Abstract
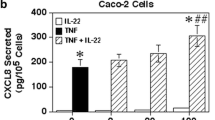
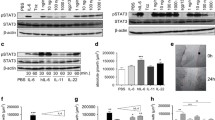
Elevated levels of interleukin-1 (IL-1) accompany inflammatory bowel disease. IL-1-stimulated intestinal epithelial cells can secrete potent chemokines like CXCL8 to exacerbate inflammation. Previously, we found that inhibiting the Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) could inhibit IL-1- or TNF-α-induced CXCL8 secretion by the Caco-2 colonic epithelial cell line. This ROCK inhibition did not affect IκBα phosphorylation and degradation, but suppressed the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Therefore, ROCK must play an important role in epithelial cell CXCL8 responses through an effect on the JNK signaling pathway. Here, we extend these studies by showing that inhibiting ROCK suppressed the IL-1-induced phosphorylation of MKK4, a known activator of JNK, but not MKK7. Yet, ROCK inhibition had no significant effect on the IL-1-induced phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2. Inhibiting ROCK also suppressed the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK after IL-1 stimulation, but this inhibition had no significant effect on the stability of CXCL8 messenger RNA (mRNA) after IL-1 stimulation. These results suggest that ROCK may be important in IL-1-induced signaling through MKK4 to JNK and the activation of p38 MAPK. Finally, inhibiting ROCK in IL-1 and TNF-α co-stimulated Caco-2 cells also resulted in a significant suppression of CXCL8 secretion and mRNA levels suggesting that inhibiting ROCK may be a mechanism to inhibit the overall response of epithelial cells to both cytokines. These studies indicate a novel signaling event, which could provide a target for suppressing intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) chemokine responses involved in mucosal inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks C, Bateman A, Payne R, Johnson P, Sheron N (2003) Chemokine expression in IBD. Mucosal chemokine expression is unselectively increased in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. J Pathol 199:28–35
Cargnello M, Roux PP (2011) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75:50–83
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P (2000) Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351:95–105
Fleming Y, Armstrong CG, Morrice N, Paterson A, Goedert M, Cohen P (2000) Synergistic activation of stress-activated protein kinase 1/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (SAPK1/JNK) isoforms by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) and MKK7. J Biochem 352:145–154
Flusberg DA, Sorger PK (2015) Surviving apoptosis: life-death signaling in single cells. Trends Cell Biol 25:446–458
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:247–269
Jijon HB, Panenka WJ, Madsen KL, Parsons HG (2002) MAP kinases contribute to IL-8 secretion by intestinal epithelial cells via a posttranscriptional mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C31–C41
Jung HC, Eckmann L, Yang S-K, Panja A, Fierer J, Morzycka-Wroblewska E, Kagnoff MF (1995) A distinct array of proinflammatory cytokines is expressed in human colon epithelial cells in response to bacterial invasion. J Clin Invest 95:55–65
Kagnoff MF, Eckmann L (1997) Epithelial cells as sensors for microbial infection. J Clin Invest 100:6–10
Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS (2010) Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol 28:573–621
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2012) Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: a 10-year update. Phys Rev 92:689–737
McGee DW, Beagley KW, Aicher WK, McGhee JR (1993) Transforming growth factor-β and IL-1β act in synergy to enhance IL-6 secretion by the intestinal epithelial cell line, IEC-6. J Immunol 151:970–978
McGee DW, Bamberg T, Vitkus SJD, McGhee JR (1995) A synergistic relationship between TNF-α, IL-1β, and TGF-β1 on IL-6 secretion by the IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cell line. Immunol 86:6–11
Mong PY, Petrulio C, Kaufman HL, Wang Q (2007) Activation of rho kinase by TNF-α is required for JNK activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 180:550–558
Perey AC, Weishaar IM, McGee DW (2015) The effect of ROCK on TNF-α-induced CXCL8 secretion by intestinal epithelial cell lines is mediated through MKK4 and JNK signaling. Cell Immunol 293:80–86
Rafferty BJ, Unger BL, Perey AC, Tammariello SP, Pavlides S, McGee DW (2012) A novel role for the rho-associated kinase, ROCK, in IL-1-stimulated intestinal epithelial cell responses. Cell Immunol 280:148–155
Riento K, Ridley AJ (2003) ROCKs: multifunctional kinases in cell behavior. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:446–456
Sunil Y, Ramadori G, Raddatzc D (2010) Influence of NFκB inhibitors on IL-1β-induced chemokine CXCL8 and -IL-10 expression levels in intestinal epithelial cell lines: glucocorticoid ineffectiveness and paradoxical effect of PDTC. Int J Colorectal Dis 25:323–333
Tournier C, Dong C, Turner TK (2001) MKK7 is an essential component of the JNK signal transduction pathway activated by proinflammatory cytokines. Genes Dev 15:1419–1426
Vitkus SJD, Hanifin SA, McGee DW (1998) Factors affecting Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cell interleukin-6 secretion. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 34:660–664
Weber A, Wasiliew P, Kracht M (2010) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal 3:105cm1
Winzen R, Kracht M, Ritter B, Wilhelm A, Chen CYA, Shyu AB, Muller M, Gaestel M, Resch K, Holtmann H (1999) The p38 MAP kinase pathway signals for cytokine-induced mRNA stabilization via MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 and an AU-rich region-targeted mechanism. EMBO J 18:4969–4980
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the US Public Health Service Grant DK089459 and a grant from the Binghamton University Harpur College.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of interest
The authors announce no conflicts of interest. The authors are solely responsible for the content of the paper.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, S., McGee, D.W. ROCK activity affects IL-1-induced signaling possibly through MKK4 and p38 MAPK in Caco-2 cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 878–884 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0050-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0050-0