Abstract
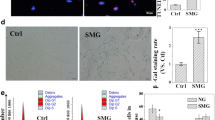
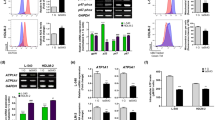
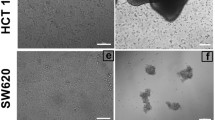
Several studies have indicated that microgravity can influence cellular progression, proliferation, and apoptosis in tumor cell lines. In this study, we observed that simulated microgravity inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in U251 malignant glioma (U251MG) cells. Furthermore, expression of the apoptosis-associated proteins, p21 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2), was upregulated and downregulated, respectively, following exposure to simulated microgravity. These findings indicate that simulated microgravity inhibits proliferation while inducing apoptosis of U251MG cells. The associated effects appear to be mediated by inhibition of IGFBP-2 expression and stimulation of p21 expression. This suggests that simulated microgravity might represent a promising method to discover new targets for glioma therapeutic strategy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey JF, Hargens AR, Cheng KK, Lotz JC (2014) Effect of microgravity on the biomechanical properties of lumbar and caudal intervertebral discs in mice. J Biomech 47:2983–2988
Blaber E, Sato K, Almeida EA (2014) Stem cell health and tissue regeneration in microgravity. Stem Cells Dev 23(Suppl 1):73–78
Coinu R, Chiaviello A, Galleri G, Franconi F, Crescenzi E, Palumbo G (2006) Exposure to modeled microgravity induces metabolic idleness in malignant human MCF-7 and normal murine VSMC cells. FEBS Lett 580:2465–2470
Dai B, Hu Z, Huang H, Zhu G, Xiao Z, Wan W, Zhang P, Jia W, Zhang L (2014) Overexpressed KDM5B is associated with the progression of glioma and promotes glioma cell growth via downregulating p21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 454:221–227
Dong Z, Dang Y, Chen Y (2014) Small double-stranded RNA mediates the anti-cancer effects of p21WAF1/ClP1 transcriptional activation in a human glioma cell line. Yonsei Med J 55:324–330
Fang L, Cheng Q, Zhao J, Ge Y, Zhu Q, Zhao M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Li L, Liu J, Zheng J (2016) A p53-independent apoptotic mechanism of adenoviral mutant E1A was involved in its selective antitumor activity for human cancer. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10221
Ferranti F, Caruso M, Cammarota M, Masiello MG, Corano Scheri K, Fabrizi C, Fumagalli L, Schiraldi C, Cucina A, Catizone A, Ricci G (2014) Cytoskeleton modifications and autophagy induction in TCam-2 seminoma cells exposed to simulated microgravity. Biomed Res Int 2014:904396
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Frankel RH, Bayona W, Koslow M, Newcomb EW (1992) p53 mutations in human malignant gliomas: comparison of loss of heterozygosity with mutation frequency. Cancer Res 52:1427–1433
Han S, Li Z, Master LM, Master ZW, Wu A (2014) Exogenous IGFBP-2 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioma cells via the integrin beta1-ERK pathway. Br J Cancer 111:1400–1409
Herranz R, Anken R, Boonstra J, Braun M, Christianen PC, de Geest M, Hauslage J, Hilbig R, Hill RJ, Lebert M, Medina FJ, Vagt N, Ullrich O, van Loon JJ, Hemmersbach R (2013) Ground-based facilities for simulation of microgravity: organism-specific recommendations for their use, and recommended terminology. Astrobiology 13:1–17
Jhala DV, Kale RK, Singh RP (2014) Microgravity alters cancer growth and progression. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 14:394–406
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y, Yousefi B (2016) Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst) 42:63–71
Komotar RJ, Otten ML, Moise G, Connolly ES Jr (2008) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma—a critical review. Clin Med Oncol 2:421–422
Li J, Zhang S, Chen J, Du T, Wang Y, Wang Z (2009) Modeled microgravity causes changes in the cytoskeleton and focal adhesions, and decreases in migration in malignant human MCF-7 cells. Protoplasma 238:23–33
Lin SC, Gou GH, Hsia CW, Ho CW, Huang KL, Wu YF, Lee SY, Chen YH (2016) Simulated microgravity disrupts cytoskeleton organization and increases apoptosis of rat neural crest stem cells via upregulating CXCR4 expression and RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK-p53 signaling. Stem Cells Dev 25:1172–1193
Lin Y, Jiang T, Zhou K, Xu L, Chen B, Li G, Qiu X, Jiang T, Zhang W, Song SW (2009) Plasma IGFBP-2 levels predict clinical outcomes of patients with high-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 11:468–476
McDonald KL, O’Sullivan MG, Parkinson JF, Shaw JM, Payne CA, Brewer JM, Young L, Reader DJ, Wheeler HT, Cook RJ, Biggs MT, Little NS, Teo C, Stone G, Robinson BG (2007) IQGAP1 and IGFBP2: valuable biomarkers for determining prognosis in glioma patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:405–417
Meloni MA, Galleri G, Pani G, Saba A, Pippia P, Cogoli-Greuter M (2011) Space flight affects motility and cytoskeletal structures in human monocyte cell line J-111. Cytoskeleton 68:125–137
Meng XM, Chung AC, Lan HY (2013) Role of the TGF-beta/BMP-7/Smad pathways in renal diseases. Clin Sci (Lond) 124:243–254
