM, Fedele CG, Astle MV, Ivetac I, Cheung V, Pearson RB, Layton MJ, Forrai A, Nandurkar HH, Mitchell CA (2006) The inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, PIPP, is a novel regulator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent neurite elongation. Mol Biol Cell 17:607–622
Rodgers SJ, Ferguson DT, Mitchell CA, Ooms LM (2017) Regulation of PI3K effector signaling in cancer by the phosphoinositide phosphatases. Biosci Rep 37:BSR20160432. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20160432
Rusinova R, Hobert EA, Koeppe RE 2nd, Anderson OS (2013) Phosphoinositides alter lipid bilayer properties. J Gen Physiol 141:673–690
Sergei VJ (2015) Hormesis and homeopathy: the artificial twins. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol 4:74–77
Stocker H, Andjelkovic M, Oldham S, Laffargue M, Wymann MP, Hemmings BA, Hafen E (2002) Living with lethal PIP3 levels: viability of flies lacking PTEN restored by a PH domain mutation in Akt/PKB. Science 295:2088–2091
Tan J, Brill JA (2014) Cinderella story: PI4P goes from precursor to key signaling molecule. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 49:33–58
Zhang M, Jang H, Gaponenko V, Nussinov R (2017) Phosphorylated calmodulin promotes PI3K activation by binding to the SH2 domains. Biophys J 113:1956–1967
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xu XY, Li XS, Yu M, Yu AM, Zong ZH, Yu BZ (2008) Protein kinase A modulates Cdc25B activity during meiotic resumption of mouse oocytes. Dev Dyn 237:3777–3786
Zheng P, Baibakov B, Wang XH, Dean J (2013) PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 is constitutively synthesized and required for spindle translocation during meiosis in mouse oocytes. J Cell Sci 126:715–721
Funding
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China Grant (81370712).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Yong, W., Gao, T. et al. Hormesis of low-dose inhibition of pAkt1 (Ser473) followed by a great increase of proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (PIPP) level in oocytes. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 57, 342–349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00546-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00546-w