Abstract
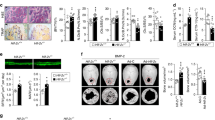
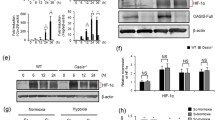
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) is one of the master regulators of hypoxia reactions, playing an important role in bone modeling, remodeling, and homeostasis. And overexpression of HIF-1α in mature osteoblasts through conditional deletion of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene profoundly increases angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Studies showed that mice with osteoblasts lacking Vhl had a high level of Hif-1α and increased bone mass and density. On the contrary, Hif-1α conditional knockout mice had decreased bone mass and density. Our in vitro study showed that osteoprotegerin (OPG), an essential regulator of osteoclastic activity, can be upregulated by HIF-1α and in turn downregulate the resorption activity of osteoclasts. We showed that HIF-1α may directly bind to the upstream site of OPG and enhance its expression. Our study suggested that a novel mechanism, which works via OPG signaling, may mediate the function of HIF-1α in bone remodeling.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeno N, Czyzyk-Krzeska MF, Gross TS, Clemens TL (2001) Hypoxia induces vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription in human osteoblast-like cells through the hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. Endocrinology 142(2):959–962
Bardos JI, Ashcroft M (2005) Negative and positive regulation of HIF-1: a complex network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1755(2):107–120
Boughner JC, Buchtova M, Fu K, Diewert V, Hallgrimsson B, Richman JM (2007) Embryonic development of Python sebae—I: staging criteria and macroscopic skeletal morphogenesis of the head and limbs. Zoology (Jena) 110(3):212–230
Boyce BF, Xing L, Chen D (2005) Osteoprotegerin, the bone protector, is a surprising target for beta-catenin signaling. Cell Metab 2(6):344–345
Brzoska MM, Rogalska J (2013) Protective effect of zinc supplementation against cadmium-induced oxidative stress and the RANK/RANKL/OPG system imbalance in the bone tissue of rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272(1):208–220
Chung UI, Kawaguchi H, Takato T, Nakamura K (2004) Distinct osteogenic mechanisms of bones of distinct origins. J Orthop Sci 9(4):410–414
Knowles HJ, Athanasou NA (2009) Canonical and non-canonical pathways of osteoclast formation. Histol Histopathol 24(3):337–346
Liu C, Zhang Y, Kong X, Zhu L, Pang J, Xu Y, Chen W, Zhan H, Lu A, Lin N (2013) Triptolide prevents bone destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis by targeting RANKL/RANK/OPG signal pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:626038
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell 40(2):294–309
Martinez MD, Schmid GJ, McKenzie JA, Ornitz DM, Silva MJ (2010) Healing of non-displaced fractures produced by fatigue loading of the mouse ulna. Bone 46(6):1604–1612
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399(6733):271–275
Nakahama K (2010) Cellular communications in bone homeostasis and repair. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(23):4001–4009
Pivonka P, Zimak J, Smith DW, Gardiner BS, Dunstan CR, Sims NA, Martin TJ, Mundy GR (2010) Theoretical investigation of the role of the RANK-RANKL-OPG system in bone remodeling. J Theor Biol 262(2):306–316
Ratcliffe PJ (2007) HIF-1 and HIF-2: working alone or together in hypoxia? J Clin Invest 117(4):862–865
Semenza GL (2001a) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: control of oxygen homeostasis in health and disease. Pediatr Res 49(5):614–617
Semenza GL (2001b) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol Med 7(8):345–350
Semenza GL (2009) Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:97–106
Semenza GL (2010) Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2(3):336–361
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Luthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R, Boyle WJ (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89(2):309–319
Tamama K, Kawasaki H, Kerpedjieva SS, Guan J, Ganju RK, Sen CK (2011) Differential roles of hypoxia inducible factor subunits in multipotential stromal cells under hypoxic condition. J Cell Biochem 112(3):804–817
Tekkesin MS, Mutlu S, Olgac V (2011) The role of RANK/RANKL/OPG signalling pathways in osteoclastogenesis in odontogenic keratocysts, radicular cysts, and ameloblastomas. Head Neck Pathol 5(3):248–253
Wan C, Shao J, Gilbert SR, Riddle RC, Long F, Johnson RS, Schipani E, Clemens TL (2010) Role of HIF-1alpha in skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1192:322–326
Wang Y, Wan C, Deng L, Liu X, Cao X, Gilbert SR, Bouxsein ML, Faugere MC, Guldberg RE, Gerstenfeld LC, Haase VH, Johnson RS, Schipani E, Clemens TL (2007) The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development. J Clin Invest 117(6):1616–1626
Yang Y (2009) Skeletal morphogenesis during embryonic development. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 19(3):197–218
Zhang YG, Yang Z, Zhang H, Wang C, Liu M, Guo X, Xu P (2010) Effect of negative pressure on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Connect Tissue Res 51(1):14–21
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371958, 81201367), the Foundation of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (12JC1408200, 13431900702), Shanghai Municipal Natural Science Foundation (10ZR1427700), Key Discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (PWZx2014-09), and Academic Leaders Training Program of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (PWRd2012-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Jin Shao and Yan Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, T. et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 51, 808–814 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9895-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9895-x