Miyata S, Urabe M, Gomi A, Nagai M, Yamaguchi T, Tsukahara T, Mizukami H, Kume A, Ozawa K, Watanabe E (2013) An R132H mutation in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 enhances p21 expression and inhibits phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein in glioma cells. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53:645–654
Mullan PB, Quinn JE, Harkin DP (2006) The role of BRCA1 in transcriptional regulation and cell cycle control. Oncogene 25:5854–5863
Patil SS, Gokulnath P, Bashir M, Shwetha SD, Jaiswal J, Shastry AH, Arimappamagan A, Santosh V, Kondaiah P (2016) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 regulates beta-catenin signaling pathway in glioma cells and contributes to poor patient prognosis. Neuro-Oncology 18:1487–1497
Paw I, Carpenter RC, Watabe K, Debinski W, Lo HW (2015) Mechanisms regulating glioma invasion. Cancer Lett 362:1–7
Petersen N, Lambrecht G, Scott J, Hirsch N, Stokes M, Mester J (2017) Postflight reconditioning for European astronauts—a case report of recovery after six months in space. Musculoskelet Sci Pract 27(Suppl 1):S23–S31
Phillips LM, Zhou X, Cogdell DE, Chua CY, Huisinga A, Hess KR, Fuller GN, Zhang W (2016) Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies. J Pathol 239:355–364
Pickard A, McCance DJ (2015) IGF-binding protein 2—oncogene or tumor suppressor? Front Endocrinol 6:25
Pietsch J, Bauer J, Egli M, Infanger M, Wise P, Ulbrich C, Grimm D (2011) The effects of weightlessness on the human organism and mammalian cells. Curr Mol Med 11:350–364
Prives C, Gottifredi V (2008) The p21 and PCNA partnership: a new twist for an old plot. Cell Cycle 7:3840–3846
Shi ZX, Rao W, Wang H, Wang ND, Si JW, Zhao J, Li JC, Wang ZR (2015) Modeled microgravity suppressed invasion and migration of human glioblastoma U87 cells through downregulating store-operated calcium entry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:378–384
Silvano M, Miele E, Valerio M, Casadei L, Begalli F, Campese AF, Besharat ZM, Alfano V, Abballe L, Catanzaro G (2015) Consequences of simulated microgravity in neural stem cells: biological effects and metabolic response. J Stem Cell Res Ther 5:289–296
Takeda M, Magaki T, Okazaki T, Kawahara Y, Manabe T, Yuge L, Kurisu K (2009) Effects of simulated microgravity on proliferation and chemosensitivity in malignant glioma cells. Neurosci Lett 463:54–59
Torsvik A, Stieber D, Enger PO, Golebiewska A, Molven A, Svendsen A, Westermark B, Niclou SP, Olsen TK, Chekenya Enger M, Bjerkvig R (2014) U-251 revisited: genetic drift and phenotypic consequences of long-term cultures of glioblastoma cells. Cancer Med 3:812–824
Uva BM, Masini MA, Sturla M, Bruzzone F, Giuliani M, Tagliafierro G, Strollo F (2002) Microgravity-induced apoptosis in cultured glial cells. Eur J Histochem 46:209–214
Van Ombergen A, Demertzi A, Tomilovskaya E, Jeurissen B, Sijbers J, Kozlovskaya IB, Parizel PM, Van de Heyning PH, Sunaert S, Laureys S, Wuyts FL (2017) The effect of spaceflight and microgravity on the human brain. J Neurol. doi:10.1007/s00415-017-8427-x
Vassy J, Portet S, Beil M, Millot G, Fauvel-Lafeve F, Gasset G, Schoevaert D (2003) Weightlessness acts on human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Adv Space Res 32:1595–1603
Wang X, Du J, Wang D, Zeng F, Wei Y, Wang F, Feng C, Li N, Dai R, Deng Y, Quan Z, Qing H (2016) Effects of simulated microgravity on human brain nervous tissue. Neurosci Lett 627:199–204
Wang YC, Lu DY, Shi F, Zhang S, Yang CB, Wang B, Cao XS, Du TY, Gao Y, Zhao JD, Sun XQ (2013) Clinorotation enhances autophagy in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Cell Biol 91:309–314
Wei L, Diao Y, Qi J, Khokhlov A, Feng H, Yan X, Li Y (2013) Effect of change in spindle structure on proliferation inhibition of osteosarcoma cells and osteoblast under simulated microgravity during incubation in rotating bioreactor. PLoS One 8:e76710
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507
Xia X, Ma Q, Li X, Ji T, Chen P, Xu H, Li K, Fang Y, Weng D, Weng Y, Liao S, Han Z, Liu R, Zhu T, Wang S, Xu G, Meng L, Zhou J, Ma D (2011) Cytoplasmic p21 is a potential predictor for cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 11:399
Xu H, Wang Z, Jin S, Hao H, Zheng L, Zhou B, Zhang W, Lv H, Yuan Y (2014) Dux4 induces cell cycle arrest at G1 phase through upregulation of p21 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 446:235–240
Zhu M, Jin XW, Wu BY, Nie JL, Li YH (2014) Effects of simulated weightlessness on cellular morphology and biological characteristics of cell lines SGC-7901 and HFE-145. Genet Mol Res 13:6060–6069
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81273879). We thank Dr. Wen-dong Bai, Dr. Chu-chao Zhu, Dr. Yuan Xing, and Dr. Lu Wang for their expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Ma, H., Wu, L. et al. The influence of simulated microgravity on proliferation and apoptosis in U251 glioma cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 53, 744–751 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-017-0178-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-017-0178-6